
Citations

 , Seoyoung Kim
, Seoyoung Kim , Dohyoung Rim
, Dohyoung Rim
Citations

 , Eun-Kyoung Pang
, Eun-Kyoung Pang
Citations

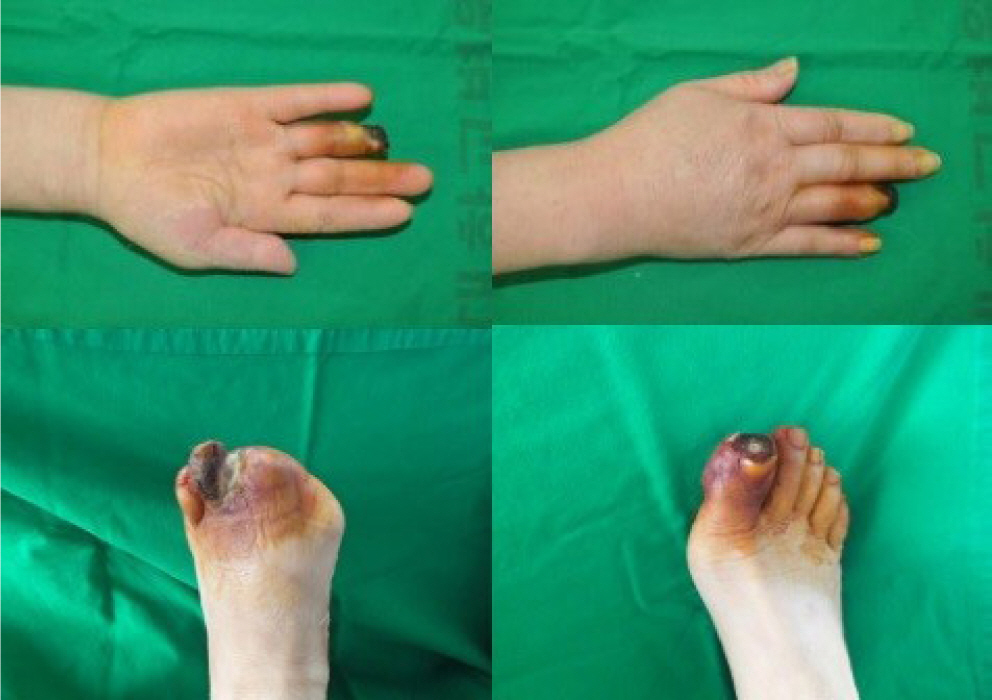
Symmetrical peripheral gangrene is a severe condition marked by symmetric acral necrosis without obstruction of the major blood vessels. This case report examines the critical decisions involved in choosing between early and delayed amputation, as well as determining the extent of the necessary amputation. We present three cases: one involving antiphospholipid syndrome, another with disseminated intravascular coagulation, and a third associated with diabetes mellitus. All three cases ultimately required amputation due to symmetrical peripheral gangrene. In the first two cases, amputation was delayed, which is typically advantageous as it allows for the clear demarcation of necrotic tissue. However, in the third case, where infection was evident, immediate amputation was necessary despite the patient's overall poor health.
 , Jae Hyun Kim
, Jae Hyun Kim
The incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is increasing in youth, largely in correlation with an increase in childhood overweight and obesity. Youth-onset T2DM is a major public health concern worldwide, and tends to show more aggressive features than adult-onset T2DM. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent the occurrence of complications and comorbidities. However, current treatment options are limited and only modestly successful in youth-onset T2DM. Over the last few decades, significant progress has been made in the understanding of youth-onset T2DM. This review summarizes the current understanding of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of T2DM in youth. (Ewha Med J 2022;45(3):e3)
Type 1 diabetes requires lifelong insulin therapy because insulin-secretion capability is diminished. Glycemic control and glucose monitoring are important to prevent type 1 diabetes complications. Diabetes technologies have developed rapidly; continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) are now common and greatly aid glycemic control, especially in children and adolescents. The National Health Insurance Service has provided partial reimbursements for both CGM and CSII devices since 2019 and 2020, respectively; the devices are thus expected to become more popular. CGM reduces the frequency of hypoglycemia and the level of glycated hemoglobin. CSII affords more precise glycemic control than multi-dose insulin therapy. CSII showed reduced frequency of hypoglycemia and improved metabolic outcome without an increase in the body mass index z-score. Technological advancement of combined CGM and CSII will eventually serve as an artificial pancreas. The National Health Insurance Service should fund not only the devices but also education of patients and caregivers. In addition, healthcare providers must be continuously updated on new diabetes technologies.
Citations

 , Hye-Sun Park
, Hye-Sun Park , Yong-ho Lee
, Yong-ho Lee , Byung-Wan Lee
, Byung-Wan Lee , Eun Seok Kang
, Eun Seok Kang , Bong-Soo Cha
, Bong-Soo Cha
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are commonly prescribed drugs for the treatment of depression in the patients with diabetes. Here, we report a case of paroxetineinduced severe recurrent hypoglycemia that developed in a 35-year-old woman with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes complicated by diabetic nephropathy and neuropathy. She discontinued her daily insulin therapy 2 months after the introduction of paroxetine, but hypoglycemic events were sustained. After discontinuation of paroxetine, no more hypoglycemic events occurred.
Citations

 , Seo Hwa Park
, Seo Hwa Park , Eun Gyu Kang
, Eun Gyu Kang , Gyu Cheon Kyung
, Gyu Cheon Kyung , Hyo Dong An
, Hyo Dong An , So-Yeon An
, So-Yeon An
Mucormycosis is a rare disease caused by fungi. Most commonly involved sites of mucormycosis infection are sinuses, lungs, skin and soft tissues. Systemic risk factors for mucormycosis are diabetes mellitus, neutropenia, corticosteroid use, hematological malignancies, organ transplantation, metabolic acidosis, deferoxamine use and advanced age. Local risk factors are history of trauma, burns, surgery and motor vehicle accidents. We present a case of cutaneous mucormycosis in a patient with diabetes mellitus. A 66-year-old female with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, admitted with necrotizing lesion after minor abrasions on leg. We took a culture of the lesion and it is diagnosed with mucormycosis. Disease progressed despite administration of systemic amphotericin B. We performed above-knee amputation and changed antifungal agents into liposomal amphotericin B. A tissue biopsy showed nonseptate, irregularly wide fungal hyphae with frequent right-angle branching. Our case report suggests that patients with risk factors should be observed carefully.
Citations

 , Soo Kyung Lim
, Soo Kyung Lim , Ji young Chang
, Ji young Chang , Eun kyo Jung
, Eun kyo Jung , Youn-i Choi
, Youn-i Choi , Jee-Young Oh
, Jee-Young Oh , Youngsun Hong
, Youngsun Hong , Yeon-Ah Sung
, Yeon-Ah Sung , Hyejin Lee
, Hyejin Lee
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) affects 2%-4% of the all pregnant women, and it is a major risk factor for development of type 2 DM. We performed this cross-sectional study to determine whether there were defects in insulin secretory capacity or insulin sensitivity in women with previous GDM.
On 6-8 weeks after delivery, 75 g oral glucose tolerance test was performed in 36 women with previous GDM and 19 non-pregnant control women matched with age and weight. Intravenous glucose tolerance test was performed on 10-14 weeks after delivery. Insulin secretory capacity measured as the acute insulin response to glucose (AIRg) and insulin sensitivity as minimal model derived sensitivity index (SI) were obtained. AIRg×SI (β-cell disposition index) was used as an index of β-cell function.
Women with previous GDM were classified into normal glucose tolerance (postpartum-NGT, n=19) and impaired glucose tolerance (postpartum-IGT, n=17). Postpartum fasting glucose levels were significantly higher in postpartum-IGT compared to postpartum-NGT and control (P<0.05). AIRg×SI was significantly lower in postpartum-IGT compared to control (P<0.05). SI was lower in postpartum-NGT and postpartum-IGT compared to control, but the difference did not have the statistical significance. Frequency of parental history of type 2 diabetes was significantly greater in postpartum-IGT compared to postpartum-NGT (P<0.05).
Women with previous GDM showed impaired insulin secretion although their glucose tolerance states were restored to normal. It suggests impaired early insulin secretion may be a major pathophysiologic factor for development of type 2 DM, and this defect may be genetically determined.
 , Sung Won Park
, Sung Won Park , Sang Min Lee
, Sang Min Lee , Kyung Soo Cho
, Kyung Soo Cho
To evaluate the CT findings of pulmonary tuberculosis in diabetic patients compared with patients without underlying disease.
The chest CT scans of pulmonary tuberculosis in 23 diabetic patients(M : F=21 : 2 ; mean age, 59 yrs.) and in 24 nondiabetic patients(M : F=12 : 12 ; mean age, 48 yrs.) were retrospectively analyzed by two radiologists ; decisions were reached by consensus.
The frequencies of consolidation(100%, 42%), inhomogeneity of consolidation(70%, 21%), multiple small low-density areas(52%, 13%), cavitation(70%, 25%), multiple small cavity(35%, 4%), bizarre-shaped cavity(22%, 0%), air-bronchogram(95%, 54%) were significantly more common in pulmonary tuberculosis in diabetic patients than in nondiabetic patients(p<.05). There was no significant difference in localization of pulmonary lesions between diabetic and nondiabetic patients.
Diabetic patients have a high prevalence of inhomogeneous consolidation containing multiple small low densities and multiple or bizarre-shaped cavities than do patients without diabetics.

