 , Taek Chung
, Taek Chung , Dong Kyu Kim
, Dong Kyu Kim , Hyungjin Rhee
, Hyungjin Rhee
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) is a heterogeneous bile duct adenocarcinoma with a rising global incidence and a poor prognosis. This review aims to present a comprehensive overview of the most recent radiological research on iCCA, focusing on its histopathologic subclassification and the use of imaging findings to predict prognosis and inform treatment decisions. Histologically, iCCA is subclassified into small duct (SD-iCCA) and large duct (LD-iCCA) types. SD-iCCA typically arises in the peripheral small bile ducts and is often associated with chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis. It presents as a mass-forming lesion with a relatively favorable prognosis. LD-iCCA originates near the hepatic hilum, is linked to chronic bile duct diseases, and exhibits more aggressive behavior and poorer outcomes. Imaging is essential for differentiating these subtypes and assessing prognostic factors like tumor size, multiplicity, vascular invasion, lymph node metastasis, enhancement patterns, and intratumoral fibrosis. Imaging-based prognostic models have demonstrated predictive accuracy comparable to traditional pathological staging systems. Furthermore, imaging findings are instrumental in guiding treatment decisions, including those regarding surgical planning, lymphadenectomy, neoadjuvant therapy, and the selection of targeted therapies based on molecular profiling. Advancements in radiological research have improved our understanding of iCCA heterogeneity, facilitating prognosis prediction and treatment personalization. Imaging findings assist in subclassifying iCCA, predicting outcomes, and informing treatment decisions, thus optimizing patient management. Incorporating imaging-based approaches into clinical practice is crucial for advancing personalized medicine in the treatment of iCCA. However, further high-level evidence from international multicenter prospective studies is required to validate these findings and increase their clinical applicability.
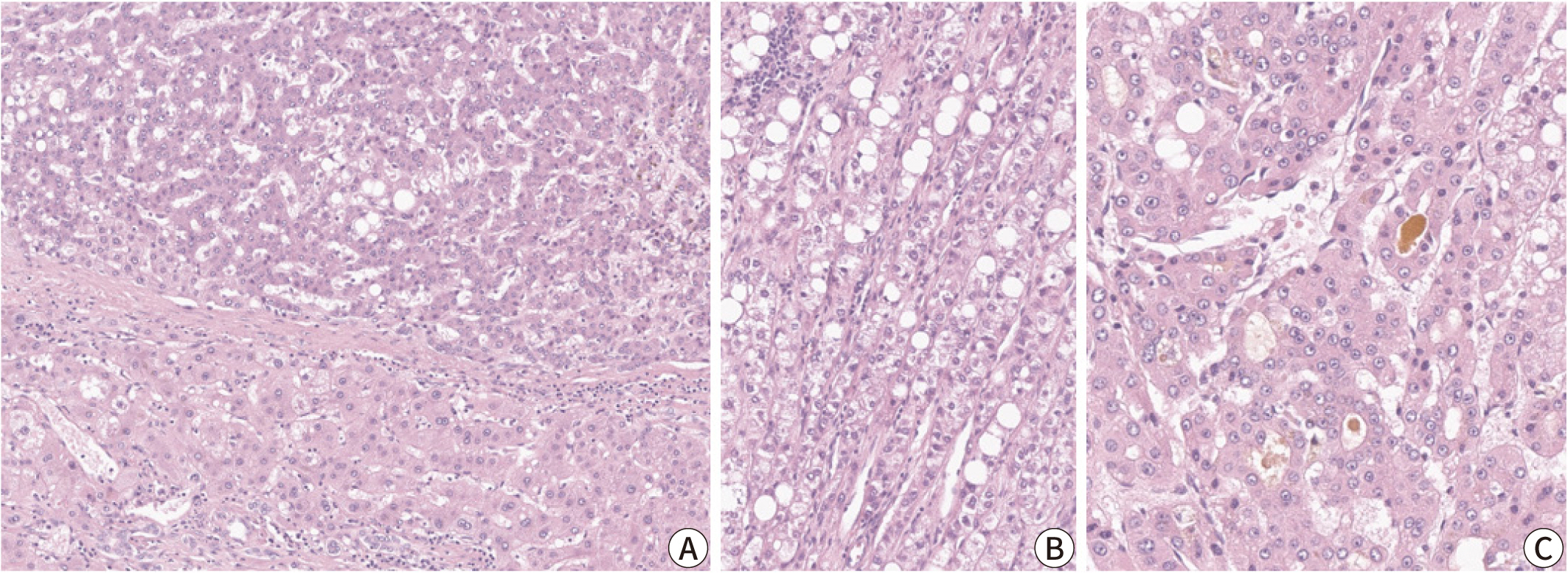
 , Haeryoung Kim
, Haeryoung Kim
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths
worldwide, with poor clinical outcomes due to challenges in early detection and
limited efficacy of current treatments such as receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitors and immunotherapy. HCC exhibits significant heterogeneity at both
histopathological and molecular levels, complicating its management but offering
potential for personalized therapeutic approaches. This review outlines the
morpho-molecular heterogeneity of HCC and summarizes various histological
subtypes, including steatohepatitic, clear cell, macrotrabecular-massive,
scirrhous, lymphocyte-rich, and fibrolamellar HCCs. Each subtype possesses
distinct clinical, histological, and molecular features; for instance,
steatohepatitic HCC is associated with metabolic dysfunction and shows
IL-6/JAK/STAT activation, while clear cell HCCs often have
Citations


The aim of this study was to investigate the frequency of psychiatric diagnoses(Axis I,II and III) using DSM-IV as well as the significances of personality traits and social of occupational functioning in a group of psychiatric outpatient insomnmiacs.
62 subjects who complained of insomnia over a 2-week period were evaluated for psychiatric and personality disorders and medical conditions by a comprehensive psychiatric diagnostic interview. Each patient also completed the MMPI test and was evaluated on GAF score.
The higher prevalence of insomnia has been reported in the age group of 21 to 50 years, married and unemployed patients in this study.
95.2% of the subjects had a principal diagnosis on Axis I and the most prevalent diagnoses were mood disorders and accompanying diagnoses were anxiety and somatoform disorders(in frequency order). 51.6% of the subjects had a principal diagnosis on Axis II and the most prevalent diagnoses were compulsive personality disorders and accompanying diagnoses were others(avoidant, dependent, and passive-aggresive) and historionic personalty disorders. 50% of the subjects had Axis III diagnoses and the most prevalent diagnoses were gastrointestinal disordrs. 72.6% of the subjects had elevated scores on one or more MMPI scales(T score of 70 or greater) and the most frequently elevated scale was the depression and accompanying scales were hysteria and hypochondriasis. The mean GAF score value of the patient was 61.65±5.64 and showed significant difference in each Axis I principal diagnoses.
In summary, strong associations between insomnia and psychiatric disorders were confirmed by this investigation
 , Chong Nahm Kim
, Chong Nahm Kim , Sung Min Chung
, Sung Min Chung , Chun Dong Kim
, Chun Dong Kim , Sung Wan Byun
, Sung Wan Byun
The aim of this study is to obtain the basic knowledge for safer clinical use of oxymetazoline, one of nasal decongestants, by observing changes of ciliary activity and histopa-thologic findings after topical application of oxymetazoline to the cultured human basak mucosa.
The nasal mucosa, obtained from the inferior tubinates in healthy non-smokers without any nasal symptoms or signs, was cultured and then, exposed to oxymetazoline solu-tion at different concentrations from 0.0123% to 0.25%, containing no preservatives. Ciliary activity was observed under an inverted microscope and the histopathology of the mucosa was examined by light microscopy 1,3,6,12,24 and 48 hours after exposure, respectively.
Oxymetazoline impaired ciliary activity and induced mucosal injury at dose- and time-dependent patterns. Once the ciliary activity disappeared, it was not restored at least for the next 48 hours. Furthermore, these functional and morphologic changes resulted from applying oxymetazoline at the concentration of clinical use.
Oxymetazoline as a topical vasoconstrictor should be administered for the minimal period even at clinical dose.

