 , YoungMoon Goh
, YoungMoon Goh , Jungwon Kwak
, Jungwon Kwak
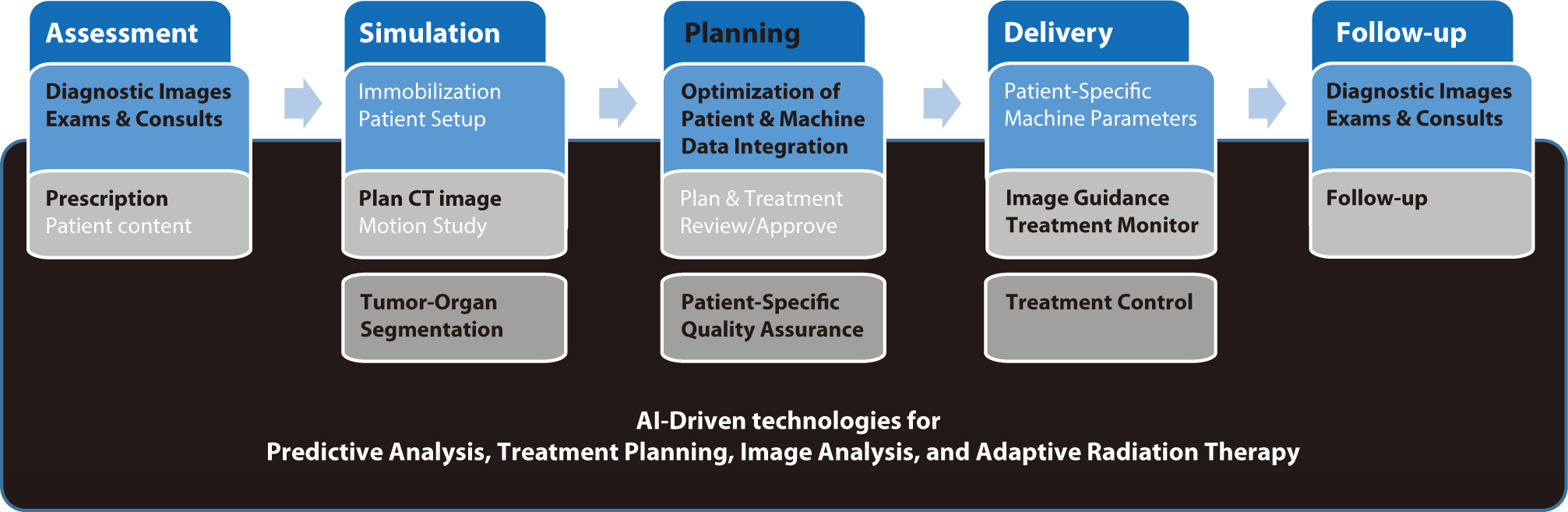
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various medical fields, including radiation oncology. This review explores the integration of AI into radiation oncology, highlighting both challenges and opportunities. AI can improve the precision, efficiency, and outcomes of radiation therapy by optimizing treatment planning, enhancing image analysis, facilitating adaptive radiation therapy, and enabling predictive analytics. Through the analysis of large datasets to identify optimal treatment parameters, AI can automate complex tasks, reduce planning time, and improve accuracy. In image analysis, AI-driven techniques enhance tumor detection and segmentation by processing data from CT, MRI, and PET scans to enable precise tumor delineation. In adaptive radiation therapy, AI is beneficial because it allows real-time adjustments to treatment plans based on changes in patient anatomy and tumor size, thereby improving treatment accuracy and effectiveness. Predictive analytics using historical patient data can predict treatment outcomes and potential complications, guiding clinical decision-making and enabling more personalized treatment strategies. Challenges to AI adoption in radiation oncology include ensuring data quality and quantity, achieving interoperability and standardization, addressing regulatory and ethical considerations, and overcoming resistance to clinical implementation. Collaboration among researchers, clinicians, data scientists, and industry stakeholders is crucial to overcoming these obstacles. By addressing these challenges, AI can drive advancements in radiation therapy, improving patient care and operational efficiencies. This review presents an overview of the current state of AI integration in radiation oncology and insights into future directions for research and clinical practice.
Citations

 , Hee-June Kim
, Hee-June Kim , Sung Hun Kim
, Sung Hun Kim , Suk-Joong Lee
, Suk-Joong Lee
Citations

 , Heasoo Koo
, Heasoo Koo
Paclitaxel(Taxol) si a chemotherapeutic agent with potent microtubule stabilizing activities that arrests cell cycle in G2-M. Since D2-m is the most radiosensitive phase of the cell cycle, paclitaxel has potential as a cell cycle-specific radiosensitizer. This study was designed to investigate the effects of paclitaxel to radiotoxicity in normal rat liver.
A single intraperitoneal infusion of paclitaxel(10mg/kg), and a single irradiation(8Gy, x-ray) to the whole abdomen, and combination of irradiation(8Gy,x-ray)24 hours after paclitaxel infusion were done in Sprague-Dawley rats. The incidence of mitosis, apoptosis and parenchymal changes of the liver were evaluated at 6 hours, 24 hours, 3 and 5 days, respectively.
Paclitaxel and irradiation significantly increased mitosis at 6 hours and apoptosis was increased by irradiation at 6 and 24 hours. Increased numbers of apoptosis at 3 days by paclitaxel alone was not significantly different from control. Combination of paclitaxel and irradiation showed significantly increased numbers of mitosis and apoptosis at 6 hours. The degree of necrosis of hepatocyte was not significantly different between 3 groups.
Since the incidence of mitosis, apoptosis and hepatocyte necrosis were not increased by paclitaxel infusion 24 hours before irradiation, paclitaxel did not show radiosensitizing effect in this experimental condition. Studies with conditions similar to clinical situation will be the next stop to define the radiosensitizing effects of paclitaxel.
 , Chung Sik Rhee
, Chung Sik Rhee
This experimental study was performed for evaluate the effects of cis-di-amminedichloroplatinum(II) (cis-DDP) on the radiation injury of rat bowel by histopathologic changes.
Rats were exposed to entire abdomen by a single doses of X-ray(6-10 Gy) without or witn cis-DDP(2.5mg/kg). Rats were divided into 3 groups such as radiation alone, cis-DDP alone and combined group. In combined group, cis-DDP was given 30minutes before or immediately after irradiation.
Cis-DDP induced the inflammatory cell infiltrations with focal necrosis of the mucosa in the small bowel and no abnormal change in the large bowel. In radiation alone group, mucosal necrosis, subrnucosal fibrosis and muscular necrosis were prominent changes in small bowel and submucosal fibrosis in the large bowel. The submucosal fibrosis in the small bowel was appealed in 10 Gy of radiation alone group and 8 Gy of cis-DDP infusion after radiation and 6 Gy of cis-DDP infusion before radiation of combined group. In the large bowel, submucosal fibrosis was noted in 8 Gy of radiation alone group and 8 Gy of cis-DDP infusion after radiation and 6 Gy of cis-DDP infusion before radiation of combined group. In the small bowel, the enhancement ratio was 1.67 in a group of cis-DDP infusion before radiation and 125 in a group of cis-DDP infusion after radiation as the end point was the submucosal fibrosis,In the large bowel, the enhancement ratio was 1.33 in a group of cis-DDP infusion before radiation and 1.0 in a cup of cis-DDP infusion after radiation as e end point was e submucosal fibrosis.
This study suggested that cis-DDP enhance the radiation effect in the small and large bowel especially when cis-DDP was infused before radiation.
 , Kyung Ja Lee
, Kyung Ja Lee
The effects of radiation and Cis dichlorodiammineplatinum(II) (Cis-DDP) were assessed in rectum of rats by histopathological changes. Rats were exposed to single doses of X ray(6~10 Gy) without or with Cis-DDP(2.5mg/kg). In combined group, Cis-DDP was given 30 minntes before or immediately after irradiation. Cis-DDP alone showed inflammatory cell infiltration and increased goblet cells in the mucosa and edema and fibrosis of submucosa with vascular sclerosis. With increased radiation dosage. such changes were aggravated. Necrosis of muscle layer developed 8 Gy irradiation. In groups with combination treatment of X-ray and Cis-DDP. changes of mucosa and submucosa were not significantly different from radiation alone group, but necrosis of the muscle layer was developed in 6 Gy combination group and degree was more severe in 8 and 10 Gy combination group compared to radiation alone group. There was no difference according to the timing of Cis DDP administration before or after irradiation. This result suggests Cis DDP enhance the radiation effect on the rectum of rats and enhancement ratio was 1.3 as the endpoint was necrosis of the muscle layer.
 , Ah Young Leem
, Ah Young Leem , Young Jae Kim
, Young Jae Kim , Eudong Hwang
, Eudong Hwang , Yujung Yun
, Yujung Yun , Sun Wook Kim
, Sun Wook Kim , Hyo Song Kim
, Hyo Song Kim
Radiation recall dermatitis refers to an acute inflammatory reaction in a previously irradiated field triggered by the administration of certain drugs days to years after the exposure to radiation. Gefitinib is an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor and is an effective treatment for patients with advanced stage of non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Here, we report a rare case of gefitinib induced radiation recall dermatitis. A 52-year-old woman with a metastatic NSCLC had received a palliative radiation therapy of 20 cGy on spine metastasis area (C6-T6). After 24 days of receiving radiation therapy, she had started to take gefitinib. Eight months after taking drug, pain, swelling and erythema of skin were occurred on previously irradiated field. These symptoms were resolved after the cessation of gefitinib for 6 days and the topical use of steroid.
Citations


