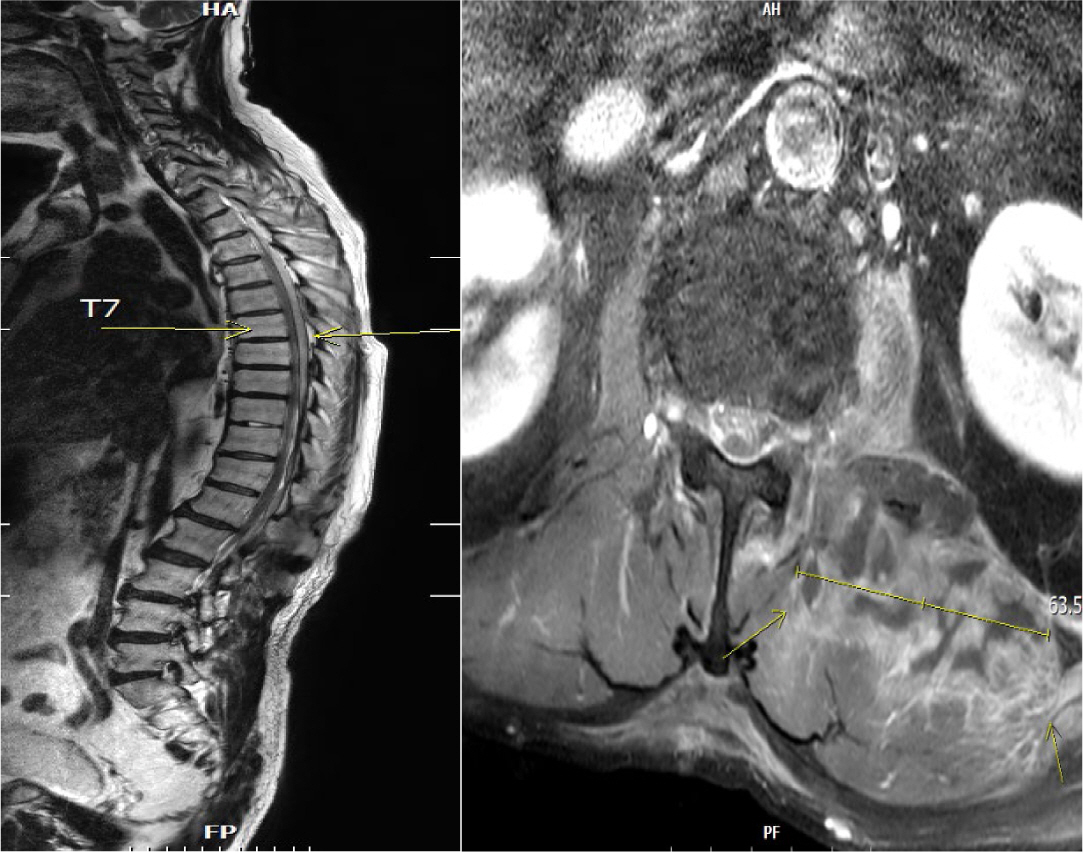

Septic embolism and stroke are serious complications in patients with sepsis and often necessitate urgent surgical intervention to control the source of infection. A 69-year-old man presented with severe pain in his back and left thigh. MRI revealed extensive posterior epidural or subdural abscesses extending from the cervical to the lumbar level, as well as an abscess in the iliopsoas muscle. The patient underwent urgent drainage of the abscesses and decompression of the lumbar spine. Postoperatively, he developed sudden-onset atrial fibrillation and altered mental status. Brain CT showed multiple embolic infarctions. His condition deteriorated due to persistent infection, leading to disseminated intravascular coagulation, acute kidney injury, and septic shock. This case highlights the risk of cerebral embolism and hemorrhagic complications in patients with sepsis who undergo surgery. Early recognition of individuals at high risk and comprehensive perioperative management are critical to reducing the likelihood of such complications.
 , Dong Il Kim
, Dong Il Kim , Hyo Jin Yun
, Hyo Jin Yun , Se Hee Yoon
, Se Hee Yoon , Sung Ro Yun
, Sung Ro Yun , Won Min Hwang
, Won Min Hwang
Prostatic abscess is not a common entity which is characterized by non-specific clinical presentations. This poses a diagnostic challenge for clinicians. Clinicians routinely consider antibiotic treatments concomitantly with drainage for the treatment of prostatic abscess. But there are no established guidelines for its optimal timing, methods and indications. Surgical drainage procedures include transurethral resection of the prostate and perineal incision and drainage. But there is variability in the prognosis of patients between the procedures. We have treated a 48-year-old diabetes patient with prostatic abscess accompanied by MRSA bacteremia using a percutaneous fine-needle aspiration under the computed tomography (CT) guidance. The patient achieved improvement of the symptoms and in follow up CT findings. A percutaneous drainage under the CT guidance is advantageous in that it causes fewer complications. However, Further studies are warranted to establish the optimal timing, methods and indications in patients with prostate abscess.
 , Sun Ho Chee
, Sun Ho Chee
The authors describe a case of the brain abscess in the left temporal lobe which was accurately diagnosed by computerized tomography brain scan and complete surgical excision of abscess capsule was accomplis with great success. SUMMARY The case presented by authors was otogenic in origin and diagnosed accurately by the computerized tomographic scan, and total excision of the abscess capsule was performed by two stage operation.
 , Hye-Kyung Jung
, Hye-Kyung Jung , Mi Yeon Kim
, Mi Yeon Kim , Min Sun Ryu
, Min Sun Ryu , So Young Ahn
, So Young Ahn , Hyoung Won Cho
, Hyoung Won Cho , In Sook Kang
, In Sook Kang , Seong Eun Kim
, Seong Eun Kim
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) is characterized by raised levels of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL), in association with thrombosis, recurrent fetal loss, and thrombocytopenia. Development of APS is related with idiopathic origin, autoimmune disease, malignancy and, on rare occasions, infection. However, in secondary APS combined with bacterial infections, aPL is usually shown with low titer and rarely associated with thrombotic events. A 52-year-old male was admitted due to pneumonia and multiple hepatosplenic abscesses. He had been treated with proper antibiotics, but he presented ascites and sudden variceal bleeding because of portal vein thrombosis. The bleeding was controlled by endoscopic variceal ligation. Acute portal vein thrombosis was successfully managed by low molecular weight heparin and hepatosplenic abscesses were completely resolved by antibiotics. This case suggests that systemic bacterial infection in immunocompetent patients possibly develops into secondary APS.
 , Tae-Hun Kim
, Tae-Hun Kim , Min-sun Ryu
, Min-sun Ryu , Da-Yeon Oh
, Da-Yeon Oh , Myung-Eun Song
, Myung-Eun Song , Shina Lee
, Shina Lee , Jae-In Ryu
, Jae-In Ryu , Hye-In Kim
, Hye-In Kim , Il-Hwan Moon
, Il-Hwan Moon , Kwon Yoo
, Kwon Yoo
The causes of pyogenic liver abscess has been known as biliary tract disease or intrabadominal infection but the large proportions of the patients has no apparent underlying disorders. Recently colonic mucosal lesions were reported in patients with cryptogenic liver abscess and it has been suggested that colonic mucosal break may play a role in developing liver abscess in otherwise healthy patients. We experienced a patient of severe recurrent liver abscess complicated with endophthalmitis only 3 months after successful treatment of initial cryptogenic liver abscess and a polypoid colon cancer was discovered by chance. It seems prudent to proceed colonoscopic examination in patients with cryptogenic liver abscess especially when it is recurrent.
 , Chang Yoon Ha
, Chang Yoon Ha , Hyun Jeong Jang
, Hyun Jeong Jang , Eun Young Yun
, Eun Young Yun , Ji Hyun Ju
, Ji Hyun Ju , Yeon Jeong Ahn
, Yeon Jeong Ahn , Hyun Ju Min
, Hyun Ju Min , Tae Hyo Kim
, Tae Hyo Kim , Hyun Jin Kim
, Hyun Jin Kim , Woon Tae Jung
, Woon Tae Jung , Ok Jae Lee
, Ok Jae Lee , Sun Young Yi
, Sun Young Yi
A 55-year-old man was admitted to our hospital with symptom of fever, chilling, abdominal discomfort and weight loss for 2months. Abdominal computed tomography(CT) revealed a 5×3.75 cm sized low attenuated lesion in the left lateral segment of liver. Esophagogastrodedodenoscopy showed a fistula with dirty exudates at the fundus and a yellowish stone and food debris at the choledochoduodenostomy site. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) was performed and stone and food materials in common bile duct was removed with snare and basket. We experienced a case of liver abscess due to sump syndrome and spontaneous drainage to the stomach.

Pyogenic liver abscess is a potentially life-threatening disease with substantial mortality rate. With the recent advances in diagnostic modalities and new treatment strategies, the overall mortality of pyogenic liver abscess has been decreased significantly but stillhigh mortality rates are recorded in patients with old age, multiple abscesses, malignant biliary obstruction and inadequate drainage. Therefore pyogenic liver abscess remains a major clinical challenge. We are going to investigate the current clinical features of pyogenic liver abscess.
Medical records of those who admitted to the Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital since 1993 and diagnosed as having Pyogenic liver abscess were reviewed. A total of 88 pyogenic liver abscess patients was detected and their clinical presentation, bacteriologic etiologies, comorbidities and treatment results were investigated.
Fifty male and 38 female (1.3 :1) patients were enrolled and the mean age was 59years. The most common presenting symptom was fever/chill (77%) followed by abdominal pain(64%), nausea/vomiting (42%) and general weakness (41%). Diabetes mellitus was combined in 17% of the patients and most of pyogenic liver abscesses were induced by ascending biliary infection (43%) or unknown cause (52%). Leukocytosis was evident in 74% of the patients and elevated akaline phosphatase in 52%. Sixty five percent of the abscess cavities were located inright lobe of the liver and most of them were solitary (73%). Pus culture was more efficient than blood culture for the detection of causative microorganis and
Rapid diagnosis of pyogenic liver abscess can be done through a complete history taking, physical examination and a prompt imaging studies and aggressive application of percutaneous aspiration or drainage of the abscess cavity with the empirical antibiotic administration targetting gram-negative aerobe may contribute to the improvement of the mangement of pyogenic liver abscess.

