 , Jihyun Ahn
, Jihyun Ahn

Citations

 , YoungMoon Goh
, YoungMoon Goh , Jungwon Kwak
, Jungwon Kwak
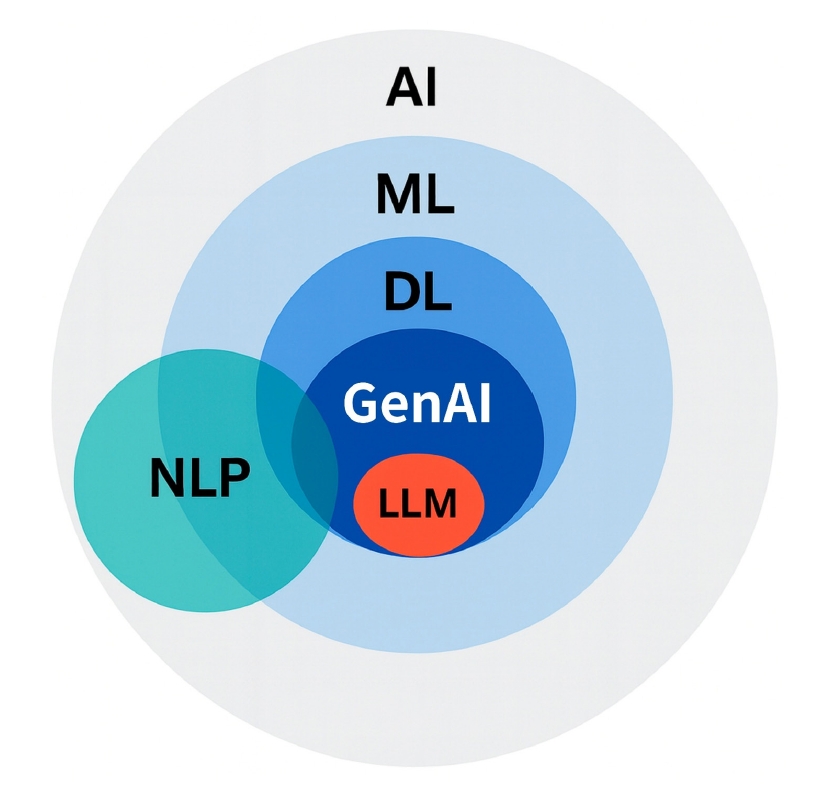
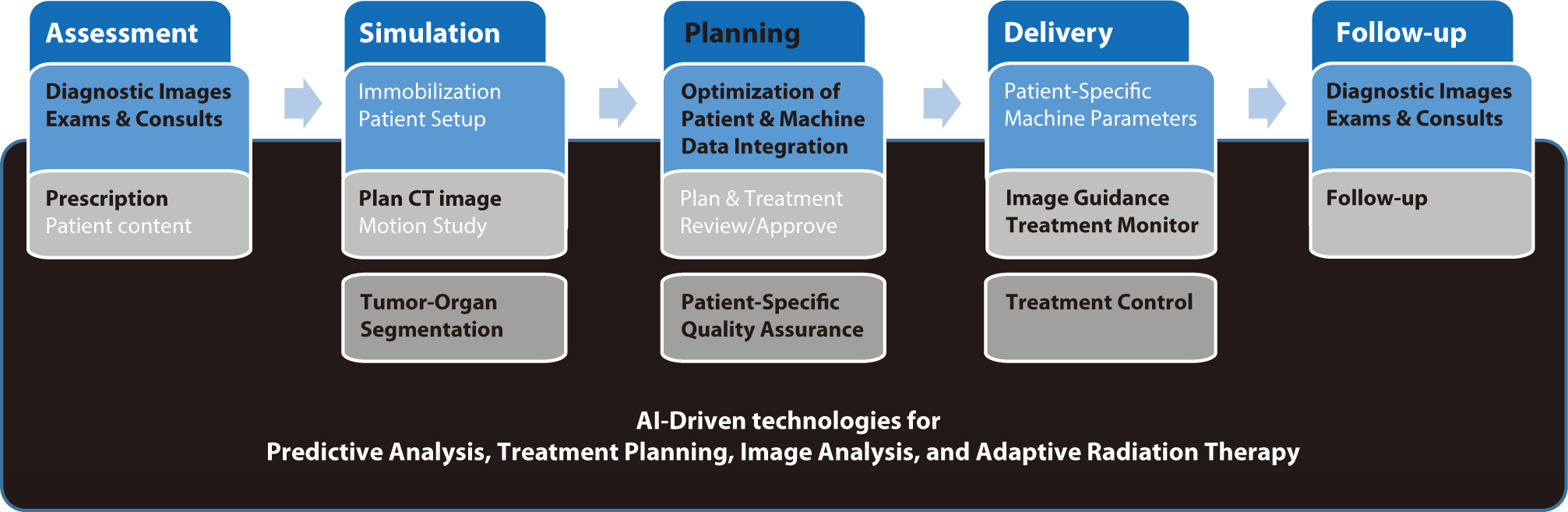
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various medical fields, including radiation oncology. This review explores the integration of AI into radiation oncology, highlighting both challenges and opportunities. AI can improve the precision, efficiency, and outcomes of radiation therapy by optimizing treatment planning, enhancing image analysis, facilitating adaptive radiation therapy, and enabling predictive analytics. Through the analysis of large datasets to identify optimal treatment parameters, AI can automate complex tasks, reduce planning time, and improve accuracy. In image analysis, AI-driven techniques enhance tumor detection and segmentation by processing data from CT, MRI, and PET scans to enable precise tumor delineation. In adaptive radiation therapy, AI is beneficial because it allows real-time adjustments to treatment plans based on changes in patient anatomy and tumor size, thereby improving treatment accuracy and effectiveness. Predictive analytics using historical patient data can predict treatment outcomes and potential complications, guiding clinical decision-making and enabling more personalized treatment strategies. Challenges to AI adoption in radiation oncology include ensuring data quality and quantity, achieving interoperability and standardization, addressing regulatory and ethical considerations, and overcoming resistance to clinical implementation. Collaboration among researchers, clinicians, data scientists, and industry stakeholders is crucial to overcoming these obstacles. By addressing these challenges, AI can drive advancements in radiation therapy, improving patient care and operational efficiencies. This review presents an overview of the current state of AI integration in radiation oncology and insights into future directions for research and clinical practice.
Citations

 , Ryung-Ah Lee
, Ryung-Ah Lee
The capabilities of artificial intelligence (AI) have recently surged, largely due to advancements in deep learning inspired by the structure and function of the neural networks of the human brain. In the medical field, the impact of AI spans from diagnostics and treatment recommendations to patient engagement and monitoring, considerably improving efficiency and outcomes. The clinical integration of AI has also been examined in specialties, including pathology, radiology, and oncology. General surgery primarily involves manual manipulation and includes preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care, all of which are critical for saving lives. Other fields have strived to utilize and adopt AI; nonetheless, general surgery appears to have retrogressed. In this review, we analyzed the published research, to understand how the application of AI in general surgery differs from that in other medical fields. Based on previous research in other fields, the application of AI in the preoperative stage is nearing feasibility. Ongoing research efforts aim to utilize AI to improve and predict operative outcomes, enhance performance, and improve patient care. However, the use of AI in the operating room remains significantly understudied. Moreover, ethical responsibilities are associated with such research, necessitating extensive work to gather evidence. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and leveraging lessons from AI success stories in other fields, AI tools could be specifically tailored for general surgery. Surgeons should be prepared for the integration of AI into clinical practice to achieve better outcomes; therefore, the time has come to consider ethical and legal implications.
Citations

 , Ji Su Chung
, Ji Su Chung , Yeo-Jin Lee
, Yeo-Jin Lee , Seonwoo Lee
, Seonwoo Lee , Juhyun Jeong
, Juhyun Jeong , Min-Kyung So
, Min-Kyung So , Miae Lee
, Miae Lee
The Panbio COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device (Panbio COVID-19 Ag, Abbott Rapid Diagnostics) is a lateral flow immunochromatographic assay targeting the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) nucleoprotein in nasopharyngeal specimens for the diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This study aimed to verify the performance of the Panbio COVID-19 Ag for implementation in clinical laboratories.
Sixty nasopharyngeal swab specimens (30 positive and 30 negative) dipped in transport medium, and COVID-19 was confirmed using real-time RT-PCR using Allplex SARS-CoV-2 assay (Seegene), were tested using the Panbio COVID-19 Ag. Reproducibility was evaluated using positive and negative control materials. Sensitivity and specificity were calculated based on the results of real-time RT-PCR as the standard test method.
Reproducibility was confirmed by the consistent results of repeated tests of the quality control materials. The overall sensitivity and specificity of Panbio COVID-19 Ag were 50.0% and 100.0%, respectively. Panbio COVID-19 Ag demonstrated high sensitivity (88.2%) in analyzing the detection limit cycle threshold (Ct) value of 26.67 provided by the manufacturer as a positive criterion, and the sensitivity was 100.0% for the positive criterion of Ct values <25, although it was less sensitive for Ct ≥25.
Considering the high sensitivity for positive samples with Ct values <25 and the rapid turnaround of results, Panbio COVID-19 Ag can be used in clinical laboratories to diagnose COVID-19 in limited settings.
 , Gyoung Tae Noh
, Gyoung Tae Noh
A 25-year-old female visited the clinic with abdominal pain and poor oral intake. She was diagnosed with Crohn’s disease and had a history of using infliximab for 4 years. She had no previous operative history. Magnetic resonance enterography demonstrated the progression of a penetrating complication that involved the distal ileum and complex entero-enteric fistula between the terminal ileum and sigmoid colon. Surgery was conducted using the da Vinci SP surgical system. In the operative field, severe adhesion was observed between the terminal ileum, adjacent ileum, cecum, and the sigmoid colon. After adhesiolysis of the small bowel and right colon was performed, the fistula tract between the sigmoid colon and terminal ileum was identified and resected. Then, simultaneous ileocecectomy and anterior resection was performed. The operation was completed without any intraoperative complications and patient’s recovery was uneventful. She was discharged postoperatively, after 8 days.
 , Yu Yil Kim
, Yu Yil Kim , Ji Hye Lee
, Ji Hye Lee , So Mang Im
, So Mang Im , Ok Hyun Kim
, Ok Hyun Kim , Han Gyeol Lee
, Han Gyeol Lee
Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a chronic and refractory pain disease. It requires longterm treatment and follow-up. Comorbid diseases can change or aggravate the pain condition and responsiveness of patients to PHN treatment. In such cases, the cause of pain should be identified through proper testing, and appropriate treatment should be administered. Herein, we report the case of a 67-year-old man with PHN in the maxillary nerve. As the pain was being controlled with medication and infraorbital nerve block, the patient experienced deterioration of pain caused by a newly worn upper complete denture. The patient's pain was relieved following correction of the upper complete denture.
 , Kwang Ho Kim
, Kwang Ho Kim , Soon Sup Chung
, Soon Sup Chung , Kyoung Sook Hong
, Kyoung Sook Hong , Ryung-Ah Lee
, Ryung-Ah Lee
In the metastatic process, interactions between circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and the extracellular matrix or surrounding cells are required. β1-integrin may mediate these interactions. The aim of this study was to investigate whether β1-integrin is associated with the detection of CTCs in colorectal cancer.
We enrolled 30 patients with colorectal cancer (experimental group) and 30 patients with benign diseases (control group). Blood samples were obtained from each group, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) mRNA for CTCs marker and β1-integrin mRNA levels were estimated by using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, and the results were compared between the two groups.
CEA mRNA was detected more frequently in colorectal cancer patients than in control patients (P=0.008). CEA mRNA was significantly reduced after surgery in the colorectal cancer patients (P=0.032). β1-integrin mRNA was detected more in colorectal cancer patients than in the patients with benign diseases (P<0.001). In colorectal cancer patients, expression of β1-integrin mRNA was detected more for advanced-stage cancer than for early-stage cancer (P=0.033) and was significantly decreased after surgery (P<0.001). In addition, expression of β1-integrin mRNA was significantly associated with that of CEA mRNA in colorectal cancer patients (P=0.001).
In conclusion, β1-integrin is a potential prognostic factor following surgical resection in colorectal cancer patients. β1-integrin may be a candidate for use as a marker for early detection of micrometastatic tumor cells and for monitoring the therapeutic response in colorectal cancer patients.

Elevated serum lgE and pheripheral blood eosinophilia are immunologic hallmark in helminthic infections. Recently, these responses are known to be regulated by Th2-specific cytokine IL-4 and IL-5, respectively. And also, the antagonistic effects of IFN-γ on Th2 cell proliferation were shown
5-6week old male BALB/c mice treated with IFN-γ were divided into 3 groups. All the mice were inoculated orally with 20 metacercariae of
The serum lgE levels in groupIand II were decreased compared with those of infected mice with no treatment with rIFN-γ, but not significantly. The number of pheripheral blood eosinophils in group I and II were decreased compared with those of infected mice with no treatment with rIFN-γ, especially significant(
These results suggest that IFN-γ decreases Th2 cytokine response in
 , Gyoung Hee Kim
, Gyoung Hee Kim
This study was performed to investigate the prevalence of abnormal behavior, ada-ptability and intelligence of child and adolescents and the usefulness of KAS(Korean Attitude System) as a screening method to detect the psychopathology of child and adolescents.
478 child and adolescents were completed the instruments of KAS that focused on development of behavior, adaptability and intelligence at the children's medical examination center.
The most influenced subcategories to the disturbance of behavior of the subjects were leadership, cooperation, and emotion (in order). The preference of adaptability was high in the fields of literature, law, technology, medicine and sociology. The mean I.Q. of the subjects was high average and not different in both sex. The subjects with below average of I.Q. were three cases(0.6%) and the two of them were boderline and only one case was mild mental retardation. The total number of patients referred to the department of psychiatry was eight cases(1.7%) and revealed the disturbance of behavior, affect, and thought.
Finally the authors concluded that KAS test performed at the children's medical examination center was useful primary screening method to detect the psychopathology of child and adolescents.
 , Chung Kang
, Chung Kang , Il Hyung Jung
, Il Hyung Jung , Hyun Gee Moon
, Hyun Gee Moon , Bo Ram Youn
, Bo Ram Youn , Nam Hun Lee
, Nam Hun Lee
Pseudomembranous colitis (PMC) is a frequent cause of morbidity and mortality among hospitalized patients. Although diarrhea is the most common manifestation, PMC may be associated with intraperitoneal fluid accumulation in the severe cases. And a few cases showing both ascites and pleural effusion have been reported in patients with PMC. We report a case of PMC who showed elevated serum and ascites levels of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) with a normal CEA level in pleural effusion and who successfully recovered after oral administration of metronidazole. After treatment, the serum CEA level returned to the reference range.
Citations

 , Sang Il Park
, Sang Il Park , Jae Yeon Lee
, Jae Yeon Lee , Yoon Hee Cho
, Yoon Hee Cho
Dentigerous cyst represents cystic enlargement of the follicle of an impacted tooth. It is the sites of predilection mirror the favored sites if impacted teeth : mandibular third molars, maxillary third molars, and maxillary canines. These cysts are most prevalent in the second to fourth decades. Most cysts are asymmetric and are discovered on routine dental radiographs, but large examples can cause displacement or resorption of adjacent teeth and infection. Microscopical examination discloses a stratified squamous epithelium covering a fibrocollagenous cyst wall.
In this case, authors present a case of huge dentigerous cyst on right piriform fossa across the midline that enucleated successfully through the right gingivobuccal approach.

