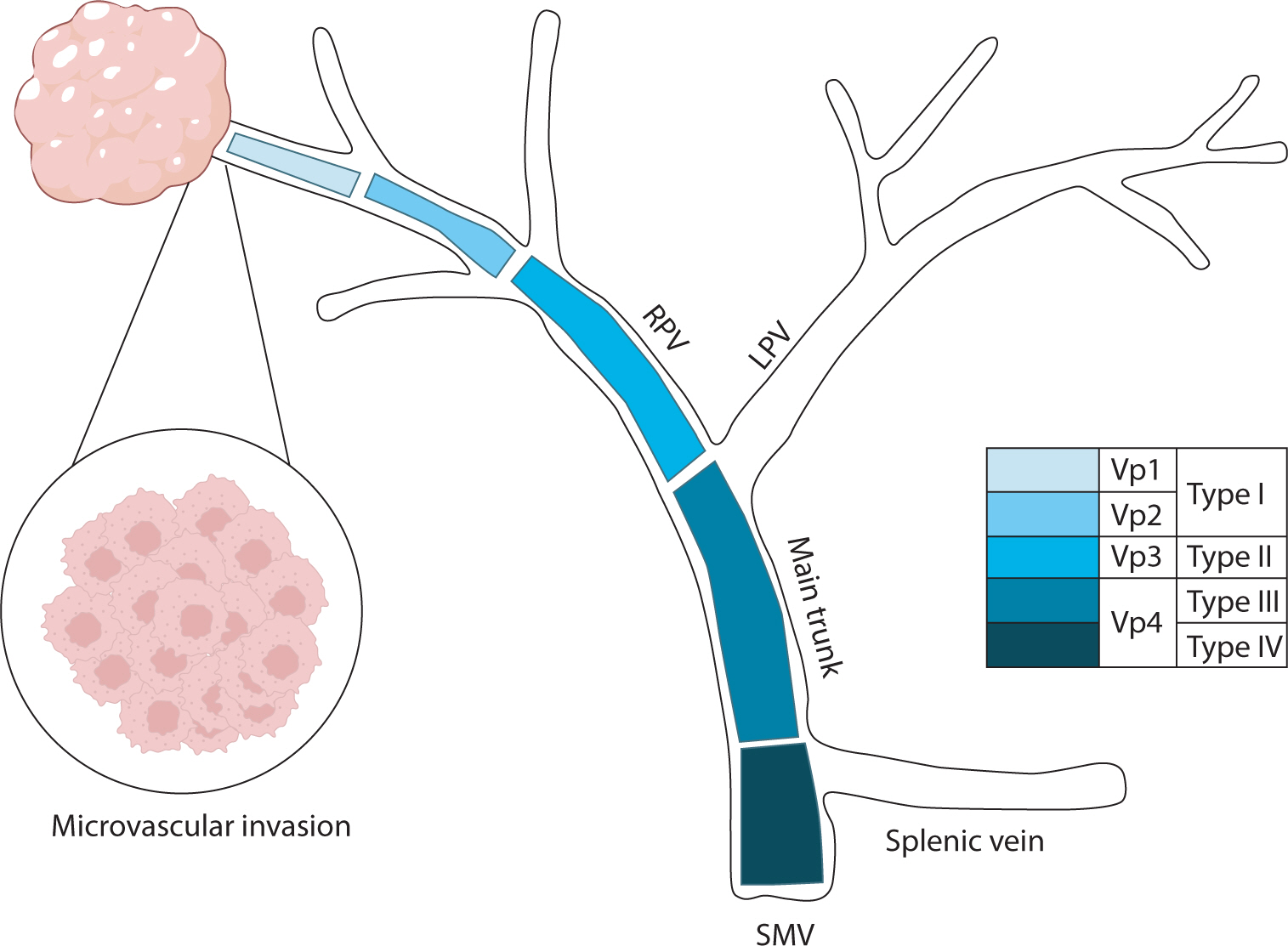
Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis presents a significant therapeutic challenge due to its poor prognosis and limited treatment options. This review thoroughly examines diagnostic methods, including imaging techniques and classification systems such as the Japanese Vp and Cheng’s classifications, to aid in clinical decision-making. Treatment strategies encompass liver resection and liver transplantation, particularly living donor liver transplantation after successful downstaging, which have shown potential benefits in selected cases. Locoregional therapies, including hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy, transarterial chemoembolization, transarterial radioembolization, and external beam radiation therapy, remain vital components of treatment. Recent advancements in systemic therapies, such as sorafenib, lenvatinib, and immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., atezolizumab plus bevacizumab) have demonstrated improvements in overall survival and progression-free survival. These developments underscore the importance of a multidisciplinary and personalized approach to improve outcomes for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombosis.
 , Jung Yeon Lee
, Jung Yeon Lee , Su Jin Heo
, Su Jin Heo , Yoen Kyung Kee
, Yoen Kyung Kee , Seung Hyeok Han
, Seung Hyeok Han
Among the possible venous thromboembolic events in nephrotic syndrome, renal vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism are common, while portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is rare. This report describes a 26-year-old man with histologically proven minimal change disease (MCD) complicated by PVT. The patient presented with epigastric pain and edema. He had been diagnosed with MCD five months earlier and achieved complete remission with corticosteroids, which were discontinued one month before the visit. Full-blown relapsing nephrotic syndrome was evident on laboratory and clinical findings, and an abdominal computed tomography revealed PVT. He immediately received immunosuppressants and anticoagulation therapy. An eight-week treatment resulted in complete remission, and a follow-up abdominal ultrasonography showed disappearance of PVT. In conclusion, PVT is rare and may not be easily diagnosed in patients with nephrotic syndrome suffering from abdominal pain. Early recognition of this rare complication and prompt immunosuppression and anticoagulation therapy are encouraged to avoid a fatal outcome.
 , Jung Hoon Song
, Jung Hoon Song , Kyung Pyo Cho
, Kyung Pyo Cho , Jae Sung Lee
, Jae Sung Lee , Yong Moon Woo
, Yong Moon Woo , Beom Jin Jeong
, Beom Jin Jeong , Young Jun Cho
, Young Jun Cho , Yun Ju Han
, Yun Ju Han
Splanchnic vein thrombosis arising from complications of acute pancreatitis is very rare. It usually occurs as a form of portal, splenic and superior mesenteric vein thrombosis, either in combination or separately. It could develop portal hypertension, bowel ischemia and gastrointestinal variceal bleeding. Treatment of splanchnic vein thrombosis includes anticoagulants, thrombolysis, insertion of shunts, bypass surgery and liver transplantation. In some cases, anticoagulation therapy may be considered to prevent complications. However, the standard protocol for anticoagulation in splanchnic vein thrombosis has not been determined yet. We report a case of 43-year-old man who had portal and splenic vein thrombosis in acute pancreatitis. The patient was successfully treated with oral anticoagulants following low molecular weight heparin therapy.
Citations

 , Hye-Kyung Jung
, Hye-Kyung Jung , Mi Yeon Kim
, Mi Yeon Kim , Min Sun Ryu
, Min Sun Ryu , So Young Ahn
, So Young Ahn , Hyoung Won Cho
, Hyoung Won Cho , In Sook Kang
, In Sook Kang , Seong Eun Kim
, Seong Eun Kim
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) is characterized by raised levels of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL), in association with thrombosis, recurrent fetal loss, and thrombocytopenia. Development of APS is related with idiopathic origin, autoimmune disease, malignancy and, on rare occasions, infection. However, in secondary APS combined with bacterial infections, aPL is usually shown with low titer and rarely associated with thrombotic events. A 52-year-old male was admitted due to pneumonia and multiple hepatosplenic abscesses. He had been treated with proper antibiotics, but he presented ascites and sudden variceal bleeding because of portal vein thrombosis. The bleeding was controlled by endoscopic variceal ligation. Acute portal vein thrombosis was successfully managed by low molecular weight heparin and hepatosplenic abscesses were completely resolved by antibiotics. This case suggests that systemic bacterial infection in immunocompetent patients possibly develops into secondary APS.

