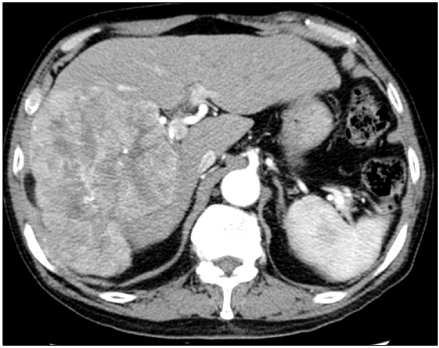
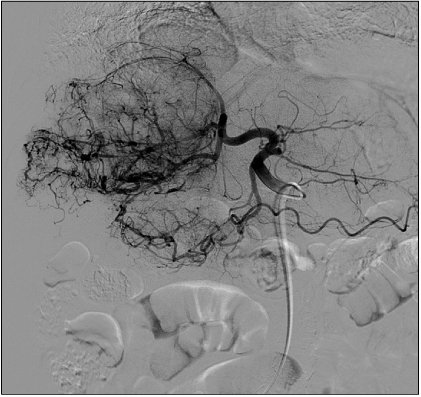
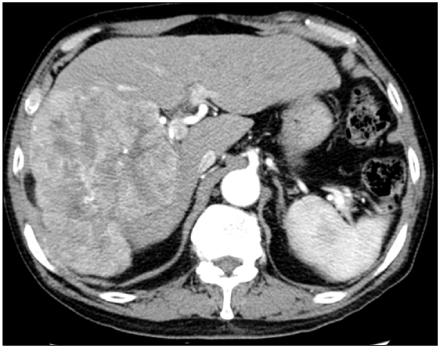
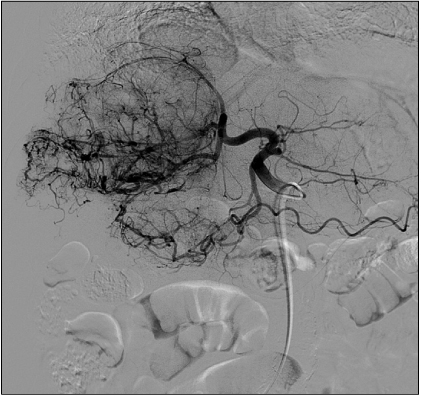
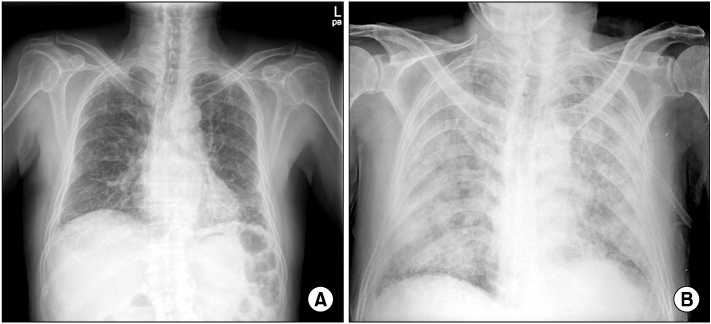
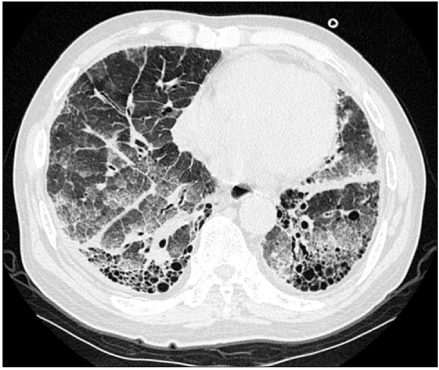
Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
1Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Copyright © 2013. Ewha Womans University School of Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.