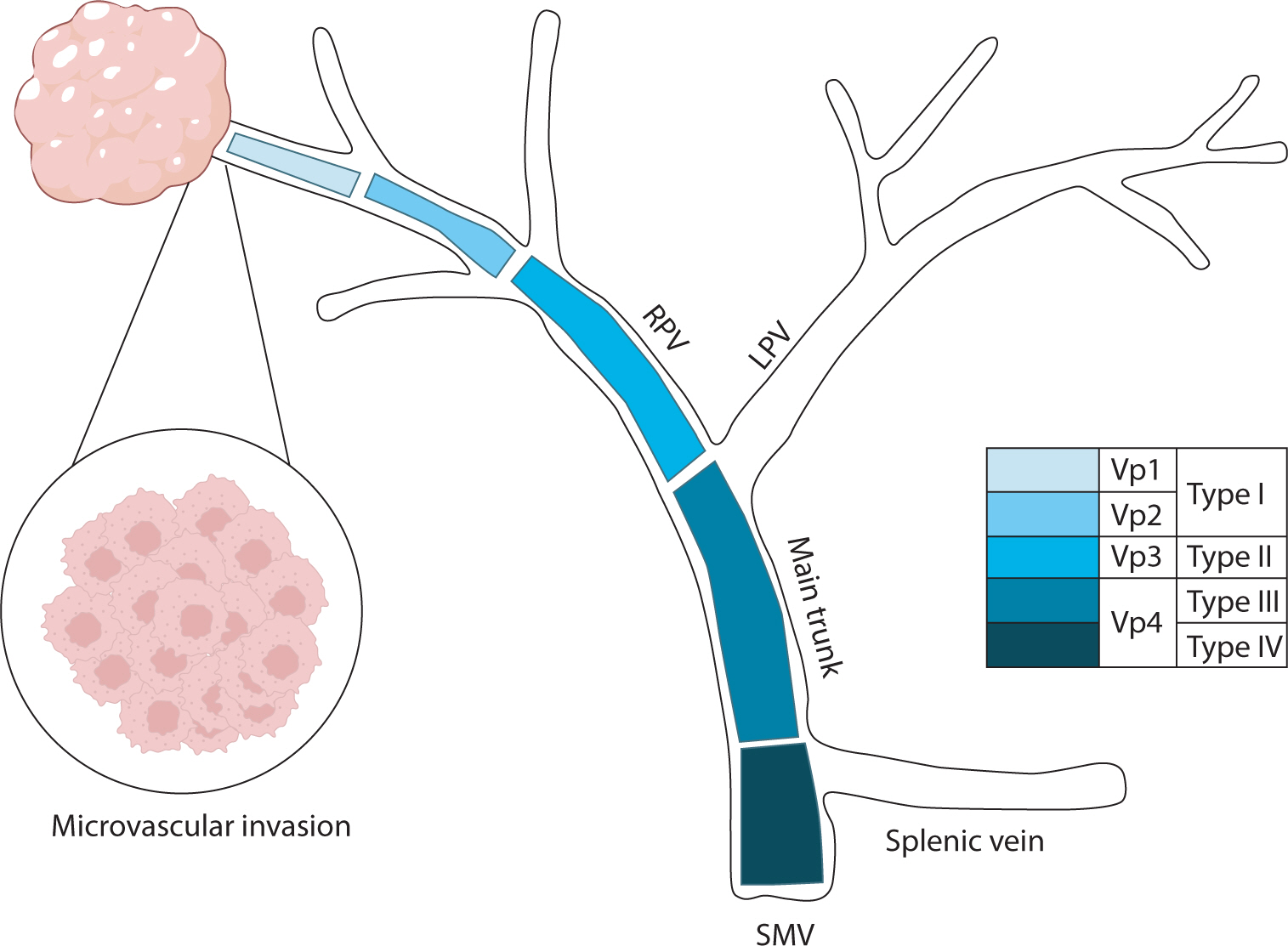
Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis presents a significant therapeutic challenge due to its poor prognosis and limited treatment options. This review thoroughly examines diagnostic methods, including imaging techniques and classification systems such as the Japanese Vp and Cheng’s classifications, to aid in clinical decision-making. Treatment strategies encompass liver resection and liver transplantation, particularly living donor liver transplantation after successful downstaging, which have shown potential benefits in selected cases. Locoregional therapies, including hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy, transarterial chemoembolization, transarterial radioembolization, and external beam radiation therapy, remain vital components of treatment. Recent advancements in systemic therapies, such as sorafenib, lenvatinib, and immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., atezolizumab plus bevacizumab) have demonstrated improvements in overall survival and progression-free survival. These developments underscore the importance of a multidisciplinary and personalized approach to improve outcomes for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombosis.

Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is increasingly recognized as a leading cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the third-leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide, driven by the global obesity epidemic. Projected to become the primary cause of HCC by 2030, MASH-HCC presents unique clinical challenges. This review examines its clinical management, including surveillance strategies and treatment advances, and discusses prospects to overcome existing challenges. MASH-HCC accounts for 10%–20% of HCC cases, particularly in Western countries, with a rising incidence due to obesity. Risk factors include cirrhosis, diabetes, obesity, alcohol, smoking, genetic polymorphisms (e.g., PNPLA3), and microbiome alterations. The pathogenesis involves fibrosis, immune dysfunction (e.g., T-cell impairment), and molecular changes. Prevention focuses on lifestyle modifications. Surveillance in patients with MASH cirrhosis is crucial but is hindered by poor ultrasound sensitivity in obese patients, necessitating alternative methods. Treatment mirrors that of other HCC types, but comorbidities and potentially reduced efficacy of immunotherapy necessitate tailored approaches. MASH is becoming the leading cause of HCC, necessitating lifestyle interventions for prevention. Improved surveillance and early detection are critical but challenging due to obesity-related factors. Treatments align with those for other HCC types, but comorbidities and potential differences in immunotherapy efficacy due to T-cell dysfunction require careful consideration. Key needs include identifying molecular drivers in non-cirrhotic metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, developing preventive therapies, refining surveillance methods, and tailoring treatments. Trials should specifically report MASH-HCC outcomes to enable personalized therapies. Further research is needed to understand T-cell dysfunction, optimize immunotherapies, and identify predictive biomarkers.
 , Haeryoung Kim
, Haeryoung Kim
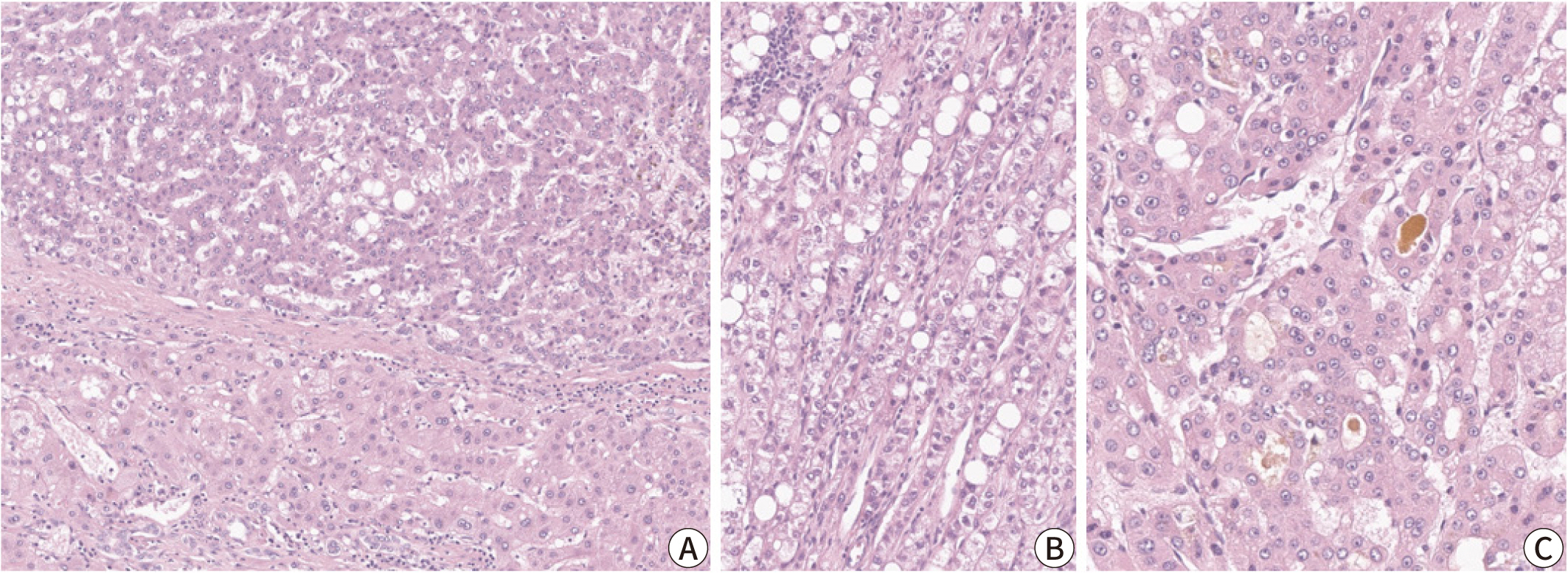
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths
worldwide, with poor clinical outcomes due to challenges in early detection and
limited efficacy of current treatments such as receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitors and immunotherapy. HCC exhibits significant heterogeneity at both
histopathological and molecular levels, complicating its management but offering
potential for personalized therapeutic approaches. This review outlines the
morpho-molecular heterogeneity of HCC and summarizes various histological
subtypes, including steatohepatitic, clear cell, macrotrabecular-massive,
scirrhous, lymphocyte-rich, and fibrolamellar HCCs. Each subtype possesses
distinct clinical, histological, and molecular features; for instance,
steatohepatitic HCC is associated with metabolic dysfunction and shows
IL-6/JAK/STAT activation, while clear cell HCCs often have
Citations

 , Won Kim
, Won Kim
Understanding the effects of sex and sex differences on liver health and disease is crucial for individualized healthcare and informed decision-making for patients with liver disease. The impact of sex on liver disease varies according to its etiology. Women have a lower prevalence of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) than men. However, postmenopausal women face a higher risk of advanced liver fibrosis due to hormonal influences. Sex differences affect the pathogenesis of MASLD, which involves a complex process involving several factors such as hormones, obesity, and the gut microbiome. Furthermore, sex-related differences in the development of MASLDrelated hepatocellular carcinoma have been observed. The sex-specific characteristics of MASLD necessitate an individualized management approach based on scientific evidence. However, research in this area has been lacking. This article reviews the current understanding of sex differences in MASLD.
Citations


Small-for-size syndrome (SFSS) is a critical complication of partial liver
transplantation, particularly in adult-to-adult living donor liver
transplantation (ALDLT) using a small graft. Minimally required liver graft size
for a successful ALDLT is classically 40% of a standard recipient’s liver
volume or 0.8% of recipient body weight. Recent progress in perioperative care
and technical improvement push the lower limit of safe graft size to 25% of the
recipient’s standard liver volume or 0.6% of the graft versus recipient
weight ratio although this is an ongoing debate. The clinical manifestations of
SFSS include various symptoms and signs related to graft dysfunction and portal
hypertension in patients with small grafts. The risk factors for SFSS include
poor preoperative patient condition, including portal pressure, surgical
techniques to reduce portal pressure, and graft quality and size. Hence, various
approaches have been explored to modulate inflow and pressure to a small graft
and to decrease the outflow block to alleviate this SFSS as well as the
selection of a patient and graft. Additionally, recent research and efforts to
prevent and treat SFSS are reviewed.
 , Rack Kyung Chung
, Rack Kyung Chung , Jae Hee Woo
, Jae Hee Woo , Geun Hong
, Geun Hong
Liver transplantation (LT) is the only treatment for end stage of liver failure. In Korea, annually it has been performed 1,300 cases. Most of LTs are performed in large volumes centers. More than half of centers performing LT in Korea are low volume hospital and started a LT program recently. We present our four-year experiences and outcomes of anesthesia for LT since 2013.
Anesthetic and surgical outcomes of 49 consecutive patients who received LT (living donor LT, 21 cases; deceased donor LT, 28 cases) between April 2013 and April 2017 were analyzed retrospectively.
All patients were adult, with the mean age of 53.5±9.2 years. The most common cause of original liver diseases was hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis (40.8%). The mean MELD (Model for End-stage Liver Disease) score was 18.8±10.7. Postreperfusion syndrome was observed in 34.7%, which were all controlled by calcium, norepinephrine, ephedrine and epinephrine. The mean postoperative intensive care unit stay of deceased donor LT recipients (13.6±9.0 days) was significantly longer than that of living donor LT recipients (8.0±3.3 days). There was no intraoperative mortality in patients receiving LT. Thirty-day post-transplant survival rate was 93.8% and 3-year survival rate was 88.6 %. The most common postoperative complication was pneumonia.
We have started LT successfully with multidisciplinary team's steady effort. Adaptation and setting up LT protocol, adequate equipment, proper training at established transplant centers are essential to begin a successful LT program.
 , Sun Young Kim
, Sun Young Kim , Min Ju Kim
, Min Ju Kim , Eun Kyung Hong
, Eun Kyung Hong , Sang Ho Lee
, Sang Ho Lee , Chang Woo Shim
, Chang Woo Shim
A 56-year-old man was diagnosed with cancer of the ascending colon along with retroperitoneal lymph node and peritoneal metastases. After six cycles of palliative chemotherapy, he presented with acute-onset jaundice. Imaging examinations did not show abnormal liver findings other than a periportal linear hypoattenuating area, and endoscopic retrograde cholangiography revealed a tight stricture of the proximal common bile duct. Total bilirubin continued to increase after endoscopic sphincterotomy and biliary stent insertion. Blind liver biopsy revealed tumor infiltration along liver lymphatics, but ruled out tumor involvement of hepatic parenchyma and sinusoids. Tumor cells were predominantly confined to within the lymphatic vessels and were not observed in the arteries or veins. Although one loading dose of cetuximab and two fractions of palliative radiotherapy were administered, the patient succumbed to acute liver injury 30 days after the development of jaundice.
 , Joo Ho Lee
, Joo Ho Lee , Yun Bin Lee
, Yun Bin Lee , Hana Park
, Hana Park , Seong Gyu Hwang
, Seong Gyu Hwang , Kyu Sung Rim
, Kyu Sung Rim
Acute clinical deterioration in patients with chronic liver disease is called acute on chronic liver failure (ACLF). Principles of management of ACLF consist of early identifying etiology of liver disease, rapid intervention of precipitating event and discreet intensive cares. Despite medical intensive cares, if liver failure progresses, liver transplantation could be the other option. Also, liver transplantation is the only treatment that offers a chance of cure for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and the underlying liver cirrhosis simultaneously. Emergent living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) can be performed for patients with acute liver failure and improves survival rate, especially in circumstances which liver graft is often not available because of deceased donors are not affordable. Here, we describe a chronic hepatitis B patient who developed ACLF accompanying early HCC. Because he did not improved with medical care, he received emergent LDLT. After LDLT, he showed great improvement without critical complications.
Citations

 , Myung Shin Kang
, Myung Shin Kang , Dong Hee Shin
, Dong Hee Shin , Ji Hye Lee
, Ji Hye Lee , Jungok Kim
, Jungok Kim
A 53-year-old female with intrauterine contraceptive device insertion was admitted for painful abdominal mass on the left upper quadrant abdomen. Abdominal computed tomography scan showed multiple enhancing masses on the right lobe of liver, left abdominal wall and right paracolic gutter. We performed incisional biopsy on the left abdominal wall lesion. Although microorganisms were not identified, the histopathologic result was consistent with actinomycosis which contained sulfur granules within the chronic granulomatous inflammation. She was treated with penicillin agents for 6 months. We report a case of hepatic actinomycosis with abdominal wall and paracolic gutter involvement.
 , Cheol Keun Park
, Cheol Keun Park , Hae Ryong Yun
, Hae Ryong Yun , Daehoon Kim
, Daehoon Kim , Soo-Kon Lee
, Soo-Kon Lee , Sang-Won Lee
, Sang-Won Lee
As a new humanized monoclonal antibody against the interleukin-6 receptor, tocilizumab is currently used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Tocilizumab was reported to provoke drug-related liver toxicity, although there have been no reports on significant liver toxicity from tocilizumab in Korean patients with RA to date. Here, we describe the first case of tocilizumab-related liver toxicity in a patient with complicated RA, accompanied with macrophage activation syndrome, who had received tacrolimus and prednisolone and in whom both conventional disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs, including methotrexate, leflunomide and sulfasalazine or tumor necrotizing factor-α blockades, were contraindicated due to drug eruption and a history of lung cancer.
Citations

 , Tae Hun Kim
, Tae Hun Kim , Kwon Yoo
, Kwon Yoo , Ye Ji Han
, Ye Ji Han , Jeong Eun Choi
, Jeong Eun Choi , Ji Yoon Kim
, Ji Yoon Kim , Min-Sun Cho
, Min-Sun Cho
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is a chronic cholestatic liver disease that may progress to end stage liver cirrhosis. Benefits of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) treatment has been investigated through large clinical studies. However, most of the studies were done in western countries and recent increase in prevalence of this relatively uncommon chronic liver disease draws attention in Korea. As early UDCA treatment effectively prevent the grave consequences of PBC progression, early diagnosis and lifelong management with UDCA is important. This study was designed to investigate the clinical features of PBC and response rates of UDCA treatments in Ewha Womans University Medical Center.
Clinical data of PBC patients diagnosed between 2001 and 2014 at Ewha Womans University Medical Center were analyzed retrospectively.
A total of 35 patients with mean follow-up duration of 42 months were enrolled. At the diagnosis, 72.7% of the patients were asymptomatic, 5.7% had decompensated liver cirrhosis. The mean serum alkaline phosphate (ALP) level was 2.65 times upper limit of normal. UDCA was prescribed in 91.4% of the patients (n=32), among which 77.4% exhibited biochemical responses defined as serum ALP less than 2 upper limit of normal at 6 months (Mayo criteria).
Most PBC patients were asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis and the average biochemical responses rate to UDCA treatment were ranged from 60.0% to 78.9% according to various response criteria. To elucidate the clinical features and courses of Korean PBC patients in detail, larger scale investigations and longer clinical follow up studies are warranted.

Since he liver is the central organ of uric acid metabolism, I investigated the utility of serum uric acid level as an indicator of the residual liver function and prediction of survival in patients with liver cirrhosis.
I measured the liver function test including uric acid level in the patients with chronic liver disease(41 patients with chronic hepatitis and 66 patients with liver cirrhosis). The serum uric acid level was analyzed for prognostic value.
The serum uric acid level was significant decreased in patients with Child-Pugh class B and C group(group III) compared with Child-Pugh class A(group II) or chronic hepatitis(group I)(p<0.001). There was no difference of the level of uric acid between alcoholic and nonalcoholic cirrhotic patients(p=0.09). The serum uric acid level was correlated inversely with serum bilirubin level in patients with cirrhosis. The sensitivity and specificity of hypouricemia in detecting liver function status in patients with liver cirrhosis were 62.5% and 100%, respectively.
The hypouricemia is one of sensitive factors to assess liver function and predictive value of survival in liver cirrhosis.
 , Heasoo Koo
, Heasoo Koo
Paclitaxel(Taxol) si a chemotherapeutic agent with potent microtubule stabilizing activities that arrests cell cycle in G2-M. Since D2-m is the most radiosensitive phase of the cell cycle, paclitaxel has potential as a cell cycle-specific radiosensitizer. This study was designed to investigate the effects of paclitaxel to radiotoxicity in normal rat liver.
A single intraperitoneal infusion of paclitaxel(10mg/kg), and a single irradiation(8Gy, x-ray) to the whole abdomen, and combination of irradiation(8Gy,x-ray)24 hours after paclitaxel infusion were done in Sprague-Dawley rats. The incidence of mitosis, apoptosis and parenchymal changes of the liver were evaluated at 6 hours, 24 hours, 3 and 5 days, respectively.
Paclitaxel and irradiation significantly increased mitosis at 6 hours and apoptosis was increased by irradiation at 6 and 24 hours. Increased numbers of apoptosis at 3 days by paclitaxel alone was not significantly different from control. Combination of paclitaxel and irradiation showed significantly increased numbers of mitosis and apoptosis at 6 hours. The degree of necrosis of hepatocyte was not significantly different between 3 groups.
Since the incidence of mitosis, apoptosis and hepatocyte necrosis were not increased by paclitaxel infusion 24 hours before irradiation, paclitaxel did not show radiosensitizing effect in this experimental condition. Studies with conditions similar to clinical situation will be the next stop to define the radiosensitizing effects of paclitaxel.
 , Tae Yeob Kim
, Tae Yeob Kim , Joo Hyun Sohn
, Joo Hyun Sohn , Jae Keun Park
, Jae Keun Park , Seung Lee
, Seung Lee , Han Joon Kim
, Han Joon Kim , JuYeon Pyo
, JuYeon Pyo , Young-Ha Oh
, Young-Ha Oh
The major risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma include hepatitis B or C virus infection and alcohol consumption in Korea which lead to liver cirrhosis development and progression. However, prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease related hepatocellular carcinoma is rising worldwide and hepatocellular carcinoma cases in patients with non-cirrhotic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis are increasing. A hypoechoic nodule was incidentally detected in a 52-year-old woman, with no evidence of liver cirrhosis or specific hepatocellular carcinoma findings on radiological examination. Non-cirrhotic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-associated hepatocellular carcinoma was diagnosed based on clinical, laboratory, and histopathological findings of liver biopsy. To our knowledge, this is the first such case report in Korea.
 , Sun Hong Yoo
, Sun Hong Yoo , Dong Ok Jeon
, Dong Ok Jeon , Hyo Jin Cho
, Hyo Jin Cho , Jin Young Choi
, Jin Young Choi , Soya Paik
, Soya Paik , Young Min Park
, Young Min Park
The use of traditional folk remedies is increasing throughout Asia.
Citations

 , Ah-Young Ji
, Ah-Young Ji , Jung-Hee Lee
, Jung-Hee Lee , Sooyun Chang
, Sooyun Chang , In-Soo Kim
, In-Soo Kim , Young Ju Kim
, Young Ju Kim , Beom Kyung Kim
, Beom Kyung Kim , Seung Up Kim
, Seung Up Kim , Jun Yong Park
, Jun Yong Park , Sang Hoon Ahn
, Sang Hoon Ahn , Kwang-Hyub Han
, Kwang-Hyub Han , Do Young Kim
, Do Young Kim
Citations

 , Tae-Hun Kim
, Tae-Hun Kim , Min-sun Ryu
, Min-sun Ryu , Da-Yeon Oh
, Da-Yeon Oh , Myung-Eun Song
, Myung-Eun Song , Shina Lee
, Shina Lee , Jae-In Ryu
, Jae-In Ryu , Hye-In Kim
, Hye-In Kim , Il-Hwan Moon
, Il-Hwan Moon , Kwon Yoo
, Kwon Yoo
The causes of pyogenic liver abscess has been known as biliary tract disease or intrabadominal infection but the large proportions of the patients has no apparent underlying disorders. Recently colonic mucosal lesions were reported in patients with cryptogenic liver abscess and it has been suggested that colonic mucosal break may play a role in developing liver abscess in otherwise healthy patients. We experienced a patient of severe recurrent liver abscess complicated with endophthalmitis only 3 months after successful treatment of initial cryptogenic liver abscess and a polypoid colon cancer was discovered by chance. It seems prudent to proceed colonoscopic examination in patients with cryptogenic liver abscess especially when it is recurrent.
 , Chang Yoon Ha
, Chang Yoon Ha , Hyun Jeong Jang
, Hyun Jeong Jang , Eun Young Yun
, Eun Young Yun , Ji Hyun Ju
, Ji Hyun Ju , Yeon Jeong Ahn
, Yeon Jeong Ahn , Hyun Ju Min
, Hyun Ju Min , Tae Hyo Kim
, Tae Hyo Kim , Hyun Jin Kim
, Hyun Jin Kim , Woon Tae Jung
, Woon Tae Jung , Ok Jae Lee
, Ok Jae Lee , Sun Young Yi
, Sun Young Yi
A 55-year-old man was admitted to our hospital with symptom of fever, chilling, abdominal discomfort and weight loss for 2months. Abdominal computed tomography(CT) revealed a 5×3.75 cm sized low attenuated lesion in the left lateral segment of liver. Esophagogastrodedodenoscopy showed a fistula with dirty exudates at the fundus and a yellowish stone and food debris at the choledochoduodenostomy site. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) was performed and stone and food materials in common bile duct was removed with snare and basket. We experienced a case of liver abscess due to sump syndrome and spontaneous drainage to the stomach.
 , Kyu Won Chung
, Kyu Won Chung , Jae Jung Park
, Jae Jung Park , Suh Eun Bae
, Suh Eun Bae , Il Hwan Moon
, Il Hwan Moon , Kwon Yoo
, Kwon Yoo , Min Sun Cho
, Min Sun Cho
Small cell lung cancer accounts for about 20% of all lung cancers. At the time of diagnosis, the majority of patients already have metastasis. The liver is one of the most common sites of distant metastasis of lung cancer. Small cell lung cancer arises from neuroendocrine cells which produce hormone, hormone producing granules can be seen under electron microscope . A 65-year-old male was admitted to hospital because of jaundice and right upper quadrant pain. The chest roentgenogram and chest computed tomography(CT) scan showed a 3 cm mass in right upper lobe with bilateral mediastinal lymphadenopathy and right pleural effusion. The abdomen CT scan revealed multiple masses in the liver with heterogenous pattern suggesting metastatic orgin. Though the immunohistochemistry and electron miscroscopy, he was diagnosed as metastatic small cell lung cancer of liver. We report a case of the Immunohistochemical and Electron Microscopic Observation of Metastatic Small Cell Lung Cancer of Liver.
 , Jae Jung Park
, Jae Jung Park , Jung Yoon Yoon
, Jung Yoon Yoon , Jung Youn Jo
, Jung Youn Jo , Eun Kyung Baek
, Eun Kyung Baek , Eun Jin Shim
, Eun Jin Shim , Kwon Yu
, Kwon Yu , Hee Jung Choi
, Hee Jung Choi
Rhodotorula species are emergent opportunistic pathogens, Particularly m mmunocompromised patients. Rhodotorula mucilaginosa was the species most frequently recovered, followed by Rhodotorula glutinis. They have been associated with endocarditis, peritonitis, meningitis and catheter-associated fungemia. We experienced a case of catheter-related blood stream infection by rhodotorula glutinis. He was 46-year old man with decompensated liver cirrhosis. He was admitted for esophageal variceal bleeding. Rhodotorula glutinis was identified on blood culture, and amphotericin B was administered for fungemia treatment.

To compare the diagnostic performance of a high-resolution picture archiving and communications system(PACS) workstation directly interfaced with computed tomography(CT) with hard-copy printouts and to compare the detection rate according to slice thickness in hepatocellular carcinomas(HCCs).
Forty-six patients with 118HCCs underwent two-phase multi-detector row helical CT imaging of the entire liver after contrast administration. Late arterial phase images were obtained serially during a single breast-hold, and portal venous-phase images were then obtained. In soft-copy, images taken in each phase were reconstructed by 3mm and 7mm in thickness. Soft-copy readouts on a workstation in PACS and hard-copy printouts were independently compared for the presence of HCC by two radiologists unaware of the possible presence of tumors, and for each phase the detection rate was determined in 7mm thickness. The detection rate of HCC displayed on a workstation was analyzed in 3mm and 7mm thickness for each phase.
No significant differences in observer performance were observed between laserprinted hard copies and CT images displayed on a workstation(p>0.05). But the detection rate of HCC displayed on workstation was higher in 3mm thickness(p<0.05).
The diagnostic performance of CT hard copies is acceptable and comparable to a high-resolution PACS workstation in hepatocellular carcinomas and the detection rate of HCC on PACS workstation is significantly higher in thin slice thickness.

Pyogenic liver abscess is a potentially life-threatening disease with substantial mortality rate. With the recent advances in diagnostic modalities and new treatment strategies, the overall mortality of pyogenic liver abscess has been decreased significantly but stillhigh mortality rates are recorded in patients with old age, multiple abscesses, malignant biliary obstruction and inadequate drainage. Therefore pyogenic liver abscess remains a major clinical challenge. We are going to investigate the current clinical features of pyogenic liver abscess.
Medical records of those who admitted to the Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital since 1993 and diagnosed as having Pyogenic liver abscess were reviewed. A total of 88 pyogenic liver abscess patients was detected and their clinical presentation, bacteriologic etiologies, comorbidities and treatment results were investigated.
Fifty male and 38 female (1.3 :1) patients were enrolled and the mean age was 59years. The most common presenting symptom was fever/chill (77%) followed by abdominal pain(64%), nausea/vomiting (42%) and general weakness (41%). Diabetes mellitus was combined in 17% of the patients and most of pyogenic liver abscesses were induced by ascending biliary infection (43%) or unknown cause (52%). Leukocytosis was evident in 74% of the patients and elevated akaline phosphatase in 52%. Sixty five percent of the abscess cavities were located inright lobe of the liver and most of them were solitary (73%). Pus culture was more efficient than blood culture for the detection of causative microorganis and
Rapid diagnosis of pyogenic liver abscess can be done through a complete history taking, physical examination and a prompt imaging studies and aggressive application of percutaneous aspiration or drainage of the abscess cavity with the empirical antibiotic administration targetting gram-negative aerobe may contribute to the improvement of the mangement of pyogenic liver abscess.
 , Jeong Soo Suh
, Jeong Soo Suh , Chung Sik Rhee
, Chung Sik Rhee
To investigate whether measurements of hepatic metastases before contrast administration are different from measuments after contrast administration. And to gain more effective follow up method by analyzing the difference of contrast between pre- and postcontrast scans.
Thirty patients with herpatic metastases were underwent conventional CT. Continuous 10mm thick slices were obtained from liver dome to pelvic inlet, then the patients received IV injection of contrast material, and same method as precontrast CT scan was performed. Additional 5mm thin slice scan was obtained in case of need. Three radiologists performed independent bidimensional measurements of the randomly selected lesion on both pre- and postcontrast images at the same level and analyzed the difference of the size and contrast.
The size of hepatic metastases were measured as smaller on postcontrast images ; average 41.4±43.5cm2 on precontrast scan & 35.2±37.5cm2 on postcontrast scan. There was significant difference by paired t-test(p<0.02). 24 of 30 cases(80%) showed better conspicuity on postcontrast images, 5(16.7%), on precontrast images and 1(3.3%) showed similiar conspicuity on both pre- and postcontrast images. The contrast of hepatic metastases was significantly higher on postcontrast scan by chi-square test(p<0.01).
Hepatic metastases are significantly smaller on postcontrast images. The contrast between metastatic lesion & liver parenchyme was better on postcontrast scan. Therefore, serial assessment of hepatic metastases size by CT should not be compared mixed pre- and postcontrast image. And postcontrast scan is more effective method than precontrast for follow up of hepatic metastasis.
 , Eun Hee Ha
, Eun Hee Ha , Hye Sook Park
, Hye Sook Park , Hyong Sook Ahn
, Hyong Sook Ahn , Jin Sook Ahn
, Jin Sook Ahn , Cha Hyung Wie
, Cha Hyung Wie
This study was designed to develop the referral system of patient in small-sized industries and the medical delivery system in occupational health field.
We sampled randomly 5 workers per each company in 57 companies and investigated the healthcare utilization behavior, the need for referral system. The survey was done from April 1. 1998 to May 30. 1998 and the respondents were 213. On the basis of the results, we planned model for the referral system between Korean Industrial Health Association(KIHA) and Ewha Medical Center(EMC).
The complaints of the utilization of medical service are cumbersome process of registration and reservation, and discord between hours of duty and consultation. The referral system is needed in 76.7% of total respondents. 85.6% of workers want the night clinic, and 91.3% want to be included their family in this referral system.
We developed the referral system linking KIHA, EMC, and department of preventive medicine of Ewha Woman's University, which based on the result of survey. The service reflect the worker's the healthcare utilization behavior and need for referral system. The number of workers who referred by this system between Feb. 1998 and Jan. 1999 was 30, and replied by EMC after treating was 12. The number of referred patient is very law(30 spells), but the satisfaction of medical service is relatively high.
To promote the referral system, it is needed to propaganda the service of referral system to workers and managers of each company, to improve of quality of services of the hospital, and to establish the official referral system between department of preventive medicine of Ewha woman's university and each clinical department of Ewha Medical Center.
 , Eun Young Lee
, Eun Young Lee , Doe Young Kim
, Doe Young Kim , Il Hwan Moon
, Il Hwan Moon
Pancreatic pseudocyst is one of the most common compications of pancreatitis or pancreatic injury. It can occur at any site in ted abdomen but rarely in the liver. The ultrasound and computed tomography are invaluable imaging techniques for the detection of a pseudocyst We have recently experienced an uncommon case of pseudocyst in 54-year-old man, who had complained of severe epigastric pain and fever. The pseudocyst in the left hepatic lobe was diagnosed by abdominal sonography and computed tomography with clinical and laboratory findings. It was treated successfully by percutaneous catheter drainage.

