
 , So Young Lee
, So Young Lee

 , Oh Haeng Lee
, Oh Haeng Lee , Hyun Kang
, Hyun Kang
Citations

 , Won Woong Lee
, Won Woong Lee , Haewoo Lee
, Haewoo Lee , Jin Yong Jun
, Jin Yong Jun , Jin-Won Noh
, Jin-Won Noh
Citations

 , Minsung Kim
, Minsung Kim
Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols are designed to minimize surgical stress, preserve physiological function, and expedite recovery through standardized perioperative care for primary colorectal surgery patients. This narrative review explores the benefits of current ERAS protocols in improving outcomes for these patients and provides insights into future advancements. Numerous studies have shown that ERAS protocols significantly reduce the length of hospital stays by several days compared to conventional care. Additionally, the implementation of ERAS is linked to a reduction in postoperative complications, including lower incidences of surgical site infections, anastomotic leaks, and postoperative ileus. Patients adhering to ERAS protocols also benefit from quicker gastrointestinal recovery, marked by an earlier return of bowel function. Some research indicates that colorectal cancer patients undergoing surgery with ERAS protocols may experience improved overall survival rates. High compliance with ERAS protocols leads to better outcomes, yet achieving full adherence continues to be a challenge. Despite these advantages, implementation challenges persist, with compliance rates affected by varying clinical practices and resource availability. However, the future of ERAS looks promising with the incorporation of prehabilitation strategies and technologies such as wearable devices and telemedicine. These innovations provide real-time monitoring, enhance patient engagement, and improve postoperative follow-up, potentially transforming perioperative care in colorectal surgery and offering new avenues for enhanced patient outcomes.
Citations

 , Kye Hwa Lee
, Kye Hwa Lee
 , Jeong-Ju Yoo
, Jeong-Ju Yoo , Sang Gyune Kim
, Sang Gyune Kim , Young Seok Kim
, Young Seok Kim
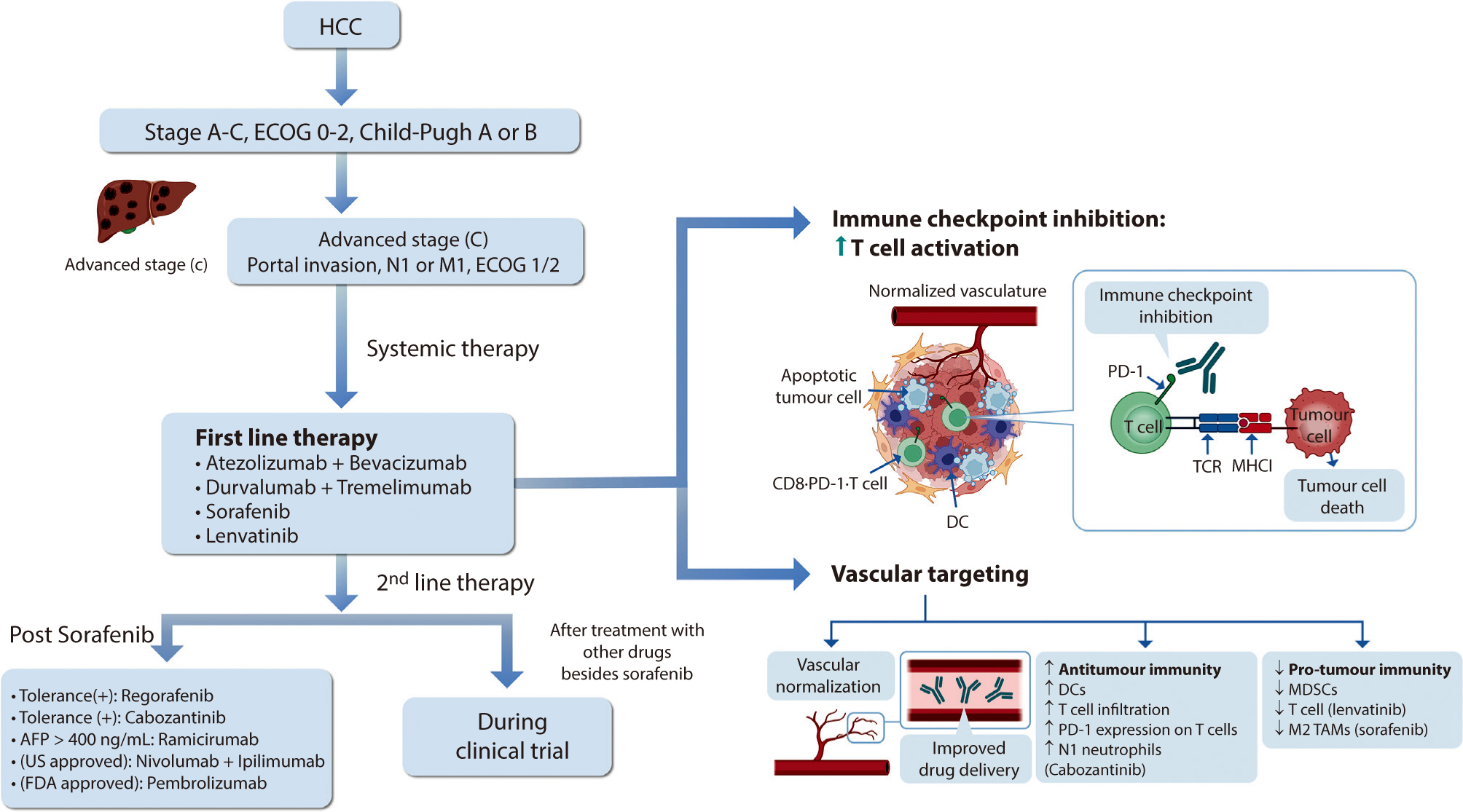
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a critical health concern in Korea, ranking as the second leading cause of cancer mortality and imposing substantial economic burdens, particularly among the working-age population. This review examines recent advancements in treating advanced HCC, referencing the updated 2022 HCC guidelines and the Barcelona Clinical Liver Cancer system. Historically, first-line systemic therapies included sorafenib and lenvatinib, with regorafenib, cabozantinib, or ramucirumab serving as second-line options. Since 2020, immune checkpoint inhibitors have shown superior overall survival than sorafenib, leading to the adoption of combination therapies such as atezolizumab with bevacizumab and durvalumab with tremelimumab as first-line treatments. The IMbrave150 study demonstrated that atezolizumab–bevacizumab significantly extended median overall survival and progression-free survival, with the longest survival reported in any phase 3 trial for advanced HCC. Similarly, the HIMALAYA study indicated that durvalumab combined with tremelimumab significantly improved survival rates. Second-line therapies now include regorafenib, cabozantinib, ramucirumab, nivolumab with ipilimumab, and pembrolizumab, each offering benefits for specific patient populations. Nonetheless, these therapies are associated with side effects that require careful management. Traditional targeted therapies can lead to hypertension, cardiovascular events, and hand-foot skin reactions, whereas immune checkpoint inhibitors may cause immune-related adverse events affecting the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and endocrine system. Clinicians must be well-versed in these treatments and their potential side effects to provide optimal patient care. The emergence of combination therapies targeting complex biological pathways signifies a new paradigm in HCC treatment, emphasizing the importance of continuous education and vigilant monitoring to optimize patient outcomes.
Citations

 , In-Young Yoon
, In-Young Yoon , Dong Yeon Kim
, Dong Yeon Kim , Sooyoung Cho
, Sooyoung Cho
OxyMask, a novel product, has recently been used to administer oxygen postoperatively to patients who have undergone general anesthesia. This study aimed to evaluate the incidence of hypoxia in patients under general anesthesia upon arrival to the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) using arterial blood gas analysis, and to compare the effectiveness of OxyMask with a non-rebreathing oxygen mask for oxygen administration.
We retrospectively investigated anesthesia-related data from the electronic medical records of 460 patients treated from April to November 2021. We analyzed patients aged 20 years or older who had undergone general anesthesia and whose perioperative arterial blood gas analysis results were available upon arrival to the PACU. These patients were grouped into the non-rebreathing oxygen mask (n=223) and OxyMask (n=237) groups, and statistical analysis was performed utilizing their anesthesia records.
No patients exhibited hypoxia upon arrival to the recovery room. The oxygen concentration increased after oxygen administration; its concentration during the recovery room period (Δ2 PaO2) was 10.7±42.3 and 13.9±38.5 mmHg in the non-rebreathing oxygen mask and OxyMask groups, respectively. This difference was not statistically significant. Moreover, the arterial oxygen saturation between the end of surgery and upon arrival to the PACU (Δ1 SaO2) and the arterial oxygen saturation 20 minutes after oxygen administration at the PACU (Δ2 SaO2) did not significantly differ between the groups.
OxyMask was not superior to a non-rebreathing oxygen mask in terms of the effectiveness of oxygen supply.
 , Zhong Yuan
, Zhong Yuan , Hu Yao
, Hu Yao
Blood and urine are commonly used specimens for clinical testing, and their contents, particularly exosomal microRNA (miRNA), are diverse, reflecting the metabolic activities of tissues and organs in the body.
Blood and urine samples were collected from six healthy adults. Exosomes were then enriched from these samples, followed by sequencing and bioinformatic analysis of exosomal miRNA.
The comparative analysis of miRNAs in blood and urine revealed that 41 miRNAs were more abundant in blood, while 61 were found at lower levels. Notably, hsa-miR-934 was among those with higher expression in blood, whereas hsa-miR-425-5p was one of the miRNAs with lower expression. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis indicated that the target mRNAs of differentially expressed exosomal miRNAs (DEexo-miRNAs) in both blood and urine are implicated in various signaling pathways, including proteoglycans in cancer, axonal guidance, and the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Additionally, the target mRNAs associated with DEexo-miRNAs in urine were also linked to processes such as ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis and the phosphatidylinositol signaling system. In contrast, the target mRNAs corresponding to DEexo-miRNAs in blood were involved in the FoxO signaling pathway and chronic myeloid leukemia, among others.
This study observed differential expression of exosomal miRNAs in blood and urine, thereby enriching the available library of exosomal miRNA for these two sample types. It also lays the groundwork for the detection of exosomal biomarkers from blood and urine.
Citations

 , Eun Mee Kim
, Eun Mee Kim
The Republic of Korea’s potential role in the peacebuilding process on the Korean Peninsula is explored, with the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea’s earnest efforts to denuclearize and become a normal country. The paper focuses on the United Nations (UN) agencies in the peacebuilding process, considering the UN’s engagement in the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea during the sanction years with humanitarian assistance, the UN’s legitimacy as an impartial international organization for assisting developing countries in forging peace and prosperity, and recently-adopted resolutions on sustaining peace and the Sustainable Development Goals. Policy recommendations are for the Republic of Korea to actively cooperate with the UN’s development and humanitarian agencies, conduct a thorough preparatory review and conduct research, and work towards expanding its engagement and role within key UN agencies.
Citations


Preoperative chemoradiotherapy (pCRT) followed by total mesorectal excision is the accepted standard treatment for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. The purpose of pCRT is to prevent the spread of viable tumor cells within the local area during surgical procedures. Additionally, pCRT can facilitate the resection of locally advanced tumors that are otherwise challenging to remove, thereby enabling a radical resection. Although a pathologic complete response is observed in fewer than 20% of patients, the reasons for the variability in tumor response to pCRT are not fully understood. Several techniques have been researched with the aim of improving the tumor response to pCRT. These techniques include intensifying or combining chemotherapy, either simultaneously or sequentially, increasing radiation dose, modifying radiation mode or schedule, adjusting the interval between radiation and surgery, and incorporating multiple agents to increase the efficacy of pCRT. This review discusses various strategies that may improve tumor response outcomes following pCRT.

Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) aims to promote postoperative recovery in patients by minimizing the surgical stress response through evidence-based multimodal interventions. In 2023, updated clinical practice guidelines were published in North America, potentially superseding the most recent guidelines previously announced at the ERAS Society in 2019. This review compares and reviews these two guidelines to examine the principle of ERAS and items related to colorectal surgery and to introduce the latest relevant study results published within the last 5 years. In the pre-hospitalization stage, the concept of pre-hospitalization is emphasized; this involves checking and reinforcing the patient’s nutritional status and physical functional status before surgery. In the preoperative stage, large-scale studies have prompted a change in the recommendation of mechanical bowel preparation combined with oral antibiotics in elective colorectal surgery. In the intraoperative stage, laparoscopic surgery has become a widespread and important component of ERAS, and more technologically advanced single-incision laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgery are the focus of active research. Ileus-prevention items, such as opioid-sparing multimodal pain management and euvolemic fluid therapy, are recommended in the postoperative stage. The adoption of ERAS protocols is expanding to encompass a wide range of surgical procedures, clinical scenarios, healthcare institutions, and professional medical societies. In order to maximize the effect by increasing adherence to ERAS, medical staff must fully understand the clinical basis and meaning of each item, and the protocol must be maintained and developed steadily through a team approach and audit system.
Citations

 , Kyoung Hwan Koh
, Kyoung Hwan Koh , In-Ho Jeon
, In-Ho Jeon
The elbow joint, with its intricate anatomy, plays a pivotal role in the upper limb's functional movements. Common surgical indications include epicondylitis, osteoarthritis, tendon tears, and neuropathies. Irrespective of the nature of surgery, appropriate postoperative rehabilitation is essential to enhance recovery, optimize functional outcomes, and minimize complications. Protective measures for the elbow vary based on the surgical procedure is performed. Extended postoperative immobilization is generally not advised. Temporary splints may be utilized to protect the soft tissues in the immediate aftermath of surgery, with patients advised to intermittently remove them to facilitate elbow movement. To increase mobility while ensuring the safety of repaired tendons or ligaments, articulated dynamic braces are recommended. This review delivers clinically useful recommendations specific to various surgical procedures, designed to be user-friendly even for non-specialists in orthopaedic surgery.
 , Kwang Ho Kim
, Kwang Ho Kim , Gyoung Tae Noh
, Gyoung Tae Noh , Ho Seung Kim
, Ho Seung Kim
Recurrent colonic perforation in patients already having colostomy is extremely rare and only a few cases had been reported. Herein, we report 2 cases of recurrent colonic perforation at the proximal part of the colostomy in geriatric patients resulting from different causes, which might be caused by stercoral perforation and recurrent colonic ischemia, respectively. Based on our experience, surgeons should consider correcting chronic constipation even in patients who already have a colostomy. Additionally, transverse colostomy should be considered as a surgical treatment in patients with sigmoid colostomy for recurrent perforation due to colonic ischemia.
 , Jinhoon Nam
, Jinhoon Nam , Ryung-Ah Lee
, Ryung-Ah Lee
We report a rare case of suture material-related colon perforation. A 60-year-old woman visited clinics because of the nonspecific abdominal discomfort for several months. There were no specific medical history except previous laparoscopic myomectomy 15 years ago. Colonoscopy and abdomen-pelvis computed tomography revealed an unknown foreign body penetrating the sigmoid colon wall adjacent to the uterus. We performed laparoscopic exploration with foreign body removal and primary colon wall repair. The foreign body was identified as a non-absorbable suture material suggestive of used in previous myomectomy. With recent trends for minimally invasive procedures in the field of pelvic organ surgery, surgeons, especially those without sufficient training have to pay attention to selecting the proper surgical suture materials. (Ewha Med J 2022;45(3):e7)
 , Ji-Eun Ban
, Ji-Eun Ban
A 16-year-old patient with pectus excavatum visited our hospital because of palpitation. He underwent first Nuss operations at the age of 3. When he was 13 years old, the slow-fast type atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia was documented during electrophysiology study. However, the catheter ablation was not conducted because of recurrent atrial fibrillation during procedure. At that time, second Nuss operation was performed due to progressive chest wall deformity. And then, atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia was successfully treated by radiofrequency catheter ablation at the higher position than usual slow pathway zone under the modified fluoroscopic view with the cranial angle although distorted right atrial geometry and radiographic obstacle of Nuss operation bar. The concern about abnormal cardiac and electrical anatomy, and the accurate and modified procedure technique are essential in patients with pectus excavatum. (Ewha Med J 2022;45(3):e6)
Citations


Small-for-size syndrome (SFSS) is a critical complication of partial liver
transplantation, particularly in adult-to-adult living donor liver
transplantation (ALDLT) using a small graft. Minimally required liver graft size
for a successful ALDLT is classically 40% of a standard recipient’s liver
volume or 0.8% of recipient body weight. Recent progress in perioperative care
and technical improvement push the lower limit of safe graft size to 25% of the
recipient’s standard liver volume or 0.6% of the graft versus recipient
weight ratio although this is an ongoing debate. The clinical manifestations of
SFSS include various symptoms and signs related to graft dysfunction and portal
hypertension in patients with small grafts. The risk factors for SFSS include
poor preoperative patient condition, including portal pressure, surgical
techniques to reduce portal pressure, and graft quality and size. Hence, various
approaches have been explored to modulate inflow and pressure to a small graft
and to decrease the outflow block to alleviate this SFSS as well as the
selection of a patient and graft. Additionally, recent research and efforts to
prevent and treat SFSS are reviewed.
Colonoscopy is commonly used to screen for and diagnose colorectal disease, and adequate bowel preparation is crucial to its quality. As bowel preparation regimens vary, it is important that clinicians understand each and select the proper one for each patient. Accordingly, here we investigated recent studies and describe how to choose the optimal bowel preparation regimen. We detail composition, dosages, efficacy, contraindications, and precautions of commonly used regimens including 4 L polyethylene glycol (PEG), 2 L PEG+ascorbic acid, 1 L PEG+ascorbic acid, trisulfate (oral sulfate solution/tablets), and sodium picosulfate/magnesium citrate. Here we describe that the most recently introduced 1 L PEG and oral sulfate tablets, which were developed to improve convenience and compliance, differ in composition and efficacy between South Korea and foreign countries. This review presents new evidence of and differences among products to increase clinician understanding.
Citations

 , Jun Seop Lee
, Jun Seop Lee , Jong Hak Kim
, Jong Hak Kim , Youn Jin Kim
, Youn Jin Kim , Jae Hee Woo
, Jae Hee Woo , Dong Yeon Kim
, Dong Yeon Kim , Jeong Jeong
, Jeong Jeong
The phase of the menstrual cycle was demonstrated to have an influence on the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) after gynecologic laparoscopic surgery, but little was known for breast surgery, which was shown to have relatively higher incidence of PONV, >60%. We performed this study to investigate the influence of the phase of menstrual cycle on PONV after breast cancer surgery.
A total of 103 patients, who were scheduled for breast cancer surgery under general anesthesia, were recruited, and patients with irregular menstrual cycles, history of previous history of PONV were excluded. Groups were divided in two ways as follows: 1) gynecologic classification: premenstrual and menstrual (days 25 to 6), follicular (days 8 to 12), ovulation (days 13 to 15), and luteal phase (days 20 to 24); 2) menstrual classification: menstrual (days 1 to 8) and non-menstrual (days 9 to 28). PONV were recorded using Rhodes index of nausea, vomiting and retching at postoperative 6 and 24 hours.
The overall incidence of PONV during postoperative 24 hours was 35.4%. At the menstrual classification, the incidence of PONV at postoperative 24 hours was higher in the menstrual group than that in the non-menstrual group (16.7% vs. 4.2%, P=0.057). The severity of PONV, measured with Rhodes index of nausea, vomiting and retching was significantly different between menstrual and non-menstrual groups (P=0.034).
The duration and severity of the PONV after breast cancer surgery were demonstrated to be prolonged and aggravated during menstruation, respectively. Therefore, consideration of menstrual cycle for scheduling breast cancer surgery could effectively prevent the PONV and reduce medical cost.
Citations


All Korean citizens should join the National Health Security System by law. The National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) and the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA) are one of major components to support this system, and all data about medical expenses for the medical claims are stored and managed in the institutions. Recently, medical research using administrative claims databases has dramatically progressed in Korea and worldwide, and the methods how to use them are briefly reviewed in this article. Research using these databases have several strengths. Researchers can perform the complete enumeration survey in a real world. They can get new valuable findings because the number in the database is usually large enough to detect the minute difference with a big statistical power. They can obtain more detailed and reproducible results. Moreover, they can investigate a very rare disease or infrequent side effects of drugs. However, we must recognize that research using administrative claims database also has several incoherent limitations. These databases have not been constructed originally for research, but for reimbursement. Therefore, there are no important data including medical history and laboratory findings of each patient, which are crucial to adjust baseline characteristics. In addition, it is hard to discover causal relationship and direct association with the included information. In spite of limitations, researchers can easily use these databases for their research now than ever, and the results may be utilized not only to expand the academic knowledge but also to influence the determination of national healthcare policy.
Citations


Despite recent advances in the development of diagnostics, therapeutics, and vaccines, the ease of international travel and increasing global interdependence have brought about particular challenges for the control of infectious diseases, highlighting concerns for the worldwide spread of emerging and reemerging infectious diseases. Korea is also facing public health challenges for controlling imported cases of infectious diseases; dengue virus, which is the most commonly reported case of imported infectious diseases; the largest outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infections outside the Arabian Peninsula in 2015; and the Zika virus infection, which was declared by the WHO as a "Public Health Emergency of International Concern." Although national and global partnerships are critical to controlling imported infectious disease threats, the role of local hospitals, public health sectors, and laboratory capacity remains the cornerstone for initial disease recognition and response. The current status of laboratory diagnosis for imported infectious diseases is reviewed.
Citations

 , Dong Il Kim
, Dong Il Kim , Hyo Jin Yun
, Hyo Jin Yun , Se Hee Yoon
, Se Hee Yoon , Sung Ro Yun
, Sung Ro Yun , Won Min Hwang
, Won Min Hwang
Prostatic abscess is not a common entity which is characterized by non-specific clinical presentations. This poses a diagnostic challenge for clinicians. Clinicians routinely consider antibiotic treatments concomitantly with drainage for the treatment of prostatic abscess. But there are no established guidelines for its optimal timing, methods and indications. Surgical drainage procedures include transurethral resection of the prostate and perineal incision and drainage. But there is variability in the prognosis of patients between the procedures. We have treated a 48-year-old diabetes patient with prostatic abscess accompanied by MRSA bacteremia using a percutaneous fine-needle aspiration under the computed tomography (CT) guidance. The patient achieved improvement of the symptoms and in follow up CT findings. A percutaneous drainage under the CT guidance is advantageous in that it causes fewer complications. However, Further studies are warranted to establish the optimal timing, methods and indications in patients with prostate abscess.
 , Kyu-Man Shin
, Kyu-Man Shin , Jun-Hyeok Song
, Jun-Hyeok Song

Arterovenous malformations(AVVMs) represent the most commonly encountered symptomatic vascular malformations in the field of vascular neurosurgery. Surgically accessible AVMs that present with hemorrhage should be removed to reduce the risk of subsequent hemorrhage. The advance of surgery is based on the size, location and pattern of venous drainage and these anatomic features influence the treatment risk. The author studied the above features for predictor of the surgical resection of AVMs.
Nineteen patients(8 male and 11 female patients) with intracranial AVMs were treated at the Ewha Womans Medical Center between March 1989 and Dec. 1996. The mean age, and sexual ratio, of the pts as will as symptoms, location, feeding arteries, pattern of venous drainage and size of the nidus were studied. AVMs were graded according to the Spetzler and martin grade system. Overall outcome and postoperative results in eighteen patients were evaluated according to Glasgow Outcome SCale(GOS).
The average age at the time of treatment was 30.8 years old(range 4-55 years old). The hemorrhage was the most common symptom, occurring in 15(80%) patients, and 2(10%) patients presented with headache, 195%) patient with seizure, 1(5%) patient with neurological deficit. The feeding arteries were as the followings ; middle cerebral artery 8(42%), anterior cerebral artery 2(10%), posterior cerebral artery 1(5%), The pattern of draining veins were described into superficial and deep ; superficial 9(47%), deep 10(53%), The size of the nidus were as the followings ; small(<3cm) 9(47.5%), medium(3-6cm) 9(47.5%), large(>6cm) 1(5%), The Spetzler-Martin's grade and the outcome according to the grade were as follows ; grade I;3(17%) resulted GOS-5 3 patients, grade II ;5(26%) did GOS-5 6 patients, grade III; 5(26%) did GOS-5 4 patients and GOS-4 1 patient, grade IV;4(21%) did GOS-5 3 patients and GOS-4 1 patient, grade V;1(5%0 did GOS-1 1 patient. Overall, there were no death in surgical treatment, patients, the morbidity value was 2(10%) patients, the remainder were completely cured.
The Spetzler-Martin grade I-IV AVMs were associated with low rates of surgical morbidity and mortality, Therefore, surgery is the best treatment in the these grades.

Rastelli procedure for right ventricular outflow tract(RVOT) obstruction has many disadvantage especially for children. Instead of using the artificial valved conduit, we applied the REV procedure for preventing the valve re-replacement after growing and observed the fate of that patch.
We performed REV procedure for RVOT reconstruction with our own hand-made monocusp patch composed of porcine pericardial cusp and bovine pericardial patch in 7 young piglets(15.3±1.3kg) and raised till adult pig9about 70 kg). After sacrificed the pig we explored their pulmonary arteries, monocusp patch and hearts.
Without any stenotic residues in the pulmonary artery, we found the deformed monocusp patch with severe calcification, which deprived the adequate valve function, but kept the pig growing normally.
We are sure that this REV procedure with monocusp patch could be extendedly applied to the RVOT obstruction, but we need to develope the anti-calcification method for the heterograft patch.
 , Jong Oh Kim
, Jong Oh Kim , Sang Hoon Ko
, Sang Hoon Ko
The purpose of this study is the evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of MRI, frequent location of injury site and injury type in meniscal injury, retrospective review of false positive cases.
From September 193 to January 1997 in our hospital, we analyzed a hundred cases of meniscal injury suggested by MRI. And we tried to correct operatively in meniscal injury by arthroscopic or open method of operation.
1)Diagnostic accuracy of MRI was 90%
2)Most common site of meniscal injury was medial meniscus posterior horn(54.4%).
3)Most common injury type was Bucket handle tearing(34.4%).
4)Cause of pitfall in false positive case was most common popliteal tendon sheath(30%).
MRI was effective method on diagnosis of meniscus injury and most common injury was medial meniscus posterior horn, And diagnostic fault was caused by popliteal tendon sheath, lateral inferior genicular artery, truncation artifect, meniscofemoral ligament, transverse geniculate ligament.

Although various kinds of spine stabilizing instruments have been developed over the past years for the treatment of unstable lumbar spinal disorders, the subject is still controversial and contradictory reports are seen in the literature.
Among such instruments, Graf instrument has attracted much interest because of the originality of the idea as s soft stabilizer.
All patients suffered from intractable symptomatic degenerative disc disease which could be localized to one or more levels.
The results of the 30 consecutive patients using the Graf stabilization system are presented from Jan. 94 to Dec. 95.
I have performed Graf soft fixation system on 30 cases of degenerative lumbar spine diseases for 2 years and more than 3 months of postoperative follow-up.
1) There were 10 males and 20 females.
2) The main preoperative diagnosis and evaluation was a severe back pain caused by degenerative disc disease with instability.
3) The most common operation level was a single level, L4/5 in 8 cases(27%), followed by two levels, L4/5+L5/S1 in 6 case(20%).
4) Out of the 30 operated cases, the follow-up results for low back pain were excellent in 14 cases(47%),good in 10 cases(33%).
Although the follow-up in relatively short, the results from this study are sufficiently encouraging to prompt this report. Compared with conventional instrumented spinal fusion, the advantages of Graf system are less surgical trauma with shorted hospital stay and faster rehabilitation with early normal life, The Graf system instead of rigid implant is highly recommendable in managing unstable lumbar disorders.
 , Hee Jin Kim
, Hee Jin Kim , Yeon Ah Sung
, Yeon Ah Sung , Nan Ho Kyung
, Nan Ho Kyung
Thyroid nodule is a common clinical problem and it is important to distinguish benign from malignant nodule. Although features found on history taking, physical examnation and imaging studies help the diagnosis, fine needle aspiration(FNA) has been accepted as an accurate and reliable diagnostic procedure of thyroid nodule. This study was aimed to assess the values of FNA and needle biopsy in the diagnosis of thyroid nodules.
We reviewed the medical records of the 405 patients who underwent FNA and needle biopsy for the diagnosis of thyroid nodule form September 1993 to July 1996.
The 414 fine needle aspiration cytologic specimens were obtained from 405 patients(male : 26, female : 379). 390 cases(94.2%) were adequate for cytologic diagnosis. And the diagnosis showed benign in 357(91.5%), malignancy in 20(5.1%) and suspicious malignancy in 13(3.3%). Among the 357 benign cases, 104 cases were benign cysts, 163 cases were adenomatous goiter and 45 cases were follicular adenoma. 46 patients underwent thyroidectomy after FNA and 21 patients(45.7%) were diagnosed as having carcinoma. The sensitivity and specificity of FNA in diagnosing malignancy were 65% and 82%, respectively, with an accuracy of 74%. Of 46 patients, needle biopsy was done in 41. The sensitivity and specificity of the needle biopsy were 79% and 73%, respectively. And the accuracy was 76%. Hoarseness was developed in one patient after FNA and needle biopsy, and small amount of hemoptysis was developed in another patient after FNA.
Although it had been expected that needle biopsy may increase the diagnostic accuracy, our study didn't show the superiority of needle biopsy as compared with FNA. FNA has limitations in suspicious and nondiagnostic results but it is a safe, simple, reliable and cost-effective means of evaluating thyroid nodules. It is the preferred initial diagnostic method in all patients with thyroid nodule.
 , Jong In Han
, Jong In Han , Jong Hak Kim
, Jong Hak Kim , Chi Hyo Kim
, Chi Hyo Kim , Guei Yong Lee
, Guei Yong Lee , Choon Hi Lee
, Choon Hi Lee , Yeon Jin Cho
, Yeon Jin Cho
There are controversies about the analgesic effects of intraaarticular morphine and local anethetics bupivacaine. This study sought to compare the effects of saline with mor-phine, bupivacaine with or without epinephrine, administrated intraarticularly upon pos-toperative pan following arthroscopic knee surgery under general anesthesia.
In a double-blined, randommized manner, 40 patients received one of saline(20ml, n=10), morphine(1mg in 20ml NaCl, n=10), bupivacaine(0.25%, 20ml, n=10), bu-pivacaine with epinephrine(0.25%, 20ml, 200ug of epinephrine, n=10) intaarticularly at the completion of surgery. The pain scores by VAS were determined after 1,2,3,4 and 24 hours after intraarticular administration.
There were no significant statistical differences between four groups in the pain score. The maximal pain scores were 37.5 in control group, 48.0 in morphine group, 33.6 in bupivacaine group postoperative 1 hour and 32.9 in bupivacaine with epinephrine group pos-toperative 2 hours. The pain scores were decreased as the time went by and were minimin as 21.4 in control group, 17.6 in morphine group, 11.2 in bupivacaine group and 12.3 in bu-pivacaine with epinephrine group 24 hour postoperatively.
Though there were no significant statistical significances with those doses, there were tendencies that the bupivacaine group with or without epinephrine had the postoperative analgesic effect rather than control group, and morphine group had a slow onset of analgesic ef-fect. So, we should study to decide the dose or volume of the drugs and appropriate time to evaluate for the anagesic effects after knee arthroscopy further.
 , Chung Sik Rhee
, Chung Sik Rhee
This experimental study was performed for evaluate the effects of cis-di-amminedichloroplatinum(II) (cis-DDP) on the radiation injury of rat bowel by histopathologic changes.
Rats were exposed to entire abdomen by a single doses of X-ray(6-10 Gy) without or witn cis-DDP(2.5mg/kg). Rats were divided into 3 groups such as radiation alone, cis-DDP alone and combined group. In combined group, cis-DDP was given 30minutes before or immediately after irradiation.
Cis-DDP induced the inflammatory cell infiltrations with focal necrosis of the mucosa in the small bowel and no abnormal change in the large bowel. In radiation alone group, mucosal necrosis, subrnucosal fibrosis and muscular necrosis were prominent changes in small bowel and submucosal fibrosis in the large bowel. The submucosal fibrosis in the small bowel was appealed in 10 Gy of radiation alone group and 8 Gy of cis-DDP infusion after radiation and 6 Gy of cis-DDP infusion before radiation of combined group. In the large bowel, submucosal fibrosis was noted in 8 Gy of radiation alone group and 8 Gy of cis-DDP infusion after radiation and 6 Gy of cis-DDP infusion before radiation of combined group. In the small bowel, the enhancement ratio was 1.67 in a group of cis-DDP infusion before radiation and 125 in a group of cis-DDP infusion after radiation as the end point was the submucosal fibrosis,In the large bowel, the enhancement ratio was 1.33 in a group of cis-DDP infusion before radiation and 1.0 in a cup of cis-DDP infusion after radiation as e end point was e submucosal fibrosis.
This study suggested that cis-DDP enhance the radiation effect in the small and large bowel especially when cis-DDP was infused before radiation.
 , Bong Suck Shim
, Bong Suck Shim , Sung Won Kwon
, Sung Won Kwon
The purpose of this study is to investigate the clinical result of Marshall-Mar-chetti-Krantz operation, one of the treatment methods for stress urinary ncontinence.
Authors have analyzed the 66 cases out of 83 stress urinary incontinence patientsin whom Marshall-Marchetti-Krantz operation and 1 year follow-up was performed at UrologyDepartment of Ewha Womans University Hospital from January 1990 to December 1993.
The results were as follows:
1) The patients' age distribution was from 33 to 53 years old (mean age 44.9 years). The average number of deliveries was 3.1 and 29 patients were multipara with more than 4 deliveries.
2) As compared with urinary incontinence grade, Grade I was seen in 22 cases (43.9%),Grade II in 40 rases (42.4%) and Grade III in 4 cases (6.1%). Overall Grade II was most frequent.
3) PUV angle between posterior urethra and bladder base seen by chain cystourethrographywas 154.0°(134-179°) in average and urethral inclination was 23.9°(14-50°)in average.
4) The operation took between 36 to 72 minutes with mean 45.2 minutes. Urethral catheter was placed after the operation for mean 5.0 days (4-8 days) ana hospitalization days weremean 8.3 days (7-15 days).
5) 6 cases (9%) of urinary retention was the only postoperative complication and all of themwere resolved 3-7 days after intermittent catheterization.
6) In the fi11ow-up after 6 months, recurrence was seen on the third month after the operationin 2 cases and on the 12th month in 3 cases which resulted in 92.4% of operation success rate.
Marshall-Marchetti-Krantz method can safely be performed in patients withstress urinary incontinence and further comparative study with otter operation method be needed.

The repair of striated muscle after injury by trauma or chemicals occurs simultaneously by the regeneration of disrupted muscle. Tlthough the efects of various external factors e.g. denervation, irradiation and steroid upon the repair of striated muscle injury has been previously studied, no attention has been focused on the effect of trauma and local anesthetics on the regenearted muscle fiber.
The author induced a constant contusion injury on the calf of rats using Drop-Weight method Lidocaine and/or epinephrine was intramuscularly injected at the site of injure.
The results of morphological and histochemical observation were as follows:
1) The striated muscle showed histological and histochemical evidences of the healing process for 90 days.
2) Formation of myotube appeared on 7th day and decreased on 15th day. Myotube persisted upto 30 days.
3) The cross sectional area of the muscle fibers was measured days 30 and 90. Local anestetic injection groups showed mire muscle fiber atrophy than trauma alone groups. Muscle fibers were significantly more atrophied on day 90 in all types of fiber after injection of mixture of lidocaine and epinephrine and on type B after injection of mixture of lidocaine and epinephrine and in type B after injection of epinephrine compared to control group.
4) Regenerative capacity of the injured muscle piber was correlated with the formation of myotubes.
 , Jung En Park
, Jung En Park , Hee Jung Sohn
, Hee Jung Sohn , Keum Mi Kim
, Keum Mi Kim , Jung Ran Byun
, Jung Ran Byun , Young Yub Koh
, Young Yub Koh , Doe Young Kim
, Doe Young Kim , Il Hwan Moon
, Il Hwan Moon
Ulcerative colitis is an waxing and waning inflammatory bowel disease characterized by rectal bleeding and diarrhea, affecting principally the mucosa of the rectum and colon. Its incidience is being higher in Europe and America and it also seems to be rising increasingly in our country because diagnostic methods are much developed and Korean life styles are westernized. So, we investigated its clinical characteristics.
We analyzed 36 cases of ulcerative colitis which had been treated in the Hospital of Ewha Womans' University from Jan. 1983 to Feb. 1993, retrospectively.
1) The most prevalent age group was 3rd decade and male to female ratio was 1:1.77.
2) The duration of symptoms was less than 6 months in 63.9%.
3) The most common clinical manifestation was hematochezia(86.1%), abdominal pain(75.0%), diarrhea(72.2%), fever(30.6%), weight loss(27.8%) in the order of frequency.
4) According to the severity, moderate type was shown in 52.8%, severe in 33.3% and mild in 13.9%.
5) According to the anatomical distribution of the lesion, pancolitis was shown in 36.1%, the involvement of the rectum and sigmoid colon in 16.6%, the left-sided colon in 13.8%, rectum only in 13.8%, transverse colon in 8.3% and backwash ileitis in 11.1%, respectively.
6) The hematologic laboratory finding was non-specific including anemia, leukocytosis, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, bypoalburninemia, electrolyte imbalance, increased serum transaminase and alkaline phosphatase.
7) Colonoscopy revealed ulceration(77.1%) commonly, including hyperemia(51.4%), bleeding(42.5%), mucosal friability(22.9%), pseudopolyp(22.9%), granularity(20.2%).
8) The Barium enema showed granularity commonly and loss of haustral marking(55.2%), luminal narrowing(34.5%), lead pipe rigidity(13.8%), pseudopolyp(3.4%). Also, normal finding was shown in 10.3%.
9) The most common histopathologic finding was inflammation(83.3%) and ryptitis(55.6%), ulceration(50%), goblet cell depletion(19.4%), pseudopolyp(19.4%), necrosis(13.9%), granolarity(8.3%) were also noted.
10) With the medical treatment, 76.5% of the cases showed initial improvement of the symptom, but the recurrence developed in 17.7%. The surgery was performed in 6 cases of patients(16.7%). Emergency operation was performed in 2 cases due to bowel perforation and elective operation in 4 cases.
Citations


In experimental neurogenerative diseases, aluminum(Al) intoxication and axotomized sensory neurons showed an abnormal accumulation of neurofilaments(NF) in the neuronal perikarya. These NF contain phosphorylated(ph) epitopes that are not detectable in normal perikaryal NF. Antimitotic drugs also cause accumulations of NF probably by depolymerization of microtubules(MT). The present study was designed to examine immunohistochemical changes of NFs following administration of antimitotic drugs, which result in accumulation of NFs in the cell body through a different pathogenetic mechanism than aluminum. Adult rabbits were injected intracisternally with 25-50µg of maytansine and maytanprine, two antimitotic agents. Tissues were obtained from experimental and control animals and processed for histological and immunocytochemical examinations. Large bundles of NF in the perikarya and proximal processes of large neurons from experimental animals reacted intensely with monoclonal antibodies(mAb) to ph epitopes of 200 KDa NF subunit as well as with mAb recognizing nonphosphorylated(non-ph) NF epitopes. Neuronal perikarya from control animals immunoreacted only with mAb to non-ph NF Immunoreaction of Ab to the microtubule associated protein 2(MAP-2) and to tubulin was similar in neurons from experimental and control animals. No immunoreaction was detected with antibodies to tau proteins. The abnormal presence of ph epitopes in accumulating NF under different conditions indicate that neurons affected in different diseases show aberrant phosphorylation of NF proteins associated with functional impairment.

The aid of treatment in patellar fracture is the restoration of knee joint function and quadriceps muscle power. In this series, we experienced 37 cases of patellar fractures from March 1981 to March 1987 which were treated with operative care and followed-up at least 2 years at Department of the Orthopedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University.
The results were as follow :
1) Most fractures were encountered in man from twenties to thirties.
2) The traffic accident was the most prevalent cause(17 cases, 47%) and 24 cases(65%) of fracture were induced by direct injury.
3) The most frequent configration of fractures was comminuted.
4) Among the operative methods, the result of the tension band wiring was superior to other operative methods, but not significantly.
5) The long-term result of patellar fracture with operative management following trauma may be directly related to this initial damage, involvement of articular surface, duration of immobilization and operative method.

We studied the postnatal development of the renal function and the incidence of the renal dysfunction in premature with reapiratory distress syndrome, admitted to NICU, E.W.U.H. from March, 1986 to August 1989.
The results were as follows.
1) Renal function in Group I, RDS premature without perinatal asphyxia, was not different from the control values.
2) Renal function in Group II, RDS premature with perinatal asphyxia was different from the control values. Serum creatinine concentration was 1.05mg% at postnatal age 3 day and decreased to 0.88mg% at P.A 7 day. But both values were significantly higher than control values(P<0.05)
Creatinine clearance, 10.8ml/min/1.73m at P.A. 3 day which was significantly lower than control, but increased to 17.4ml/min/1.73m at P.A. 7 day which was not different from control value. Urine Na excretion and FENa were 5.2lmEg/kg/d and 3.81% at P.A. 3 day and decreaed to 3.42mEg/kg/d and 1.86% at P.A. 7 day. But both values were significantly higher than control values.(P<0.05) The incidence of proteinuria, oliguria and azotemia were significantly higher than control.(P<0.05)
In conclusion, RDS per se did not compromise the renal function. But associated perinatal asphyxia delayed the postnatal development of the glomerular function and the tubular reabsorptive capacity which seemed to be transient.
 , Ki-Nam Shim
, Ki-Nam Shim , Hye-In Kim
, Hye-In Kim , Hyeon Ju Kang
, Hyeon Ju Kang , Min Sun Ryu
, Min Sun Ryu , So-Young Ahn
, So-Young Ahn , Hye Kyung Jung
, Hye Kyung Jung , Sung-Ae Jung
, Sung-Ae Jung
To investigate the rate of first-line eradication and the rate of second-line eradication of
Among the 2,717 patients who received
The first-line eradication rate was 77%
In this study, no decrease in tendency of first-line eradication rate could be found. In addition, the patients with the non-ulcerative gastric disease seemed to show significantly lower eradication rate. This finding suggests eradication treatment may be affected by the category of gastric diseases, and careful considerations should be taken assessing the effects and needs for the
Citations

 , Hee Yeon Choi
, Hee Yeon Choi , Jin Woo Kim
, Jin Woo Kim , Sun Jong Kim
, Sun Jong Kim , Seung Sin Lee
, Seung Sin Lee , Jung Ho Pae
, Jung Ho Pae , Weon-Jeong Lim
, Weon-Jeong Lim , Hyang Woon Lee
, Hyang Woon Lee
The prevalence of sleep disorder is about 30% of the population. Common sleep disorders are insomnia, obstructive sleep apnea, narcolepsy, restless legs syndrome, rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder and parasomnia. These sleep disorders lead various medical and mental complications. However, most sleep disorders are underdiagnosed and not treated appropriately. Sleep medicine is important for treating these sleep disorders and maintaining general healthy conditions. Specialized and comprehensive treatments for sleep disorder are important in sleep medicine.
 , Jin Hwa Lee
, Jin Hwa Lee , Sun Hee Sung
, Sun Hee Sung , Seong Hoon Park
, Seong Hoon Park
Amiodarone has been widely used for supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias and many patients benefit from its effectiveness in treating potentially life-threatening arrhythmias. However, this drug can cause multi-organ toxicity, including amiodarone-induced pulmonary toxicity (APT). Not only does amiodarone have a long half-life but also is lipophilic and therefore can easily accumulate in tissues. Hence, it is difficult to monitor therapeutic levels and side effects, making it difficult to predict toxicities. In this case, we describe multi-organ complications secondary to amiodarone use, especially APT combined with pneumonia with atypical pathogens and pulmonary hemorrhage. The patient reached a high cumulative dose of amiodarone despite a low maintenance dose of amiodarone. This case highlights an unusual presentation of APT with multi-organ toxicity and we review articles regarding the association between the cumulative dose of amiodarone and amiodarone-induced toxicities.
Citations

 , Jeong-Mi Lee
, Jeong-Mi Lee , Ja Yoon Choi
, Ja Yoon Choi , Dong-Hoon Lew
, Dong-Hoon Lew , Ra Ri Cha
, Ra Ri Cha , Hye Won Oh
, Hye Won Oh , Hong-Jun Kim
, Hong-Jun Kim , Hyun Ju Min
, Hyun Ju Min , Hyun Jin Kim
, Hyun Jin Kim , Woon-Tae Jung
, Woon-Tae Jung , Ok-Jae Lee
, Ok-Jae Lee , Chang Yoon Ha
, Chang Yoon Ha , Sun Young Yi
, Sun Young Yi
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) has become an effective alternative treatment strategy for patients with inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Although TACE is relatively safe, acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with pulmonary lipiodol embolism is a rare and potentially fatal complication. We report a rare case of acute respiratory distress syndrome after TACE for inoperable HCC. A 75-year-old man, with huge HCC in right lobe, was treated by TACE for the first time. Seven hours after uneventful TACE procedure, he felt dyspneic and his oxygen saturation recorded by pulse oximetry (SpO2) fell to 80% despite of applying non-rebreathing mask. He underwent mechanical ventilation with a protective ventilatory strategy. We experienced a case of acute respiratory distress syndrome after TACE for HCC.

Anterior microforaminotomy (AMF) is an alternative procedure to treat unilateral cervical pathology. Although the results have been reported favorable in the previous studies, postoperative degeneration may occur. We analyze long-term outcome to determine the critical size of AMF.
A retrospective study was performed. Clinical data with chart review, radiologic data with picture archiving and communication system (PACS) images were obtained. Long-term clinical outcomes were accessed by a questionnaire, including visual analogue scale (VAS) and neck disability index (NDI). Various clinical, radiological data were statistically analyzed.
Eight-two patients were enrolled in this study. Main pathology was spondylotic spur (53.7%), soft disc herniation (36%). Mean age was 49 years old. There was no surgery-related complication. Mean follow-up was 6.1 years. 90.3% showed favorable clinical outcome. Mean VAS score was decreased from 8.2 to 2.9, and NDI score was decreased from 24.5 to 6.7 (P<0.05). 88.7% showed decrease of disc height (DH), and mean change was 1 mm. DH change was correlated positively with the disc invasion and AMF diameter (P<0.05). Mean diameter of AMF was 5.2 mm. According to statistical analysis, the critical diameter of AMF was 4.7 mm, directly affecting DH decrease. Any radiological parameters did not affect the clinical outcome.
AMF was an effective procedure to treat unilateral cervical pathology. Critical DH decreases and/or disc invasion may be the trigger of sequential degeneration. To preserve DH, AMF diameter should be small and disc invasion should be avoided.
 , Sung-Ae Jung
, Sung-Ae Jung , Ki-Nam Shim
, Ki-Nam Shim , Jung-Hwa Chung
, Jung-Hwa Chung , Seok-Hyung Kang
, Seok-Hyung Kang , Do-Kyeung Song
, Do-Kyeung Song , Seung-Jung Jun
, Seung-Jung Jun , Hye-In Kim
, Hye-In Kim
Until recently, colorectal polyps were classified predominantly as hyperplastic or adenomatous. While adenomatous polyps are well-characterized precursor lesions of adenocarcinomas, hyperplastic polyps have been considered as benign lesion. However, some hyperplastic polyps with serrated morphology of the crypts have been recognized to have distinctive features and these polyps were termed 'serrated adenomas'. Recent data show that sessile serrated adenomas (SSA) might be the precursors of serrated colonic cancers, underlining the necessity of identifying them. SSA is approximately 3% of all polyps, commonly appears as flat or sessile and yellowish due to mucus production. In the pathogenesis of SSA, progression to high grade dysplasia or early invasive carcinoma may be associated with serrated neoplasia pathway different from adenoma-carcinoma sequence. We report a case with a colon polyp diagnosed as sessile serrated adenoma with high grade dysplasia after endoscopic submucosal dissection.
 , Ki-Sook Hong
, Ki-Sook Hong
According to current knowledge, apolipoprotein B/A1 (apoB/A1) ratio is like to be risk factor in coronary artery disease. There is evidence form case-control studies that apoB/A1 ratio may be a superior to LDL and HDL cholesterol in discriminating coronary artery disease case subject from control subject. However, relationship between apoB/A1 ratio and cerebral ischemic stroke is undefined. The main object of this study is to determine whether the risk of cerebral ischemic stroke is related to levels of apoB/A1.
The study group included 643 patients (Men, 372; Women, 271) who diagnosed cerebral ischemic stroke between January 2008 to December 2010. The control groups were composed of 378 patients (Men, 139; Women, 239) who diagnosed other neurological disease. The correlation between lipid profiles and odds ratio of 10 preliminary risk factors (total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL, HDL, apoA1, apoB, apoB/A1 ratio, non HDL, total cholesterol/HDL ratio, LDL/HDL ratio) for stroke were analyzed.
ApoB/A1 ratio was significantly increased in case patients compared with control subjects. Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified decrease of apoB/A1 ratio (odds ratio [OR], 1.583; 95% confidence intercal [CI], 1.105~2.269) as significantly associated with stroke. Individual apoA1 (OR, 1.303; 95% CI, 0.967~1.755) and apoB (OR, 1.397; 95% CI, 0.773~2.523) were also not significantly associated with cerebral ischemic stroke.
Increase of apoB/A1 ratio is associated with an increase risk of cerebral ischemic stroke. Use of apoB/A1 ratio is efficient as conventional lipids, for the identification of subjects at increased risk of stroke. So apoB/A1 ratio to standard lipid profile testing could improve the evaluation of risk factors of cerebral ischemic stroke.
Citations

 , Ki Sook Hong
, Ki Sook Hong
Cardiac troponin T(cTnT) levels are elevated in patients with chronic renal fail-ure(CRF) with dialysis which represent myocardial damage. But the cut-off levels were different in laboratories and clinical physicians. We conducted a study to find out the cut-off levels of acute myocardial infarction(AMI), ischemic heart disease(IHD), and cardiovascular disease (CVD) in CRF patients with dialysis and prognostic aspect according to cTnT levels.
Cardiac troponin T(cTnT) of total 98 patients(men 43, women 55, mean age 60.4±13.0 years) was reviewed the diagnosis and progress for 3 years by the medical records. Serum cTnT by Elecsys 2010(Roche diagnostics, Germany), the 4th generation assay was performed.
Mean cTnT level of total 98 patients was 0.26ng/mL and the patients with CVD were 59(60.2%) and their cTnT level was 0.41 ng/mL. The mean levels of cTnT in AMI, IHD, and CVD were 1.10, 0.52, and 0.41 ng/mL, respectively. cTnT, CK, CK-MB, and glucose were increased according to severity of cardiovascular disease. The cut-off levels of cTnT in AMI, IHD, and CVD was 0.10, 0.07 and 0.06 ng/mL. The sensitivity and specificity of AMI, IHD, and CVD in each cut-off level were 88.2/71.6%, 76.2/71.4%, and 81.4/71.8%, respectively. The survival rate above cTnT 0.1 ng/mL during 3 years was significantly decreased(p<0.001) than less than 0.1 ng/mL.
The degree of cTnT elevation in CRF patients with dialysis represents severity of cardiovascular disease and poor survival rate.
 , Soo A Oh
, Soo A Oh , Kyoung-Eun Lee
, Kyoung-Eun Lee , Eun-Sun Yoo
, Eun-Sun Yoo , Moon Young Choi
, Moon Young Choi , Jee-Young Ahn
, Jee-Young Ahn , Chu-Myong Seong
, Chu-Myong Seong
Leukotriene B4(LTB4) is lipid mediator derived from membrane phospholipids during the process of inflammation, having many roles(ie; inducer of chemotaxis, the production of nitric oxide, transepithelial migration of neutrophil). The major activities of LTB4 include the recruitment and activation of leukocytes, suggesting that it may involve the process for transendothelial migration of nuclear cells in bone marrow environment. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) have a cell signaling roles that are involved in signal transduction cascades of numerous growth factor-, cytokine-, and hormone-mediated pathways, and regulate many biological systems. In this present study, we focused on the role of LTB4 and ROS on transmigration of bone marrow nuclear cells across endothelial or stromal cell monolayer.
MS-5, murine stromal cell line cells, or bEnd.3, murine microvascular cell line cells, were grown to confluence on microporous transwell membrane. Murine marrow cells were placed on top of the prepared transwell membrane. The transwells were then seated in wells containing media and LTB4 with or without pretreatment of N-acetylcysteine(NAC), an oxygen free radical scavenger, or diphenylene iodonium(DPI), an inhibitor of NADPH oxidase-like flavoproteins. Cells that migrated through the stromal or endothelial layer into the wells were assayed for transendothelial migration.
The numbers of migrated bone marrow nuclear cells through the bEnd.3 were increased by treatment of LTB4(control, 12.5±0.2%; 50nM, 22.7±0.9%; 100nM, 44.3±1.4%; 200 nM, 36.3±0.9%; p<0.05). The numbers of migrated bone marrow nuclear cells through the MS-5 were also increased by treatment of LTB4(control, 11.0±0.9%; 50nM, 25.7±0.9%; 100nM, 35.8±1.8%; 200nM, 32.1±0.9%; p<0.05). However, increasing effect of LTB4 to the transmigration of bone marrow nuclear cells through the MS-5 or bEnd.3 were inhibited by pretreatment of NAC or DPI.
Through our data, it is suggested that LTB4 could induce the transmigration of bone marrow nuclear cells and ROS might be involved on the transendothelial migration of bone marrow nuclear cells by LTB4. It would be very interesting to test the effects of LTB4 and ROS on stem cell mobilization and homing in the future.
 , Sung-Ae Jung
, Sung-Ae Jung , Hyun Joo Song
, Hyun Joo Song , Jae Jung Park
, Jae Jung Park , Kyung Jong Lee
, Kyung Jong Lee , Eun Kyung Baek
, Eun Kyung Baek , Seog Ki Min
, Seog Ki Min
Nowadays, upper gastrointestinal endoscopy is very commonly performed procedure as a diagnostic tool or therapeutic purpose. Although perforation rate during diagnostic evaluation has been reported as low about 0.03%, gastrointestinal perforation is a critical problem to the patients owing to significant morbidity and hospital stay. Therefore, all endoscopists should know the risk factors for the perforation and pay attention to avoid this complication. We experienced a case of 66 year-old-male with duodenal microperforation after endoscopic biopsy. During endoscopic examination, a submucosal mass was detected at duodenal second portion and endoscopic biopsy was performed. After this, he complained of severe abdominal pain during colonoscopy. Emergent simple abdomen and abdominal computed tomography revealed multiple free air in retroperitoneal space and duodenal perforation was suspicious. He was treated with primary closure and then recovered completely. Therefore, we report a case with microperforation after endoscopic duodenal biopsy.
 , Miae Lee
, Miae Lee , Whasoon Chung
, Whasoon Chung
Undergraduate medical students should learn oral presentation skills, which are central to physician-physician communication. The purpose of this study was to compare checklist scores with global ratings for evaluation of oral case presentation and to investigate interrater agreement in the scoring of checklists.
The study group included twenty-one teams of undergraduate medical students who did clerkship for 2 weeks in the department of Laboratory Medicine of Mokdong Hospital, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University from January 2005 to October 2006. Three faculty raters independently evaluated oral case presentations by checklists, composing of 5 items. A consensus scores of global ratings were determined after discusssion. Inter-rater agreement was measured using intraclass correlation coefficient(ICC). As the ICC values approaches 1.0, it means higher inter-rater agreement.
The mean of consensus global ratings was significantly higher than that of checklists by three faculty raters(12.6±1.7 vs 11.1±2.0,
These results suggest that checklist scores by faculty raters could be one of the most useful tools for evaluation of oral case presentation, if checklist would be modified to make less ambiguous and more objective and faculty raters would have opportunities to be educated and trained for evaluation skills of oral case presentation.
Citations

 , Guie Young Lee
, Guie Young Lee
No abstract available in English.
Citations


Smoking cessation is the mainstay of treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD) and prevention of related malignancy. But smoking cessation cliniss generally have low success rates. The aim of this study is to evaluate the abstinece rates and factors determining success among during out patient(OPD) run by pulmonologist(smoking cessation specialist).
125 smokers with COPD(97) and bronchal asthma(28) were consulted in the smoking cessation clinic during treatment of out patients department from 2003 to 2005.
Patients palnned to cisit every 4 weeks and the patients were ercerived brief intervenrion(5-10 minutes) by a same pulmonologist(smoking cesation specialist) every 4weeks. Medication was evaluated every 4 weeks and followed-up for 6 months.
Overall, 33%(41/125) of patients were absinent at 6 months. Success rate was higher among the older(mean age of 54.0 vs. 45.6, p=0.00). Logistic regression was to identify predictors of abstinence at the end of the medication phase.
Mulivariate predictors of abstinence were the following : older age(p<0.00), numbers of visit to OPD[OR=1.85(95% CI : 1.21-2.86)], duration of medication [OR=18.3(95% CI : 1.54-217.00)], doctor's recommendation[OR=16.62(95%CI : 1.29-214.17)].
Brief, frequent and intensive motivational intervention with medication(bupropion) during OPD by specialist was effective for cessation smoking in view of time and cost for smokers with COPD and bronchial asthma who require quitting of smoking inevitably for treatmint and prevention of diease.

