 , Joonil Hwang
, Joonil Hwang , Hai-Jeon Yoon
, Hai-Jeon Yoon , So Hyun Ahn
, So Hyun Ahn
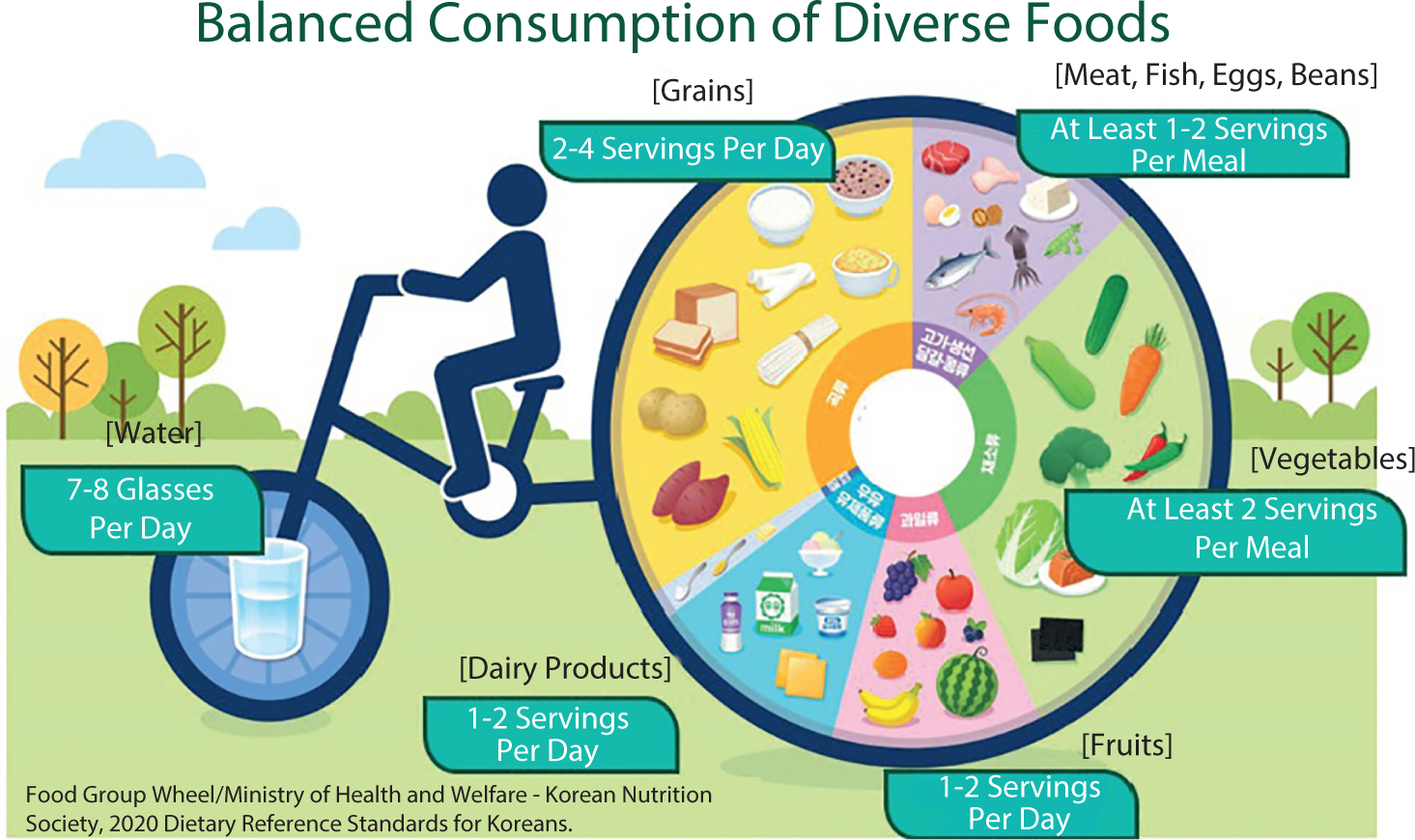
Breast cancer is a complex disease influenced by environmental, genetic, dietary, and hormonal factors. This underscores the importance of postoperative nutritional management in supporting recovery, minimizing complications, and enhancing long-term outcomes. This review synthesizes clinical guidelines, expert recommendations, and observational studies to provide a comprehensive overview of dietary interventions for breast cancer patients following surgery. Post-surgical nutritional care is centered around three primary objectives: supporting wound healing through high-quality protein intake, maintaining optimal nutritional status to prevent malnutrition, and promoting healthy lifestyle habits to reduce the risk of recurrence. To achieve these objectives, postoperative dietary strategies focus on several key components: ensuring adequate hydration for metabolic processes and tissue repair, consuming a balanced diet rich in fresh vegetables and fruits to mitigate oxidative stress, incorporating whole grains to support overall healing, and maintaining sufficient intake of high-quality protein from sources such as fish, meat, and dairy products to aid tissue repair and immune system recovery. Patients are also advised to avoid alcohol, limit saturated fats, and reduce intake of salty, sugary, and smoked foods to minimize inflammation. As research progresses, the implementation of personalized dietary plans remains essential for optimizing recovery outcomes in breast cancer patients.
 , Hyeonuk Hwang
, Hyeonuk Hwang , Hyungju Kwon
, Hyungju Kwon
Conventional open thyroidectomy is a safe procedure, but it has the disadvantage of leaving noticeable scars on the neck. Bilateral axillo-breast approach (BABA) robotic thyroidectomy was developed as an alternative technique to remove thyroid glands without making incisions in the neck. In traditional BABA robotic thyroidectomy, dividing the isthmus is a routine step to improve the efficiency of the dissection during thyroid surgery. However, there are safety concerns when performing this procedure on patients with thyroid cancer located in the isthmus. We report a case of BABA robotic total thyroidectomy carried out without dividing the isthmus in a patient with isthmic papillary thyroid carcinoma. Our experience suggests that BABA robotic surgery can be a feasible and safe option for selected patients with isthmic papillary thyroid carcinoma.
 , Eun-Suk Cha
, Eun-Suk Cha , Jee Eun Lee
, Jee Eun Lee , Jeoung Hyun Kim
, Jeoung Hyun Kim , Bom Sahn Kim
, Bom Sahn Kim , Jin Chung
, Jin Chung
We aimed to compare the diagnostic performances of digital mammography (DM), digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), ultrasound (US), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), breast specific gamma imaging (BSGI) and/or positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) for the detection of invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC).
Index ILCs and multifocal/multicentric (multiple) ILCs were analyzed using various imaging modalities. The final surgical pathology was regarded as the reference standard. The detection rate for index cancers and the diagnostic performance for multiple ILCs per breast were evaluated.
Seventy-eight ILCs in 76 women were enrolled. Twenty-six breasts had multiple ILCs. DM (n=72), DBT (n=15), US (n=77), MRI (n=76), BSGI (n=50), and /or PET/CT (n=74) were performed. For index cancer, the detection rate was 100% for DBT, US, and MRI. For multiple ILCs, the sensitivity was 100% for DBT and MRI (P<0.001). The diagnostic accuracy for multiple ILCs were 73.3% for DBT and 73.0% for PET/CT (P=0.460).
DBT was the most accurate imaging modality for both index and multiple ILCs. PET/CT was also valuable for multiple ILCs, whereas DM and BSGI showed relatively low diagnostic performances. DBT and PET/CT have promising roles in the diagnosis of multiple ILCs.
Citations

 , Jun Seop Lee
, Jun Seop Lee , Jong Hak Kim
, Jong Hak Kim , Youn Jin Kim
, Youn Jin Kim , Jae Hee Woo
, Jae Hee Woo , Dong Yeon Kim
, Dong Yeon Kim , Jeong Jeong
, Jeong Jeong
The phase of the menstrual cycle was demonstrated to have an influence on the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) after gynecologic laparoscopic surgery, but little was known for breast surgery, which was shown to have relatively higher incidence of PONV, >60%. We performed this study to investigate the influence of the phase of menstrual cycle on PONV after breast cancer surgery.
A total of 103 patients, who were scheduled for breast cancer surgery under general anesthesia, were recruited, and patients with irregular menstrual cycles, history of previous history of PONV were excluded. Groups were divided in two ways as follows: 1) gynecologic classification: premenstrual and menstrual (days 25 to 6), follicular (days 8 to 12), ovulation (days 13 to 15), and luteal phase (days 20 to 24); 2) menstrual classification: menstrual (days 1 to 8) and non-menstrual (days 9 to 28). PONV were recorded using Rhodes index of nausea, vomiting and retching at postoperative 6 and 24 hours.
The overall incidence of PONV during postoperative 24 hours was 35.4%. At the menstrual classification, the incidence of PONV at postoperative 24 hours was higher in the menstrual group than that in the non-menstrual group (16.7% vs. 4.2%, P=0.057). The severity of PONV, measured with Rhodes index of nausea, vomiting and retching was significantly different between menstrual and non-menstrual groups (P=0.034).
The duration and severity of the PONV after breast cancer surgery were demonstrated to be prolonged and aggravated during menstruation, respectively. Therefore, consideration of menstrual cycle for scheduling breast cancer surgery could effectively prevent the PONV and reduce medical cost.
Citations

 , Hyung Jun Park
, Hyung Jun Park , Kyoung-Gyu Choi
, Kyoung-Gyu Choi , Key Hwan Lim
, Key Hwan Lim , Kee Duk Park
, Kee Duk Park
Orbital metastases are rare and predominantly unilateral occurrences. Bilateral metastases affecting the extraocular muscles are extremely rare. A few case reports of bilateral metastases to extraocular muscles described binocular diplopia with conspicuous bilateral external ophthalmoplegia as an initial symptom. We report a case in which unilateral ptosis was an initial symptom and bilateral incomplete ophthalmoplegia was found on initial neurologic examination in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. The patient had hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, and so was treated by hormonal therapies and closely monitored. The presence of a secondary orbital lesion presents many difficulties of differential diagnosis and treatment. A thorough neurologic examination to detect ocular manifestations is most important for localization and broad differential diagnosis including mechanical orbital metastatic lesion.
Citations

 , Joohyun Woo
, Joohyun Woo , Hyang Suk Choi
, Hyang Suk Choi , Seok Joon Lee
, Seok Joon Lee , Jihye Choi
, Jihye Choi , Chan Sub Park
, Chan Sub Park , Min-Ki Seong
, Min-Ki Seong , Woo Chul Noh
, Woo Chul Noh
The evaluation of menopausal status is an important subject in the field of treatment of hormone receptor positive breast cancer. According to the menopausal status, endocrine therapy should be categorized by individual patient. However, the gonadal injury caused by various therapeutic drugs and its recovery would confuse the interpretation of clinical and biological markers for ovarian reserve. There are some methods to examine the functional ovarian reserve indirectly. Ultrasonography for counting follicles is a relatively reliable procedure, although it is not feasible because of time-labor consumption and high cost. Biological marker from blood samples such as serum follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), serum estradiol (E2), serum inhibin, or anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) would be a better choice. The examination of serum FSH and E2 is already recommended as biomarkers for measuring functional ovarian reserve in many guidelines. However, there are limitation of serum FSH and E2 in patients with chemotherapy-induced amenorrhea and treated by tamoxifen. AMH is promising biomarker in the field of infertility treatment even in the patients treated by chemotherapy. It might be a possible biomarker to determine the menopausal status for decision-making whether aromatase inhibitor could be applicable or not in hormone positive breast cancer patients with chemotherapy induced amenorrhea or treated by tamoxifen.
 , Jinsu Kim
, Jinsu Kim , Seokyoung Yoon
, Seokyoung Yoon , Eung-Ho Cho
, Eung-Ho Cho , Changwon Jung
, Changwon Jung , Hye Jin Kang
, Hye Jin Kang
A 37-year-old woman underwent a total mastectomy and adjuvant chemotherapy for HER2-positive breast cancer (pT1N0M), and then recurred in the right lung followed by the pancreas. Lung lobectomy and pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy were performed, and systemic chemotherapies including trastuzumab were sequentially administered. However, metastasis to the pancreatic tail was detected. She underwent image-guided radiation therapy, but this was not effective. Lapatinib plus capecitabine combination was administered as forth-line treatment and the metastatic lesion was disappeared. She is continuing this regimen with a complete response for 48 months until now.
Citations

 , Yeon-Soon Lim
, Yeon-Soon Lim , Hae-Young Choi
, Hae-Young Choi , Ki-Bum Myung
, Ki-Bum Myung
A case of unilateral accessory axillary breast tissue developed as a subcutaneous nodule unassociated with menstrual periods, pregnancy, or lactation in a 33-year-old parous woman. Histopathologic finding of the nodule revealed lobules of normal breast tissue forming islands of glandular tissue, This case belongs to one of the unusual forms of supernumerary breast tissue characterized by the presence of aberrant gland tissue alone. The literature is briefly reviewed.

Tuberculosis of the breast is an extremity rare disease in western countries and about 0.5% among entire breast in Korea and most of which involved persons between 20 to 40 years of age in female but it rarely developed in male, elderly patient and prepubertal woman. It may be primary-confined to the breast or secondary to tuberculosis elsewhere because of it's diagnostic difficult. Tuberculosis of breast, is confused to actinomycosis infection, abscess and carclnom.
So, it is only diagnosed by histopathologic finding or inoculation in experimental animal. I expirienced 3 cases of tuberculosis of the breast in 23 years which were treated with antibiotics, antituberculosis medication and combined with surgical excision.
 , Eun Young Kim
, Eun Young Kim , Min-Ji Seo
, Min-Ji Seo , Eun Chung
, Eun Chung , Min-Jung Cho
, Min-Jung Cho , Hyun-Jin Oh
, Hyun-Jin Oh , Ji-Hye Jang
, Ji-Hye Jang , Ji-Chan Park
, Ji-Chan Park , Jung-Uee Lee
, Jung-Uee Lee , Suk-Young Park
, Suk-Young Park
Gastric metastasis from breast cancer is rare and only six cases have been reported in Korea. Colon metastasis is more rare than gastric metastasis. We report a 63-year-old woman with gastric and colon metastases of invasive lobular carcinoma of breast. She was diagnosed as right breast cancer, received right modified radical mastectomy 10 years ago and has been treated with chemotherapy and hormone therapy. Investigating for melena and a small caliber of stool, we found gastric and colon metastases. The diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer was made through gross pathologic and immunohistochemistry staining. We report a case with gastric and colon metastases from breast cancer and a review of the associated six case reports in Korea.
Citations

 , Woosung Lim
, Woosung Lim
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in Korean women and its mortality rate has increased steadily. Although breast cancer is heterogeneous tumor, hormone receptor-positive tumors comprise about 75 percent of all breast cancers. Therefore endocrine therapy that works by targeting estrogen receptor is a pivotal treatment for breast cancers. There are selective estrogen receptor modulators, such as tamoxifen and raloxifene, aromatase inhibitors, such as anastrozole, letrozole and exemestane, fulvestrant and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonists used in endocrine therapy. Endocrine therapy is effective in treating early breast cancer as an adjuvant therapy and metastatic breast cancer as a palliative therapy. Also in women who are at high risk for breast cancer, tamoxifen or raloxifene can prevent breast cancer. Studies for neoadjuvant endocrine therapy are emerging. Considering side effects of each drug and overcoming drug resistance are needed to maximize effectiveness of treatment and advance endocrine therapy.
Citations

 , Byung-In Moon
, Byung-In Moon
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in Korean women and its incidence has increased. Among the various treatment methods for breast cancer, chemotherapy plays an important role. The use chemotherapy to treat breast cancer began at the mid 20th century and first combination chemotherapy was conducted in mid 1970s. This chemotherapy reduced breast cancer mortality up to 25~30%, anthracycline and taxane based chemotherapeutic regimens are widely used. Chemotherapy could be classified to neoadjuavnt, adjuvant and palliative setting according to its aim and role. In this review, various drug therapeutic options and their backgrounds are considered based on neoadjuvant, adjuvant and metastatic systemic therapies.
Citations


Malignant neoplasm is the most common cause of death in Korea since 1988. In terms of incidence, still gastric cancer is the most common cancer in male, but breast cancer became the second most common female cancer followed by thyroid cancer. The reasons why incidence of breast cancer is increasing, (1) Westernized food patterns; high fat and high calorie diet, (2) late marriage with lower birth rate, (3) shorter period of breast feeding, (4) longer exposure to estrogen; early menarche with late menopause, hormone replacement therapy, (5) low physical activity with high body mass index, (6) environmental stress, and etc. Still incidence of breast cancer in Korea is relatively low comparing to those of American and European populations, but it is very rapidly increasing with annual increase rate of about 6%. So Korean breast cancer specialists should try to study breast cancer in terms of basic and also clinical aspect and also educate laymen for etiology, symptoms and signs, early detection method including breast self-examination and prevention.
Citations

 , Byung In Moon
, Byung In Moon , Kum Ja Choi
, Kum Ja Choi , Hye Young Choi
, Hye Young Choi
The goal of this study was to compare the diagnostic accuracy, complication rate between 11 and 8 gauge Mammotome probe during ultrasound-guided Mammotome biopsy.
Sixty eight patients who showed breast mass in sonography were included in this study. Statistical comparisons between the 11 and 8 gauge group were done.
75 biopsies were performed using the Mammotome biopsy system guided by sonography. 63 LESIONS(84.0%) had benign pathology and 12 lesions(16.0%) were malignant. 49(65.3%) of these biopsies were performend with the 11-gauge Mammotome probe, and 26(34.7%) with the 8-gauge probe. Complications such as pain, bleeding , hematoma and skin discoloration were compared between 11 and 8 gauge group. There were nostatistically significant differences in complications such as pain, bleeding, hematoma and skin discoloration. All complications had no significant difference between 11 gauge group and 8 gauge group.
The ultrasound-guided 8 gauge Mammotome biopsy system is as safe as ultrasound-guided 11 gauge Mammotome biopsy system.
 , Hye-Young Choi
, Hye-Young Choi , Chung Sik Rhee
, Chung Sik Rhee , Sun Hee Sung
, Sun Hee Sung
To evaluate pathologic findings of fibrocystic disease correlated with sonographic findings in the patients with solid lesion on ultrasonography.
Total 63 pathologically proven fibrocystic disease in 57 patients are retrospectively evaluated. On ultrasonography, the lesions were divided into solid and non-solid mass-like lesions. We analyzed the margin and echogenicity of solid mass-like lesions that were correlated with pathologic findings and also statistically analyzed Chi-square and Fisher's exact test.
Ultrasonogram of fibrocystic disease showed solid mass-like lesion in 73% and non solid mass-like lesion in 27%. Among the solid lesions, well-defined margin revealed in 72%, ill-defined margin in 28% and hypoechoic in 59%, isoechoic 41%. On the pathologic analysis, the solid and the non-solid mass-like lesion showed respectively : fibrous stroma in 56.5% and 53%, fibroadenomatous change in 50% and 12%, mixed stroma in 41% and 35.3%, cystic change in 37% and 70.6%, ductectasia in 28% and 58.8%, lobular hyperplasia in 26% and 12%, ductal hyperplasia 13% and 5.9%, and adenosis in 8.7% and 0%. The solid lesions showed more fibroadenomatous change and the difference between there was statistically significant(p=0.008).
The solid mass-like lesion, which represented as a well-defined isoechoic benign mass on ultrasonogram was more common than as expected, and this was due to the fibroadenomaous change on histopathology.

