 , Abdulraheem Almokhtar
, Abdulraheem Almokhtar , Hashem Bukhary
, Hashem Bukhary , Raed Sharaf
, Raed Sharaf , Khalid Alhomayani
, Khalid Alhomayani

 , Ga-Yang Shim
, Ga-Yang Shim
 , Jae-Young Lim
, Jae-Young Lim

 , Jung-Ha Kim
, Jung-Ha Kim
 , Oh Haeng Lee
, Oh Haeng Lee , Hyun Kang
, Hyun Kang

 , Juhee Seo
, Juhee Seo , Hyun Jung Park
, Hyun Jung Park
 , So-Hee Hong
, So-Hee Hong
 , Jooyoung Choi
, Jooyoung Choi
 , Bong-Kwang Jung
, Bong-Kwang Jung , Hyun-Jong Yang
, Hyun-Jong Yang
Citations

 , Bruno B. Andrade
, Bruno B. Andrade , Ju Sang Kim
, Ju Sang Kim , Yoolwon Jeong
, Yoolwon Jeong
Citations


Citations


Citations


Citations

This study explores the development, roles, and key initiatives of the Regional Environmental Health Centers in Korea, detailing their evolution through four distinct phases and their impact on environmental health policy and local governance. It chronicles the establishment and transformation of these centers from their inception in May 2007, through four developmental stages. Originally named Environmental Disease Research Centers, they were subsequently renamed Environmental Health Centers following legislative changes. The analysis includes the expansion in the number of centers, the transfer of responsibilities to local governments, and the launch of significant projects such as the Korean Children’s Environmental Health Study (Ko-CHENS ). During the initial phase (May 2007–February 2009), the 10 centers concentrated on research-driven activities, shifting from a media-centered to a receptor-centered approach. In the second phase, prompted by the enactment of the Environmental Health Act, six additional centers were established, broadening their scope to address national environmental health issues. The third phase introduced Ko-CHENS, a 20-year national cohort project designed to influence environmental health policy by integrating research findings into policy frameworks. The fourth phase marked a decentralization of authority, empowering local governments and redefining the centers' roles to focus on regional environmental health challenges. The Regional Environmental Health Centers have significantly evolved and now play a crucial role in addressing local environmental health issues and supporting local government policies. Their capacity to adapt and respond to region-specific challenges is essential for the effective implementation of environmental health policies, reflecting geographical, socioeconomic, and demographic differences.
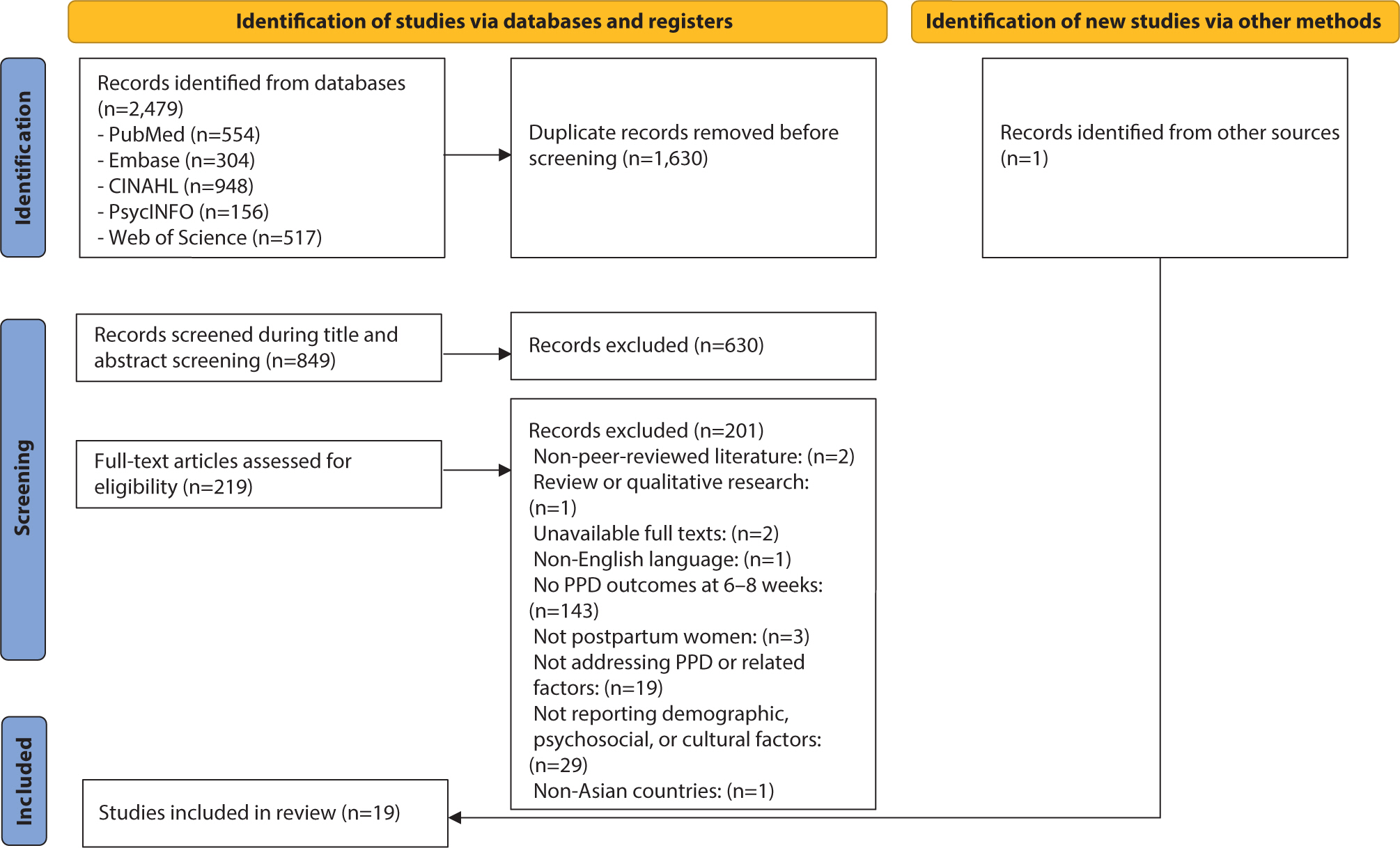
The prevalence of postpartum depression (PPD) in Asia is reported to range from 13.53% to 22.31%. However, there remains a gap in the identification of PPD, particularly regarding cultural cutoff points. Therefore, the purpose of this scoping review was to determine the prevalence and associated factors of PPD in Eastern, South-eastern, Western, and Southern Asian countries and analyze the cutoff points of the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) used across these countries. Following Arksey and O'Malley’s five-step scoping review framework, the population was defined as mothers, the concept as the EPDS, and the context as the Asian region. A literature search was conducted using PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Web of Science. The data analysis focused on demographic characteristics, EPDS cutoffs and features, PPD prevalence, and its associated factors. Nineteen studies were selected. Most countries used translated versions of the EPDS with demonstrated reliability and validity. The cutoff scores varied, with most using scores of 10 or higher. The prevalence of PPD ranged from 5.1% to 78.7%. Key associated factors for PPD included cultural factors such as relationships with in-laws and preferences for the newborn’s sex. To improve the accuracy of PPD screening in Asia, the EPDS should be used consistently, and appropriate cutoff criteria must be established. In addition, prevention strategies and programs that reflect the cultural characteristics and social context of Asia need to be developed for the early detection and prevention of PPD.
Autism spectrum disorder involves challenges in social communication and restricted, repetitive behaviors. Historically, males have received autism diagnoses at comparatively high rates, prompting an underrepresentation of females in research and an incomplete understanding of sex-specific symptom presentations and comorbidities. This review examines sex differences in the prevalence of common comorbidities of autism to inform tailored clinical practices. These conditions include attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, anxiety disorders, conduct disorder, depression, epilepsy, intellectual disability, and tic disorders. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is prevalent in both sexes; however, females may more frequently exhibit the inattentive subtype. Anxiety disorders display inconsistent sex differences, while conduct disorder more frequently impacts males. Depression becomes more common with age; some studies indicate more pronounced symptoms in adolescent girls, while others suggest greater severity in males. Epilepsy is more prevalent in females, especially those with intellectual disabilities. Despite displaying a male predominance, intellectual disability may exacerbate the severity of autism to a greater degree in females. No clear sex differences have been found regarding tic disorders. Overall, contributors to sex-based differences include biases stemming from male-centric diagnostic tools, compensatory behaviors like camouflaging in females, genetic and neurobiological differences, and the developmental trajectories of comorbidities. Recognizing these factors is crucial for developing sensitive diagnostics and sex-specific interventions. Inconsistencies in the literature highlight the need for longitudinal studies with large, diverse samples to investigate autism comorbidities across the lifespan. Understanding sex differences could facilitate earlier identification, improved care, and personalized interventions, thus enhancing quality of life for individuals with autism.
Citations

 , Soon-Hyo Kwon, Young Bok Lee
, Soon-Hyo Kwon, Young Bok Lee , Hei Sung Kim
, Hei Sung Kim , Jie Hyun Jeon
, Jie Hyun Jeon , Gwang Seong Choi
, Gwang Seong Choi
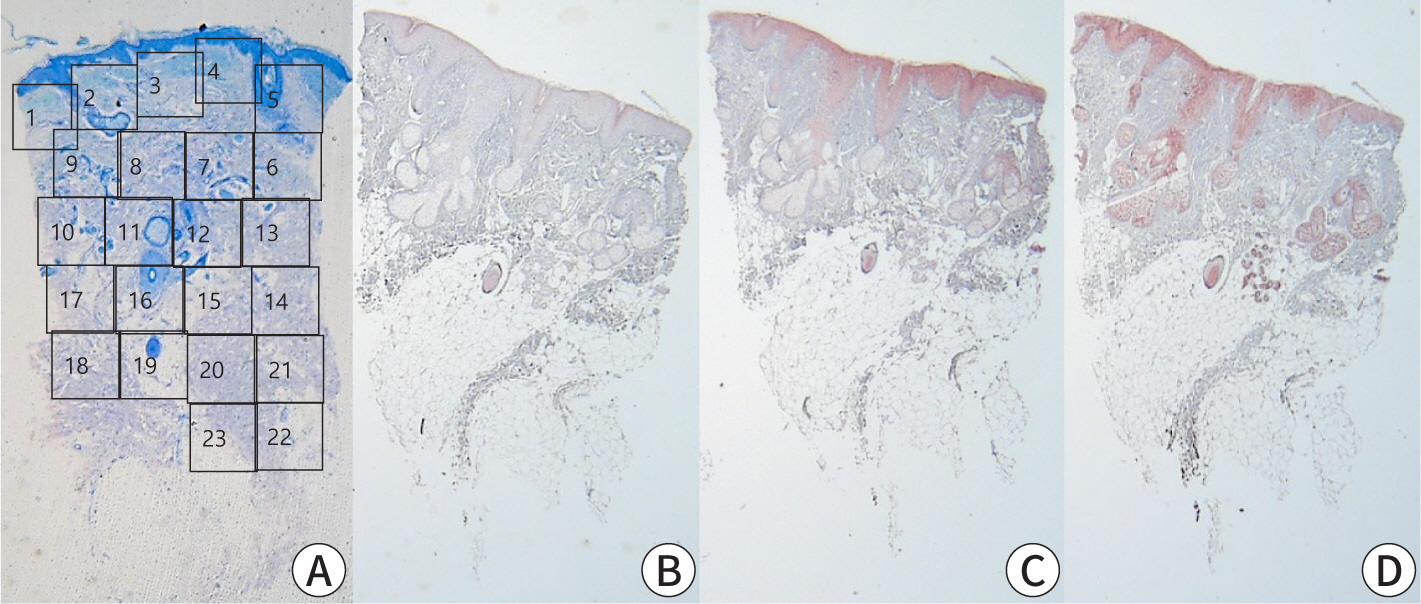
Scabies is a skin disease caused by the parasite
Citations

 , Soon-Hyo Kwon, Young Bok Lee
, Soon-Hyo Kwon, Young Bok Lee , Hei Sung Kim
, Hei Sung Kim , Jie Hyun Jeon
, Jie Hyun Jeon , Gwang Seong Choi
, Gwang Seong Choi
Treatment should be initiated for all suspected, clinical, or confirmed cases of scabies. Patients affected should be adequately isolated, and high-risk groups with close contact histories should be treated regardless of their symptoms. Optimal treatment strategies can be selected based on age, clinical subtype, and the patient's health status. In Korea, commercially available preparations for scabies treatment include topical 5% permethrin, topical 10% crotamiton, and oral ivermectin. Topical 5% permethrin is the first-line selective treatment for both classic and crusted scabies. Alternative treatments include topical 10% crotamiton and oral ivermectin. After completing treatment, follow-up visits at 2 and 4 weeks are recommended to monitor the therapeutic response. Treatment is considered to have failed if scabies mites or burrows are detected, new clinical characteristics develop, or there is an aggravation of pruritus. Scabies itch should be adequately managed with emollients, oral antihistamines, and topical corticosteroids. Preventive measures, including personal hygiene, patient education, and environmental control, should besd implemented to reduce the transmission of scabies.
Citations

 , Minsung Kim
, Minsung Kim
Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols are designed to minimize surgical stress, preserve physiological function, and expedite recovery through standardized perioperative care for primary colorectal surgery patients. This narrative review explores the benefits of current ERAS protocols in improving outcomes for these patients and provides insights into future advancements. Numerous studies have shown that ERAS protocols significantly reduce the length of hospital stays by several days compared to conventional care. Additionally, the implementation of ERAS is linked to a reduction in postoperative complications, including lower incidences of surgical site infections, anastomotic leaks, and postoperative ileus. Patients adhering to ERAS protocols also benefit from quicker gastrointestinal recovery, marked by an earlier return of bowel function. Some research indicates that colorectal cancer patients undergoing surgery with ERAS protocols may experience improved overall survival rates. High compliance with ERAS protocols leads to better outcomes, yet achieving full adherence continues to be a challenge. Despite these advantages, implementation challenges persist, with compliance rates affected by varying clinical practices and resource availability. However, the future of ERAS looks promising with the incorporation of prehabilitation strategies and technologies such as wearable devices and telemedicine. These innovations provide real-time monitoring, enhance patient engagement, and improve postoperative follow-up, potentially transforming perioperative care in colorectal surgery and offering new avenues for enhanced patient outcomes.
Citations

 , Kye Hwa Lee
, Kye Hwa Lee
 , Claudia Santosa
, Claudia Santosa , Sherly Desnita Savio, Erica Kholinne
, Sherly Desnita Savio, Erica Kholinne , Made Bramantya Karna, Anak Agung Gde Yuda Asmara
, Made Bramantya Karna, Anak Agung Gde Yuda Asmara  , Hee-June Kim
, Hee-June Kim , Sung Hun Kim
, Sung Hun Kim , Suk-Joong Lee
, Suk-Joong Lee
Citations

 , Pyoeng Gyun Choe
, Pyoeng Gyun Choe
The rise of multidrug-resistant organisms represents a serious global public health concern. In Korea, the increasing prevalence of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) is particularly concerning due to the difficulties associated with treatment. Data from the Korea Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System indicate a yearly increase in CRE cases, with carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales being the predominant type. The capacity of CRE to resist multiple broad-spectrum antibiotics leads to higher medical costs and mortality rates, underscoring the need for urgent action. Effective prevention is crucial to curbing CRE outbreaks and transmission. Antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) play a key role and require commitment from healthcare professionals to minimize unnecessary antibiotic use, as well as from policymakers to ensure adherence to ASP guidelines. Given the complexity of CRE transmission, ASP efforts must be integrated with infection control strategies for maximum effectiveness. These strategies include adherence to standard and contact precautions, environmental disinfection, preemptive isolation, and comprehensive education and training for healthcare personnel. Additionally, surveillance testing for patients at high risk for CRE and the use of real-time diagnostic kits can facilitate early detection and reduce further transmission. Strategies for the prevention of CRE infection should be tailored to specific healthcare settings. Ongoing research is essential to update and refine infection control guidelines and effectively prevent CRE outbreaks.
Citations

 , Yoon Jin Choi
, Yoon Jin Choi , Ji Yeon Byun
, Ji Yeon Byun , You Won Choi
, You Won Choi , Joo Young Roh
, Joo Young Roh , Hae Young Choi
, Hae Young Choi
Nontuberculous mycobacterial infections, which are often acquired from environmental sources such as water and soil, exhibit a variety of cutaneous manifestations that frequently lead to misdiagnoses and delays in treatment. A 77-year-old woman presented with multiple skin lesions in a sporotricoid distribution on her right leg, which persisted despite standard antibiotic treatments. Based on the skin biopsy, revealing granulomatous inflammation with acid-fast bacilli, and PCR testing, a nontuberculous mycobacterial infection was diagnosed. Antimycobacterial drug combinations, including clarithromycin, isoniazid, and rifampicin for 4 months, complete the skin lesion's clearance. This case underscores the need for heightened suspicion and the use of appropriate diagnostic techniques, including tissue biopsies and molecular methods such as PCR.
Citations

 , Gwang Ha Kim
, Gwang Ha Kim , Dong Chan Joo
, Dong Chan Joo , Moon Won Lee
, Moon Won Lee , Bong Eun Lee
, Bong Eun Lee , Kyung Bin Kim
, Kyung Bin Kim
We report a rare case of gastric adenocarcinoma with enteroblastic differentiation (GAED) that was treated with endoscopic submucosal dissection followed by additional distal gastrectomy with lymph node dissection. A 67-year-old man underwent endoscopic submucosal dissection for a gastric lesion, which was diagnosed as GAED with submucosal and lymphatic invasion. Histologically, GAED is characterized by a tubulopapillary growth pattern and clear cells that resemble those of the primitive fetal gut. Immunohistochemically, GAED variably expresses oncofetal proteins such as glypican-3, alpha-fetoprotein, and spalt-like transcription factor 4. Despite negative margins, additional gastrectomy with lymph node dissection was performed due to submucosal and lymphatic invasion. No residual tumor or metastasis was detected, and the patient remained disease-free for 2 years before dying from causes unrelated to GAED. Given its aggressive nature, frequent lymphovascular invasion, and high metastatic potential, clinicians should recognize the histopathological diagnosis of this rare tumor and its propensity for aggressiveness.
 , Jieun Jang
, Jieun Jang , Nayoung Kim
, Nayoung Kim
Citations

 , Eunha Kim
, Eunha Kim
Neurodevelopmental disorders, which emerge early in development, include a range of neurological phenotypes and exhibit marked differences in prevalence between sexes. A male predominance is particularly pronounced in autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Although the precise cause of ASD is still unknown, certain genetic variations and environmental influences have been implicated as risk factors. Preclinical ASD models have been instrumental in shedding light on the mechanisms behind the sexual dimorphism observed in this disorder. In this review, we explore the potential processes contributing to sex bias by examining both intrinsic differences in neuronal mechanisms and the influence of external factors. We organize these mechanisms into six categories: 1) sexually dimorphic phenotypes in mice with mutations in ASD-associated genes related to synaptic dysfunction; 2) sex-specific microglial activity, which may disrupt neural circuit development by excessively pruning synapses during critical periods; 3) sex steroid hormones, such as testosterone and allopregnanolone, that differentially influence brain structure and function; 4) escape from X chromosome inactivation of the O-linked-N-acetylglucosamine transferase gene in the placenta; 5) sexually dimorphic activation of the integrated stress response pathway following maternal immune activation; and 6) immunological responses that are differentially regulated by sex. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for deciphering the underlying causes of ASD and may offer insights into other disorders with notable sex disparities.
Citations

 , Won Kim
, Won Kim
Understanding the effects of sex and sex differences on liver health and disease is crucial for individualized healthcare and informed decision-making for patients with liver disease. The impact of sex on liver disease varies according to its etiology. Women have a lower prevalence of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) than men. However, postmenopausal women face a higher risk of advanced liver fibrosis due to hormonal influences. Sex differences affect the pathogenesis of MASLD, which involves a complex process involving several factors such as hormones, obesity, and the gut microbiome. Furthermore, sex-related differences in the development of MASLDrelated hepatocellular carcinoma have been observed. The sex-specific characteristics of MASLD necessitate an individualized management approach based on scientific evidence. However, research in this area has been lacking. This article reviews the current understanding of sex differences in MASLD.
Citations

 , Heisook Lee
, Heisook Lee
This review aims to highlight the importance of research on structural, functional, molecular-biological, and disease-specific sex differences in the brain, and to examine current bibliometric indicators related to research on sex differences. The Web of Science Core Collection was searched for related articles from 2010 to 2023. Structural and functional brain differences according to sex, including variations in communication patterns between hemispheres, may play a role in mental disorders. Sex differences in neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and γ-aminobutyric acid contribute to disparities in mental health, addiction, and neurodevelopmental conditions. Neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism spectrum disorder and schizophrenia exhibit sex-based differences in prevalence, symptoms, brain changes, and neurotransmitter disruptions under hormonal influence. There is a growing body of research on depression, adolescence, the hippocampus, the amygdala, and cognition, highlighting the importance of considering sex/gender factors. Recent studies on sex differences in brain diseases have identified variations in brain structure, function, and neurophysiological substances, as well as in hormones and genes between the sexes. The incidence of psychiatric disorders such as autism spectrum disorder, depression, anxiety, and Alzheimer’s disease is increasingly being linked to sex differences, and the need for research into the mechanisms underlying these differences is gaining recognition. However, there remains a significant gap in sex-specific neuroscience research related to the diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and management of these conditions. Advancing inclusive research will require comprehensive training, a consensus on methodology, diverse perspectives through collaborative frameworks, governmental/institutional support, and dedicated funding to create suitable research environments and implementation strategies.
Citations

 , Gwang Ha Kim
, Gwang Ha Kim , Bong Eun Lee
, Bong Eun Lee , Moon Won Lee
, Moon Won Lee , Cheolung Kim
, Cheolung Kim
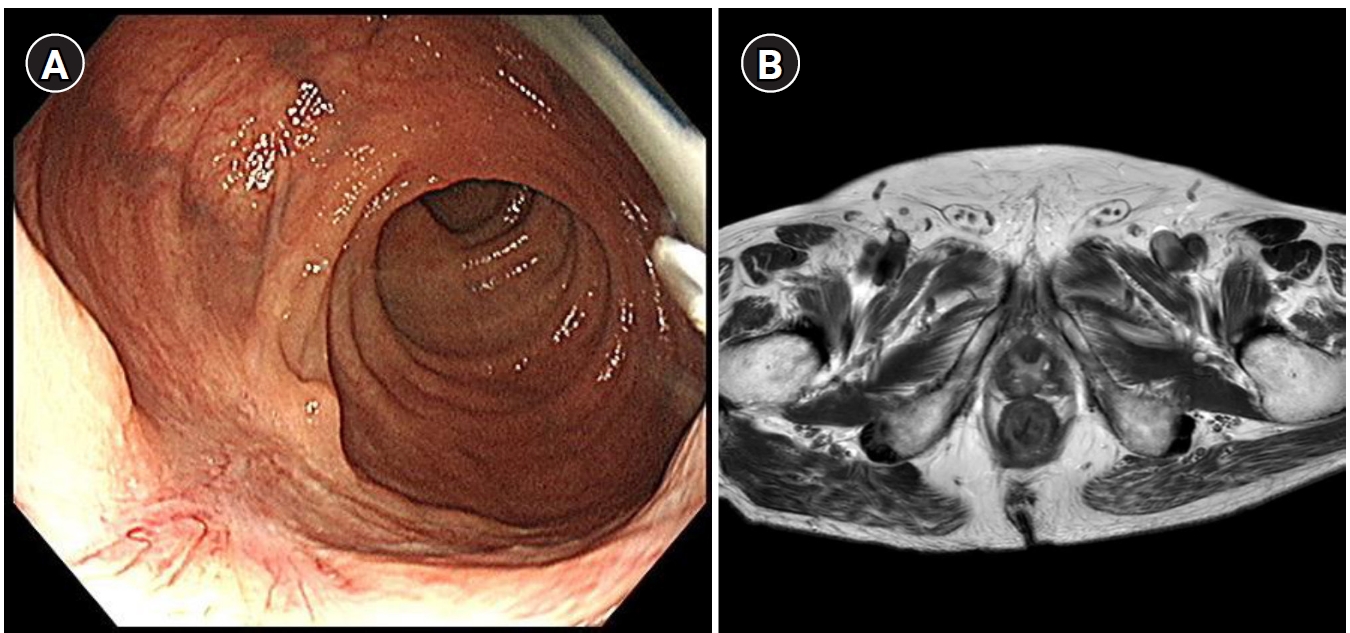
Subepithelial tumors in the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract are often detected during nationwide endoscopic gastric cancer screening in Korea. Most GI lipomas are asymptomatic and do not necessitate further treatment. However, large tumors may lead to complications such as bowel obstruction, intussusception, and bleeding. These GI lipomas require endoscopic or surgical resection. On radiological examination, GI lipomas typically manifest as hypodense lesions with similar density to that of fat tissue. White-light endoscopy generally reveals a yellowish subepithelial tumor exhibiting a positive cushion sign, while endoscopic ultrasonography shows a homogeneous hypoechoic mass within the third layer of the GI tract. We present the case of an 81-year-old woman with symptomatic duodenal lipoma following endoscopic resection.
 , Hyeonuk Hwang
, Hyeonuk Hwang , Hyungju Kwon
, Hyungju Kwon
Conventional open thyroidectomy is a safe procedure, but it has the disadvantage of leaving noticeable scars on the neck. Bilateral axillo-breast approach (BABA) robotic thyroidectomy was developed as an alternative technique to remove thyroid glands without making incisions in the neck. In traditional BABA robotic thyroidectomy, dividing the isthmus is a routine step to improve the efficiency of the dissection during thyroid surgery. However, there are safety concerns when performing this procedure on patients with thyroid cancer located in the isthmus. We report a case of BABA robotic total thyroidectomy carried out without dividing the isthmus in a patient with isthmic papillary thyroid carcinoma. Our experience suggests that BABA robotic surgery can be a feasible and safe option for selected patients with isthmic papillary thyroid carcinoma.

Heart failure (HF) represents a serious public health concern, characterized by substantial morbidity and mortality. Despite advances in pharmacological management, a gap persists in understanding and accounting for sex-related differences in HF treatment. This review was performed to clarify the impact of sex on the clinical outcomes of HF medications. Insights from various clinical trials and studies have highlighted differences between men and women in drug responses and adverse effects, indicating the need for a more nuanced approach to HF management. Promoting greater representation of women in clinical trials and the development of research methodologies that consider sex differences are crucial steps in advancing precision medicine. Such efforts ensure that therapeutic strategies are optimally tailored to the unique biological and genetic profiles of each person. Ultimately, this review emphasizes the vital need for a more inclusive and personalized approach to HF pharmacotherapy, underscoring the critical role of sex-related differences in shaping effective and individualized treatment pathways.
Citations


Anastomotic leakage (AL) after colorectal surgery is a significant concern, as it can lead to adverse functional and oncologic outcomes. Numerous studies have been conducted with the aim of identifying risk factors for AL and developing strategies to prevent its occurrence, thereby reducing the severe morbidity associated with AL. The intraoperative method for reducing AL includes a mechanical assessment of AL, an assessment of bowel perfusion, drain placement, and the creation of diverting stomas. The anastomosis technique is also associated with AL, and the appropriate selection and accurate application of anastomotic methods are crucial for preventing AL. Indocyanine green fluorescence imaging has recently gained popularity as a method for assessing bowel perfusion. While it is useful for detecting bowel perfusion, standardized protocols and measurement methods need to be established to ensure its reliability and effectiveness in clinical practice. The use of intraoperative drains to reduce AL has produced inconsistent results, and the routine adoption of this practice is not currently recommended. Diverting stomas can be used to help reduce the morbidity associated with AL. However, it is important to carefully consider the complications that can arise directly from the stoma itself. It should be noted that while a stoma can reduce AL, it cannot completely prevent it. This descriptive review examines various intraoperative methods aimed at reducing AL, discussing their effectiveness in reducing AL.
Citations

Over the past 3 years, the COVID-19 pandemic has posed significant challenges to the healthcare system, leading to delays in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases due to the need for social distancing measures. Colorectal cancer has not been immune to these disruptions, and research in various countries has explored the impact of COVID-19 on the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer. One notable consequence has been the postponement of colorectal cancer screenings, potentially resulting in disease progression, which can adversely affect surgical and oncological outcomes. Furthermore, the treatment approach for colorectal cancer may vary depending on the extent of disease progression and the healthcare policies implemented in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. In this systematic review, we examine treatment strategies, surgical outcomes, and oncological variables across multiple studies focusing on colorectal cancer treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic. The purpose of this analysis was to assess how medical policies enacted in response to the COVID-19 pandemic have influenced the outcomes of colorectal cancer treatment. We hope that this review will provide valuable insights and serve as a foundational resource for developing guidelines to address potential medical crises in the future.
 , Eun Jung Park
, Eun Jung Park
In stage IV colorectal cancer (CRC), peritoneal metastasis is associated with a poor prognosis. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) after cytoreductive surgery (CRS) is an effective treatment option that offers survival benefits in patients with peritoneal metastatic CRC. For over the past several decades, a multitude of studies have been conducted on CRS and HIPEC for peritoneal metastatic diseases, and research in this area is ongoing. Proper patient selection and a meticulous preoperative assessment are crucial for achieving successful postoperative outcomes. The completeness of cytoreduction and the surgical techniques employed are key factors in improving oncologic outcomes following CRS and HIPEC. The role of HIPEC for both therapeutic and prophylactic purposes is currently being evaluated in recent clinical trials. This article reviews the fundamental principles of CRS combined with HIPEC and discusses recent clinical trials concerning the treatment of CRS and HIPEC in CRC patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis.

The primary objective in the treatment of early rectal cancer is to achieve optimal oncological control while minimizing the long-term impact of therapeutic interventions on patients' quality of life. The current standard of care for most stage I and II rectal cancers involves radical surgery, specifically total mesorectal excision. Although total mesorectal excision is generally curative for early rectal cancers, it can significantly affect patients' quality of life by potentially necessitating a permanent colostomy and causing bowel, bladder, and sexual dysfunction. Given the morbidity associated with radical surgery, alternative approaches to managing early rectal cancer, such as local excision through transanal excision, transanal endoscopic microsurgery, and transanal minimally invasive surgery, have been investigated. If these surgical approaches are applied cautiously to carefully selected cases of early rectal cancer, it is anticipated that these local procedures will achieve comparable oncological outcomes to the established standard of radical surgery, potentially offering superior results regarding morbidity, mortality, and overall quality of life.

Preoperative chemoradiotherapy (pCRT) followed by total mesorectal excision is the accepted standard treatment for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. The purpose of pCRT is to prevent the spread of viable tumor cells within the local area during surgical procedures. Additionally, pCRT can facilitate the resection of locally advanced tumors that are otherwise challenging to remove, thereby enabling a radical resection. Although a pathologic complete response is observed in fewer than 20% of patients, the reasons for the variability in tumor response to pCRT are not fully understood. Several techniques have been researched with the aim of improving the tumor response to pCRT. These techniques include intensifying or combining chemotherapy, either simultaneously or sequentially, increasing radiation dose, modifying radiation mode or schedule, adjusting the interval between radiation and surgery, and incorporating multiple agents to increase the efficacy of pCRT. This review discusses various strategies that may improve tumor response outcomes following pCRT.
 , Il Tae Son
, Il Tae Son , Bo Young Oh
, Bo Young Oh
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a globally prevalent and challenging malignancy. Accurate prognosis prediction is essential for optimizing patient care. This comprehensive review discusses the intricate relationships between inflammatory response markers and CRC prognosis. Inflammatory response markers have gained prominence as a prognostic tool. Elevations in the preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-lymphocyte ratio, and C-reactive protein-albumin ratio predict a poor prognosis for patients with CRC. A decreased lymphocyte-monocyte ratio is also a poor prognostic factor. A high Glasgow prognostic score and a high modified Glasgow prognostic score are associated with adverse outcomes, including reduced survival. While significant progress has been made, challenges remain in standardizing the clinical application of these inflammatory response markers. Prospective research and further investigations are warranted to refine the prognostic models. Enhanced understanding and utilization of these inflammatory response markers will help advance personalized treatment strategies, refine surveillance protocols, and improve the management of CRC.
Citations


Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) aims to promote postoperative recovery in patients by minimizing the surgical stress response through evidence-based multimodal interventions. In 2023, updated clinical practice guidelines were published in North America, potentially superseding the most recent guidelines previously announced at the ERAS Society in 2019. This review compares and reviews these two guidelines to examine the principle of ERAS and items related to colorectal surgery and to introduce the latest relevant study results published within the last 5 years. In the pre-hospitalization stage, the concept of pre-hospitalization is emphasized; this involves checking and reinforcing the patient’s nutritional status and physical functional status before surgery. In the preoperative stage, large-scale studies have prompted a change in the recommendation of mechanical bowel preparation combined with oral antibiotics in elective colorectal surgery. In the intraoperative stage, laparoscopic surgery has become a widespread and important component of ERAS, and more technologically advanced single-incision laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgery are the focus of active research. Ileus-prevention items, such as opioid-sparing multimodal pain management and euvolemic fluid therapy, are recommended in the postoperative stage. The adoption of ERAS protocols is expanding to encompass a wide range of surgical procedures, clinical scenarios, healthcare institutions, and professional medical societies. In order to maximize the effect by increasing adherence to ERAS, medical staff must fully understand the clinical basis and meaning of each item, and the protocol must be maintained and developed steadily through a team approach and audit system.
Citations

 , Zahra Salimi
, Zahra Salimi , Fatemeh Zarei
, Fatemeh Zarei , Farshad Moradpour
, Farshad Moradpour , Mohammad Rasool Khazaei
, Mohammad Rasool Khazaei , Mozafar Khazaei
, Mozafar Khazaei , Maryam Pourjalili
, Maryam Pourjalili
Alzheimer disease (AD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by memory impairment, dementia, and diminished cognitive function. This disease affects more than 20 million people worldwide. Amyloid beta (Aβ) plaques and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) are important pathological markers of AD. Multiple studies have indicated a potential association between elevated cholesterol levels and increased risk of AD, suggesting that lowering the cholesterol level could be a viable strategy for AD treatment or prevention. Statins, potent inhibitors of cholesterol synthesis, are widely used in clinical practice to decrease the plasma levels of LDL cholesterol in patients with hyperlipidemia. Statins are known to play a neuroprotective role in limiting Aβ pathology through cholesterol-lowering therapies. In addition to Aβ plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, the brains of AD patients exhibit signs of oxidative stress, neuroinflammatory responses, and synaptic disruption. Consequently, compounds with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and/or neuroprotective properties could be beneficial components of AD treatment strategies. In addition to lowering LDL cholesterol, statins have demonstrated therapeutic efficacy in various forms, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects. These properties of statins are potential mechanisms underlying their beneficial effects in treating neurodegenerative diseases. Therefore, this review was conducted to provide an overview of the protective effects of statins against AD.
Citations

 , Kwang Ho Kim
, Kwang Ho Kim , Gyoung Tae Noh
, Gyoung Tae Noh , Ho Seung Kim
, Ho Seung Kim
Recurrent colonic perforation in patients already having colostomy is extremely rare and only a few cases had been reported. Herein, we report 2 cases of recurrent colonic perforation at the proximal part of the colostomy in geriatric patients resulting from different causes, which might be caused by stercoral perforation and recurrent colonic ischemia, respectively. Based on our experience, surgeons should consider correcting chronic constipation even in patients who already have a colostomy. Additionally, transverse colostomy should be considered as a surgical treatment in patients with sigmoid colostomy for recurrent perforation due to colonic ischemia.
 , Mina Kang
, Mina Kang , Young Min Hur
, Young Min Hur , Young Ju Kim
, Young Ju Kim , Sunwha Park
, Sunwha Park
Ectopic pregnancy (EP) refers to blastocyst implantation outside the uterine endometrium. EP is major cause of maternal morbidity and mortality. Treatment options include surgery, medical therapy with methotrexate, or expectant management. Methotrexate is the primary regimen used in cases of early, unruptured ectopic pregnancies. Most side effects of methotrexate are minor, including nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, and photosensitive skin reaction. Serious side effects, including bone marrow suppression, and pulmonary fibrosis, are invariably observed when methotrexate is administered in high doses with frequent dosing intervals, in chemotherapeutic protocols for malignancy. These side effects are uncommon with the doses used to treat ectopic pregnancies. Since cases of methotrexate-induced pancreatitis are rare, we report a case of pancreatitis in a patient with EP treated with methotrexate and expect to consider pancreatitis as a side effect of methotrexate in a patient with upper abdominal pain undergoing methotrexate chemotherapy.
Citations

 , Ji Su Chung
, Ji Su Chung , Yeo-Jin Lee
, Yeo-Jin Lee , Seonwoo Lee
, Seonwoo Lee , Juhyun Jeong
, Juhyun Jeong , Min-Kyung So
, Min-Kyung So , Miae Lee
, Miae Lee
The Panbio COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device (Panbio COVID-19 Ag, Abbott Rapid Diagnostics) is a lateral flow immunochromatographic assay targeting the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) nucleoprotein in nasopharyngeal specimens for the diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This study aimed to verify the performance of the Panbio COVID-19 Ag for implementation in clinical laboratories.
Sixty nasopharyngeal swab specimens (30 positive and 30 negative) dipped in transport medium, and COVID-19 was confirmed using real-time RT-PCR using Allplex SARS-CoV-2 assay (Seegene), were tested using the Panbio COVID-19 Ag. Reproducibility was evaluated using positive and negative control materials. Sensitivity and specificity were calculated based on the results of real-time RT-PCR as the standard test method.
Reproducibility was confirmed by the consistent results of repeated tests of the quality control materials. The overall sensitivity and specificity of Panbio COVID-19 Ag were 50.0% and 100.0%, respectively. Panbio COVID-19 Ag demonstrated high sensitivity (88.2%) in analyzing the detection limit cycle threshold (Ct) value of 26.67 provided by the manufacturer as a positive criterion, and the sensitivity was 100.0% for the positive criterion of Ct values <25, although it was less sensitive for Ct ≥25.
Considering the high sensitivity for positive samples with Ct values <25 and the rapid turnaround of results, Panbio COVID-19 Ag can be used in clinical laboratories to diagnose COVID-19 in limited settings.

The rate of colorectal cancer (CRC) has altered. Early-onset CRC patients are increasing, and it is one of the main causes of cancer-related death. Based on epidemiologic change, the CRC screening program needs to be changed. To increase compliance, non-invasive screening techniques are developed. Although CRC survival has increased, the oncologic prognosis of metastatic CRC is remains poor. Even in metastatic CRC, which is the most difficult to treat, attempts are being made to increase the survival rate by active surgical therapy with the creation of chemotherapeutic regimens and targeted treatment based on genomic information. Due to the introduction of aggressive chemotherapy regimens, targeted therapy based on genomic features, and improvements in surgical technique, the role of surgical treatment in metastatic CRC has expanded. Metastatic CRC surgery was indicated for liver, lung, and even peritoneal seeding. Local ablation therapy was also effectively used for liver and lung metastasis. Cytoreductive surgery and intraperitoneal chemotherapy were tried for peritoneal seeding and demonstrated good results in a subgroup of patients, although the right indication was carefully assessed. At the same time, one of the key goals of treatment for CRC was to maintain functional outcomes. Neoadjuvant treatment, in particular, helped rectal cancer patients preserve functional results while maintaining oncologic safety. Rectal cancer organ preservation techniques are now being researched heavily in a variety of neoadjuvant treatment settings, including immunotherapy and whole neoadjuvant therapy. Precision medicine based on patient and disease characteristics is currently being used for the diagnosis and treatment of CRC.
Citations

 , Sooyoung Cho
, Sooyoung Cho , Dong Yeon Kim
, Dong Yeon Kim , Seung Hee Yoo
, Seung Hee Yoo
Variant angina, which is associated with coronary artery spam, is difficult to recognize on routine preoperative evaluation. Coronary spasm results in myocardial ischemia and even lethal arrhythmia in severe cases. Since patients are unconscious and cannot complain of symptoms during general anesthesia, early detection of such an event is difficult, and it could lead to severe bradycardia or cardiac arrest. We report a case of a patient with previously undiagnosed variant angina who experienced severe hypotension and ventricular fibrillation during general anesthesia.
Citations


Low anterior resection syndrome (LARS) is a condition of anorectal dysfunction that occurs frequently following anal sphincter-preserving surgery for rectal cancer and can reduce the quality of life. In this review, we summarize the main symptoms and pathophysiology of this syndrome and discuss the treatment approaches. Early evaluation and initiation of appropriate treatment postoperatively are crucial. The most frequently used tool to evaluate the severity of LARS is the LARS score, and an anorectal manometer is used for objective evaluation. LARS is believed to be caused by multiple factors, and some of its causes include direct structural damage to the anal sphincter, damage to the innervation, loss of rectoanal inhibitory reflex, and decreased rectal volume and compliance. Diet modifications, medications, pelvic floor muscle training and biofeedback are the primary treatments, and rectal irrigation can be added as a secondary treatment. If LARS symptoms persist even after 1 to 2 years and significantly reduce the quality of life, antegrade irrigation, sacral nerve stimulation or definitive stoma may be considered. High-quality evidence-based studies on LARS treatment are lacking, and randomized controlled trials aimed at developing severity-based treatment algorithms are needed.
Citations


