
 , Juhee Seo
, Juhee Seo , Hyun Jung Park
, Hyun Jung Park
 , Gyeongmin Im
, Gyeongmin Im
 , Seungpil Jeong
, Seungpil Jeong , Eunhee Ha
, Eunhee Ha
 , Won Woong Lee
, Won Woong Lee , Haewoo Lee
, Haewoo Lee , Jin Yong Jun
, Jin Yong Jun , Jin-Won Noh
, Jin-Won Noh
Citations


Citations

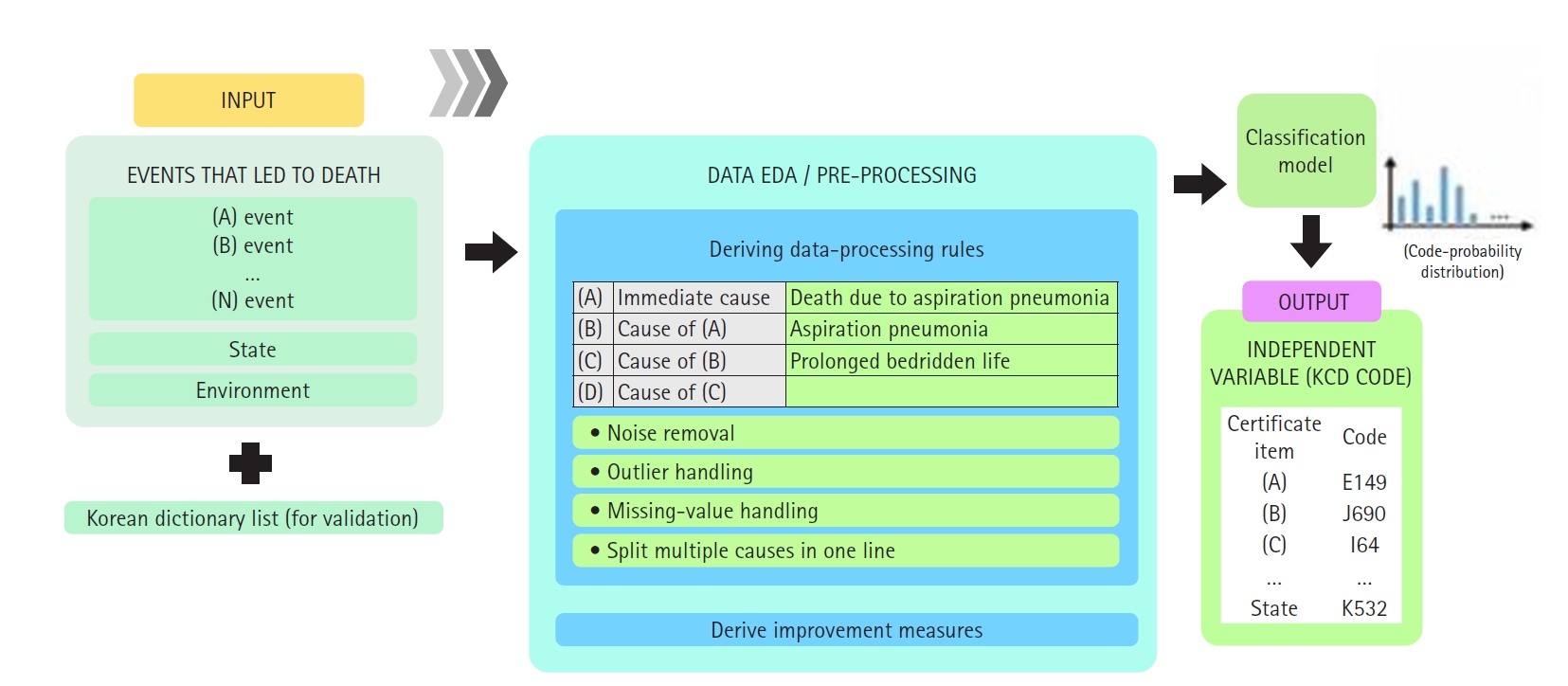
This review examines the challenges associated with occupational disease surveillance in Korea, particularly emphasizing the limitations of current data sources such as the Industrial Accident Compensation Insurance (IACI) statistics and special health examinations. The IACI system undercounts cases due to its emphasis on severe diseases and restrictions on approvals. Special health examinations, although they cover a broad workforce, are constrained by their annual scheduling, which leads to missed acute illnesses and subclinical conditions. The paper also explores the history of occupational disease surveillance in Korea, highlighting the fragmented and disease-specific approach of earlier systems. The authors introduce the newly established Korea Occupational Disease Surveillance Center (KODSC), a comprehensive nationwide system designed to gather, analyze, and interpret data on occupational diseases through a network of regional centers. By incorporating hospital-based surveillance and focusing on acute poisonings and other sentinel events, the KODSC aims to overcome the limitations of previous systems and promote collaboration with various agencies. Although it is still in the early stages of implementation, the KODSC demonstrates potential for improving data accuracy and contributing valuable insights for public health policy.
Citations

Health and safety issues in micro and small enterprises (MSEs) are recognized as a global challenge. This study aimed to examine Workers' Health Centers (WHCs) as a representative public organization providing occupational health services to MSEs in Korea. WHCs were established in 2011 after a trial period aimed at addressing occupational diseases in MSEs with limited resources. As of 2024, there are 24 WHCs, 22 branch offices, and 23 trauma counseling centers for workers. These health centers are managed by the Korea Occupational Safety and Health Agency, with their actual operation delegated to private organizations. Each WHC employs an average of 13 staff members and is organized into four specialized teams: cardiovascular disease prevention, workplace environment improvement, musculoskeletal disease prevention, and occupational stress management. These centers also offer common basic programs along with region-specific specialized initiatives. In 2023, the total cumulative number of users reached 203,877, with employees from MSEs comprising approximately 88.5% of the total. WHCs can thus be seen as playing a pivotal role as case managers of health requirements in the workplace by fostering strong relationships with MSEs and linking them to other relevant programs through a problem-solving-oriented approach. Given the limited resources of these enterprises, proactive policies and the equitable application of safety and health regulations are essential. A balanced strategy that combines regulatory enforcement with practical assistance is critical to ensure the success of WHCs in improving health and safety conditions in MSEs.
This study explores the development, roles, and key initiatives of the Regional Environmental Health Centers in Korea, detailing their evolution through four distinct phases and their impact on environmental health policy and local governance. It chronicles the establishment and transformation of these centers from their inception in May 2007, through four developmental stages. Originally named Environmental Disease Research Centers, they were subsequently renamed Environmental Health Centers following legislative changes. The analysis includes the expansion in the number of centers, the transfer of responsibilities to local governments, and the launch of significant projects such as the Korean Children’s Environmental Health Study (Ko-CHENS ). During the initial phase (May 2007–February 2009), the 10 centers concentrated on research-driven activities, shifting from a media-centered to a receptor-centered approach. In the second phase, prompted by the enactment of the Environmental Health Act, six additional centers were established, broadening their scope to address national environmental health issues. The third phase introduced Ko-CHENS, a 20-year national cohort project designed to influence environmental health policy by integrating research findings into policy frameworks. The fourth phase marked a decentralization of authority, empowering local governments and redefining the centers' roles to focus on regional environmental health challenges. The Regional Environmental Health Centers have significantly evolved and now play a crucial role in addressing local environmental health issues and supporting local government policies. Their capacity to adapt and respond to region-specific challenges is essential for the effective implementation of environmental health policies, reflecting geographical, socioeconomic, and demographic differences.
 , Shinjeong Song
, Shinjeong Song , Chang Mo Moon
, Chang Mo Moon , Hye Ah Lee
, Hye Ah Lee , Junbeom Park
, Junbeom Park
 , Jeong-Ju Yoo
, Jeong-Ju Yoo , Sang Gyune Kim
, Sang Gyune Kim , Young Seok Kim
, Young Seok Kim
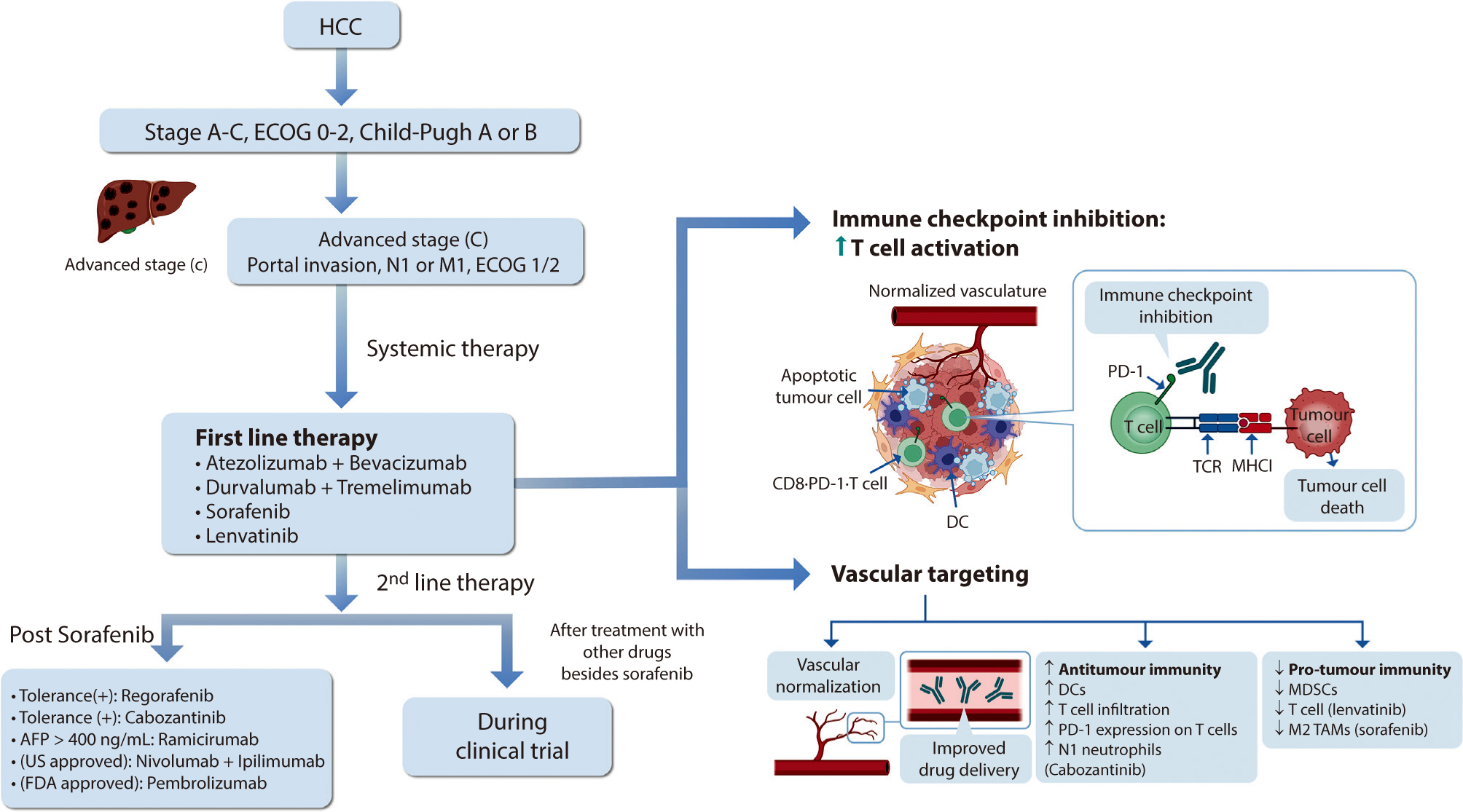
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a critical health concern in Korea, ranking as the second leading cause of cancer mortality and imposing substantial economic burdens, particularly among the working-age population. This review examines recent advancements in treating advanced HCC, referencing the updated 2022 HCC guidelines and the Barcelona Clinical Liver Cancer system. Historically, first-line systemic therapies included sorafenib and lenvatinib, with regorafenib, cabozantinib, or ramucirumab serving as second-line options. Since 2020, immune checkpoint inhibitors have shown superior overall survival than sorafenib, leading to the adoption of combination therapies such as atezolizumab with bevacizumab and durvalumab with tremelimumab as first-line treatments. The IMbrave150 study demonstrated that atezolizumab–bevacizumab significantly extended median overall survival and progression-free survival, with the longest survival reported in any phase 3 trial for advanced HCC. Similarly, the HIMALAYA study indicated that durvalumab combined with tremelimumab significantly improved survival rates. Second-line therapies now include regorafenib, cabozantinib, ramucirumab, nivolumab with ipilimumab, and pembrolizumab, each offering benefits for specific patient populations. Nonetheless, these therapies are associated with side effects that require careful management. Traditional targeted therapies can lead to hypertension, cardiovascular events, and hand-foot skin reactions, whereas immune checkpoint inhibitors may cause immune-related adverse events affecting the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and endocrine system. Clinicians must be well-versed in these treatments and their potential side effects to provide optimal patient care. The emergence of combination therapies targeting complex biological pathways signifies a new paradigm in HCC treatment, emphasizing the importance of continuous education and vigilant monitoring to optimize patient outcomes.
Citations


This paper discusses the implications of South Korea's birth notification system and Protected Birth Act, which is set to take effect on July 19, 2024. The legislation aims to prevent infanticide and child abandonment by mandating birth reporting and allowing anonymous births for women in crisis. However, concerns have been raised about the Act's effectiveness in protecting both women and children, particularly regarding issues of disability and migrant families. This paper focuses on gender and healthcare issues, highlighting how the Act perpetuates discrimination against out-of-wedlock pregnancies and upholds normal family ideologies. It notes the absence of critical discussions on women's autonomy, safe pregnancy termination, and paternal responsibility. The importance of healthcare providers understanding and preparing for the Act's implementation is emphasized. The paper calls for strengthening social safety nets to improve healthcare access for vulnerable populations and eliminate discrimination against non-traditional families. Additionally, it addresses the need for comprehensive support systems for crisis pregnancies, including financial assistance, psychological support, parenting education, housing solutions, and expanded healthcare services. This paper acknowledges the Act's significance in providing a systematic state-level approach to protecting pregnant women in crisis, replacing the previous reliance on private organizations. Nonetheless, it also emphasizes the importance of continually reviewing and supplementing the system to address potential rights infringements and ensure its effectiveness. In conclusion, this paper advocates for ongoing discussions on gender and healthcare issues, and for future amendments to the law that reflect real-world circumstances and provide genuine protection for crisis pregnancies and infants.
Citations

 , So Hyun Ahn
, So Hyun Ahn , Hyeon Jong Yang
, Hyeon Jong Yang , Seung Jung Kim
, Seung Jung Kim , Yuhyeon Chu, Jihye Gwak, Naeun Im, Seoyeong Oh, Seunghyun Kim, Hye Soo Yun, Eun Hee Ha
, Yuhyeon Chu, Jihye Gwak, Naeun Im, Seoyeong Oh, Seunghyun Kim, Hye Soo Yun, Eun Hee Ha
Citations

 , Jin Hoon Nam
, Jin Hoon Nam , Jongmin Oh
, Jongmin Oh , Gyoung Tae Noh
, Gyoung Tae Noh , Eunhee Ha
, Eunhee Ha , Ryung Ah Lee
, Ryung Ah Lee
Citations


Infectious spondylitis, an infection of the vertebral body, intervertebral disc,
or paraspinal tissues, poses diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. This review
examines the clinical approach and management of infectious spondylitis in
Korea. The incidence of pyogenic spondylitis has increased, primarily due to the
aging population, more frequent use of invasive procedures, and higher
prevalence of immunocompromising conditions. Conversely, tuberculous spondylitis
has declined, reflecting shifts in population demographics and medical
practices.
Citations

 , Pyoeng Gyun Choe
, Pyoeng Gyun Choe
The rise of multidrug-resistant organisms represents a serious global public health concern. In Korea, the increasing prevalence of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) is particularly concerning due to the difficulties associated with treatment. Data from the Korea Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System indicate a yearly increase in CRE cases, with carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales being the predominant type. The capacity of CRE to resist multiple broad-spectrum antibiotics leads to higher medical costs and mortality rates, underscoring the need for urgent action. Effective prevention is crucial to curbing CRE outbreaks and transmission. Antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) play a key role and require commitment from healthcare professionals to minimize unnecessary antibiotic use, as well as from policymakers to ensure adherence to ASP guidelines. Given the complexity of CRE transmission, ASP efforts must be integrated with infection control strategies for maximum effectiveness. These strategies include adherence to standard and contact precautions, environmental disinfection, preemptive isolation, and comprehensive education and training for healthcare personnel. Additionally, surveillance testing for patients at high risk for CRE and the use of real-time diagnostic kits can facilitate early detection and reduce further transmission. Strategies for the prevention of CRE infection should be tailored to specific healthcare settings. Ongoing research is essential to update and refine infection control guidelines and effectively prevent CRE outbreaks.
Citations

 , Yoon Jin Choi
, Yoon Jin Choi , Ji Yeon Byun
, Ji Yeon Byun , You Won Choi
, You Won Choi , Joo Young Roh
, Joo Young Roh , Hae Young Choi
, Hae Young Choi
Nontuberculous mycobacterial infections, which are often acquired from environmental sources such as water and soil, exhibit a variety of cutaneous manifestations that frequently lead to misdiagnoses and delays in treatment. A 77-year-old woman presented with multiple skin lesions in a sporotricoid distribution on her right leg, which persisted despite standard antibiotic treatments. Based on the skin biopsy, revealing granulomatous inflammation with acid-fast bacilli, and PCR testing, a nontuberculous mycobacterial infection was diagnosed. Antimycobacterial drug combinations, including clarithromycin, isoniazid, and rifampicin for 4 months, complete the skin lesion's clearance. This case underscores the need for heightened suspicion and the use of appropriate diagnostic techniques, including tissue biopsies and molecular methods such as PCR.
Citations


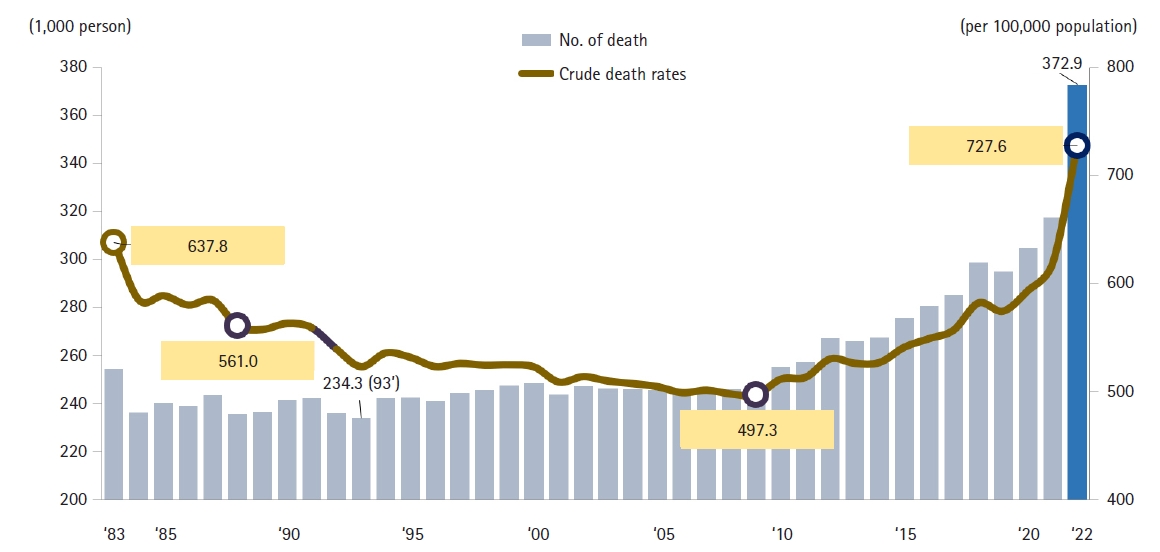
This study analyzed drug-induced death statistics in Korea between 2011 and 2021.
Cause-of-death statistics data from Statistics Korea were examined based on the Korean Standard Classification of Diseases and Causes of Death and the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th revision.
In 2021, there were 559 drug-induced deaths, marking a 172.7% increase compared to 2011, which recorded 205 deaths. The rate of drug-induced deaths per 100,000 people was 1.1 in 2021, up 153.6% from 0.4 in 2011. The mortality rate for men aged 25−34 years and women aged 35−44 years each increased fourfold from 2011 to 2021: from 0.3 to 1.2 for the former and 0.3 to 1.3 for the latter. Of the drug-induced deaths in 2021, 75.0% (419/559) were due to intentional self-harm, and 10.4% (58/559) were accidental. The number of deaths attributed to medical narcotics in 2021 was 169, a 5.5-fold increase from 2011. The most commonly implicated drugs in these deaths were sedative-hypnotic drugs, benzodiazepines, and opioids. Sedative-hypnotic drugs and benzodiazepines were frequently involved in cases of intentional self-harm, while opioids and psychostimulants were more often associated with accidental deaths.
The death rate from drug-induced causes is considerably lower in Korea than in the United States (1.1 vs. 29.2). However, the number of such deaths has increased recently. Since these deaths occur predominantly among younger age groups and are often the result of intentional self-harm, there is a clear need for systematic management and the implementation of targeted policies.
Citations

 , Eun Mee Kim
, Eun Mee Kim
The Republic of Korea’s potential role in the peacebuilding process on the Korean Peninsula is explored, with the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea’s earnest efforts to denuclearize and become a normal country. The paper focuses on the United Nations (UN) agencies in the peacebuilding process, considering the UN’s engagement in the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea during the sanction years with humanitarian assistance, the UN’s legitimacy as an impartial international organization for assisting developing countries in forging peace and prosperity, and recently-adopted resolutions on sustaining peace and the Sustainable Development Goals. Policy recommendations are for the Republic of Korea to actively cooperate with the UN’s development and humanitarian agencies, conduct a thorough preparatory review and conduct research, and work towards expanding its engagement and role within key UN agencies.
Citations

 , Taeyang Jang
, Taeyang Jang
This study investigated the epidemiological and etiological trends associated with elbow pain over the past decade in South Korea.
Nationwide health statistics data from 2011 to 2020 pertaining to elbow pain-related diseases and soft tissue damages were sourced from the Healthcare Bigdata Hub with disease codes M771 (lateral epicondylitis), M770 (medial epicondylitis), S53 (elbow injury, dislocation, sprain), and G56 (mononeuropathies of the upper limb). The study assessed the annual fluctuations in the total medical cost and the number of patients associated with these codes. Trends over time were characterized by evaluating the crude and age-standardized prevalence rates and the annual percentage change. Changes in the proportion of medical expenses based on age distribution were also investigated.
A significant surge in medical costs was observed across all four codes. The M771, M770, and G56 codes experienced a pronounced increase in crude and age-standardized prevalence. Conversely, only S53 registered a significant drop in age-standardized prevalence. Moreover, within the total medical expenditures for the M771 code, the age bracket of 50 to 59 represented the largest proportion.
The data suggest that the average age of patients reporting elbow pain is rising. Given this shifting trend in South Korea's health statistics concerning elbow pain, there will be an increasing need for socioeconomic support, which will in turn necessitate improving health policies that address allocating medical expenses and resources for elbow pain.
Public health risks and anxiety have been increasing since the outbreak of Coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19). The public expresses questions related to the COVID-19 issue through the web base. The aim of this study was to analyze public perception and sentiments of COVID-19 Pandemic in South Korea.
We collected the text data (questions: 252,181) related to COVID-19 from Naver Knowledge-iN during January 1, 2020 to December 31, 2020. The search keywords included related to COVID-19 using Korean words for “SARS-Cov-2”, “COVID19”, “COVID-19”, “Wuhan pneumonia”, “Coronavirus”, “Corona”. A topic modeling analysis was used to investigate and search trends of public perception. The sentiment analysis was conducted to analyze of public emotions in the questions related to COVID-19. We performed the Pearson’s correlation analysis between daily number of COVID-19 cases and daily proportion of negative sentiment in documents related to COVID-19 by COVID-19 outbreak period.
A total of 241,776 documents used in this study. The most frequent words in the documents to appear cough, symptoms, tests, confirmed patients, mask and etc. Twenty topics (COVID-test, Economy, School, Hospital/Diagnose, Travel/Overseas, Health, Social issue, Symptom 1 (respiratory), Relationships, Symptom 2 (e.g., fever), Workplace, Mask/Social distancing, infection/Vaccine, Stimulus Package, Family, Delivery Service, Unclassified, Region, Study/Exam, Worry, Anxiety) were extracted using the topic modeling. There was a positive association between the daily counts of COVID-19 patients and proportion of negative sentiment. By COVID-19 period, Stage 4 had the highest correlation.
This study identified the South Korean public’s interest and emotions about
COVID-19 during the prolonged pandemic crisis.
Citations

 , Eun Ja Kwon
, Eun Ja Kwon , Jeong Hye Kim
, Jeong Hye Kim , Kyuwon Kim
, Kyuwon Kim , Jae Yong Lee
, Jae Yong Lee , Hee Seung Hong
, Hee Seung Hong , Seung Wook Hong
, Seung Wook Hong , Jin Hwa Park
, Jin Hwa Park , Sung Wook Hwang
, Sung Wook Hwang , Dong-Hoon Yang
, Dong-Hoon Yang , Byong Duk Ye
, Byong Duk Ye , Jeong-Sik Byeon
, Jeong-Sik Byeon , Seung-Jae Myung
, Seung-Jae Myung , Suk-Kyun Yang
, Suk-Kyun Yang , Jeong Yun Park
, Jeong Yun Park , Sang Hyoung Park
, Sang Hyoung Park
It is important that inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients adhere to their prescribed medication regimens to avoid the repeat exacerbations, complications, or surgeries associated with this disorder. However, there are few studies on medication adherence in patients with IBD, especially in Asian populations. So, we analyzed the factors associated with medication adherence in Korean IBD patients.
Patients who had been diagnosed with Crohn’s disease (CD) or ulcerative colitis (UC) more than 6 months previously and receiving oral medications for IBD were enrolled. Medication adherence was measured using the Medical Adherence Reporting Scale (MARS-5), a self-reported medication adherence measurement tool.
Among 207 patients in the final study population, 125 (60.4%) had CD and 134 (64.7%) were men. The mean age was 39.63 years (SD, 13.16 years) and the mean disease duration was 10.09 years (SD, 6.33 years). The mean medication adherence score was 22.46 (SD, 2.86) out of 25, and 181 (87.4%) patients had score of 20 or higher. In multiple linear regression analysis, self-efficacy (β=0.341, P<0.001) and ≥3 dosing per day (β=-0.192 P=0.016) were revealed to be significant factors associated with medication adherence. Additionally, there was a positive correlation between self-efficacy and medication adherence (r=0.312, P<0.001). However, disease related knowledge, depression, and anxiety were not significantly associated with medication adherence.
To improve medication adherence among patients with IBD, a reduction in the
number of doses per day and an improved self-efficacy will be helpful.
Citations

Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the cause of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), is a type of human coronavirus that causes severe pneumonia, similar to SARS-CoV-1 and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. In Korea, the SARS-CoV-2 testing has started quickly from February 2020 to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic. In this article, I would like to introduce the characteristics of coronavirus and PCR test methods that play a large role in COVID-19 quarantine measures. Real-time reverse transcription (RT)-PCR is one of the molecular diagnostic method, and it detect SARS-CoV-2 RNA by amplifying SARS-CoV-2 specific
Citations

 , Jia Ryu
, Jia Ryu
Although acute occupational poisonings are very rare officially, it seems that there are a considerable number of unreported cases seen from non-intentional poisoning cases of the national injury and poisoning survey on discharged patients. Establishing a proper national surveillance system for acute occupational poisonings is needed. It is difficult for clinical physicians to diagnose acute occupational poisonings appropriately because the victims who usually are not mentally alert can not provide the information on the workplace hazard. Consulting a specialist of occupational and environmental medicine may help to reveal the cause of poisoning. Furthermore, reporting to the public organization such as workers health center and Korea occupational safety and health is helpful to prevent additional injuries.
Citations

 , Mei Zi Biao
, Mei Zi Biao , Jung Sun Kim
, Jung Sun Kim
In order to avdance understaning of the complex social process of individual drinking behavior, this cross-cultural study examined the effects of cultural and psychological factors on drinking behaviors among Koreans, Korean-Chinese and Chineas. Using the survey data collectedfrom lune, 1994 to April, 1995 both in Korea and Yanbian, China, we tested the hypothesisthat the social and cultural environment would lead differnt drinking behavior among Koreans,Korean-Chinese and Chinese in addition to the individual psychological factors. Subjects were 206 Koreans, 211 Korean-Chines and 204 Chines, total 621 subjects.
The results are :
1) The average amount of alcohol consumption and of blood level is highest in Koreans.
2) In terms of drinking motivation, the effect of blind drunkeness and group solidarity factors are higher for Koreans than others, whereas business purpose and controlling drinkingbehavior are higher among Korean-Chinese and Chinese.
3) There is no significant differences in the social motivation, while emotional motivation ishigher among Chinese for the individual motivation.
4) Age and emotional motivation are the main factors affecting the total amount of alcoholintake and the drinking frequency among Koreans. Group solidarity and blind drunkeness alsotend to lead the frequent drinking event for them. The factors of blind drunkeness and groupsolidarity also has causal effects on the frequencies of drinking for Korean-Chinese in Yanabian,while higher emotional motivaiotn as a psychological factors tends to lead a more frequentdrinking among Chinese.
5) These results show that there are differences in drinking behaviors due to the social and cultural differences among Korean-Chinese and Chinese especially in the frequencies of drinking rather than the total amount of alcohol intake.
Citations


This study was performed to analyse the social character of Koreans which was percepted bycollege students, and to compare with the social charater presented by the previous researches.The evaluation method was the opened questionaire which was composed of the content,Which is the unique and major social charater of Koreans?. The subjects of this survey were500 college students sampled by random sampling method.
The results of this study were as follows :
1) These traits were Presented as the major social charater of koreans : first quick-tempered,second emotional and affectionate, third lack of accuracy, fourth sensitive toward other'sresponse, fifth familialistic and collectivistic, sixth show-off, seven self-centered, eighth resistant to change, ninth introverted, tenth authoritative trait.
2) The neucler traits among 10 social carater of Koreans was e emotinal and affectionate,familialistic and collectivistic tendency which was consistant with the previous research results.
3) It was found that compared the results of this study with the previous researches, the social chararter of emotinality and affectionateness was continued but the authoritative trait wasdecresed and the quirk-temperedness was intensified.

Malignant neoplasm is the most common cause of death in Korea since 1988. In terms of incidence, still gastric cancer is the most common cancer in male, but breast cancer became the second most common female cancer followed by thyroid cancer. The reasons why incidence of breast cancer is increasing, (1) Westernized food patterns; high fat and high calorie diet, (2) late marriage with lower birth rate, (3) shorter period of breast feeding, (4) longer exposure to estrogen; early menarche with late menopause, hormone replacement therapy, (5) low physical activity with high body mass index, (6) environmental stress, and etc. Still incidence of breast cancer in Korea is relatively low comparing to those of American and European populations, but it is very rapidly increasing with annual increase rate of about 6%. So Korean breast cancer specialists should try to study breast cancer in terms of basic and also clinical aspect and also educate laymen for etiology, symptoms and signs, early detection method including breast self-examination and prevention.
Citations


