
 , Jung-Ha Kim
, Jung-Ha Kim
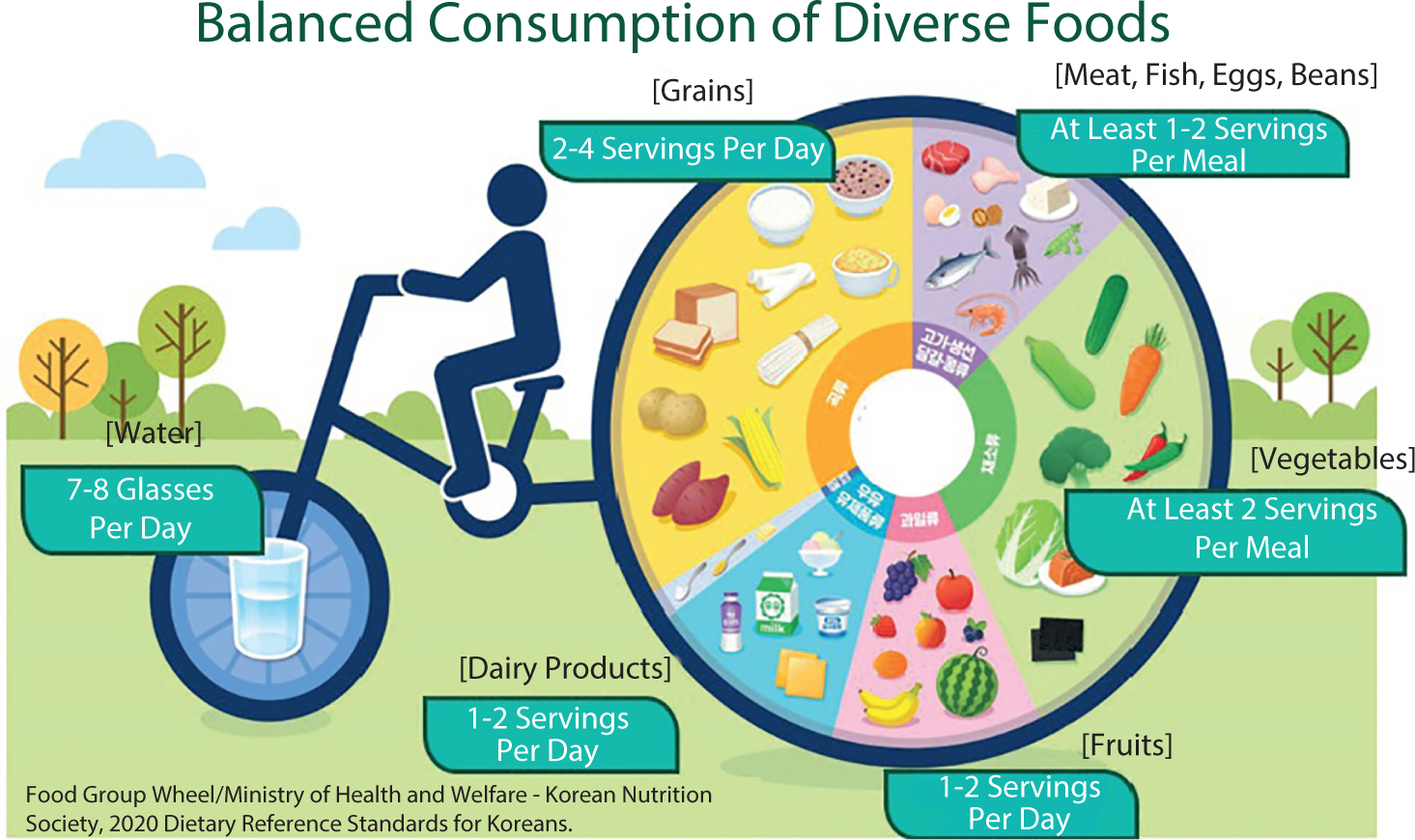
Breast cancer is a complex disease influenced by environmental, genetic, dietary, and hormonal factors. This underscores the importance of postoperative nutritional management in supporting recovery, minimizing complications, and enhancing long-term outcomes. This review synthesizes clinical guidelines, expert recommendations, and observational studies to provide a comprehensive overview of dietary interventions for breast cancer patients following surgery. Post-surgical nutritional care is centered around three primary objectives: supporting wound healing through high-quality protein intake, maintaining optimal nutritional status to prevent malnutrition, and promoting healthy lifestyle habits to reduce the risk of recurrence. To achieve these objectives, postoperative dietary strategies focus on several key components: ensuring adequate hydration for metabolic processes and tissue repair, consuming a balanced diet rich in fresh vegetables and fruits to mitigate oxidative stress, incorporating whole grains to support overall healing, and maintaining sufficient intake of high-quality protein from sources such as fish, meat, and dairy products to aid tissue repair and immune system recovery. Patients are also advised to avoid alcohol, limit saturated fats, and reduce intake of salty, sugary, and smoked foods to minimize inflammation. As research progresses, the implementation of personalized dietary plans remains essential for optimizing recovery outcomes in breast cancer patients.
 , Kee-Duck Park
, Kee-Duck Park , Kyoung-Gyu Choi
, Kyoung-Gyu Choi
Patients suffering from neurological disorder, such as cerebral infarctoin, often face serious swallowing difficulty and malnutrion. Although the importance of nutritional support has been well demonstrated, malnutrition remains a frequently neglected condition in the clinical setting.
In this study, we investigate the effectiveness of enteral nutritional support to neurological patients using nutritional beverage Nucare. 50 patients with acute and chronic neurological disease with eating problem were participated. 27 patients(experimental group : 17, control group :7), fed more than 7 days, were selected and statically analyzed by the changes of hematologic, biochemical parameters and nutritional index compared with control roup(
This suggests that enteral nutritional support with Nucare can improve the nutritional status and clinical outcome of patient with acute and chronic neurological disease.

