 , Abdulraheem Almokhtar
, Abdulraheem Almokhtar , Hashem Bukhary
, Hashem Bukhary , Raed Sharaf
, Raed Sharaf , Khalid Alhomayani
, Khalid Alhomayani

 , YangIm Hur
, YangIm Hur

 , Gyu Bae Lee
, Gyu Bae Lee , Jihyun Yoon
, Jihyun Yoon , Yang-Hyun Kim
, Yang-Hyun Kim

 , Ga-Yang Shim
, Ga-Yang Shim
 , Jae-Young Lim
, Jae-Young Lim




 , Jung-Ha Kim
, Jung-Ha Kim

 , Jihyun Ahn
, Jihyun Ahn
Citations

 , Hyun Kang
, Hyun Kang
 , Oh Haeng Lee
, Oh Haeng Lee , Hyun Kang
, Hyun Kang

 , Juhee Seo
, Juhee Seo , Hyun Jung Park
, Hyun Jung Park
 , Gyeongmin Im
, Gyeongmin Im
 , Seungpil Jeong
, Seungpil Jeong , Eunhee Ha
, Eunhee Ha
 , Sohyun Ahn
, Sohyun Ahn , Ji Yeon Byun
, Ji Yeon Byun
Citations

 , So-Hee Hong
, So-Hee Hong
 , Jooyoung Choi
, Jooyoung Choi

Citations

 , Seoyoung Kim
, Seoyoung Kim , Dohyoung Rim
, Dohyoung Rim

Citations

 , Eun-Kyoung Pang
, Eun-Kyoung Pang
Citations

 , Won Woong Lee
, Won Woong Lee , Haewoo Lee
, Haewoo Lee , Jin Yong Jun
, Jin Yong Jun , Jin-Won Noh
, Jin-Won Noh
Citations


Citations

 , Bong-Kwang Jung
, Bong-Kwang Jung , Hyun-Jong Yang
, Hyun-Jong Yang
Citations

 , Bruno B. Andrade
, Bruno B. Andrade , Ju Sang Kim
, Ju Sang Kim , Yoolwon Jeong
, Yoolwon Jeong
Citations

 , Joonil Hwang
, Joonil Hwang , Hai-Jeon Yoon
, Hai-Jeon Yoon , So Hyun Ahn
, So Hyun Ahn

Citations


Citations


Citations


Citations

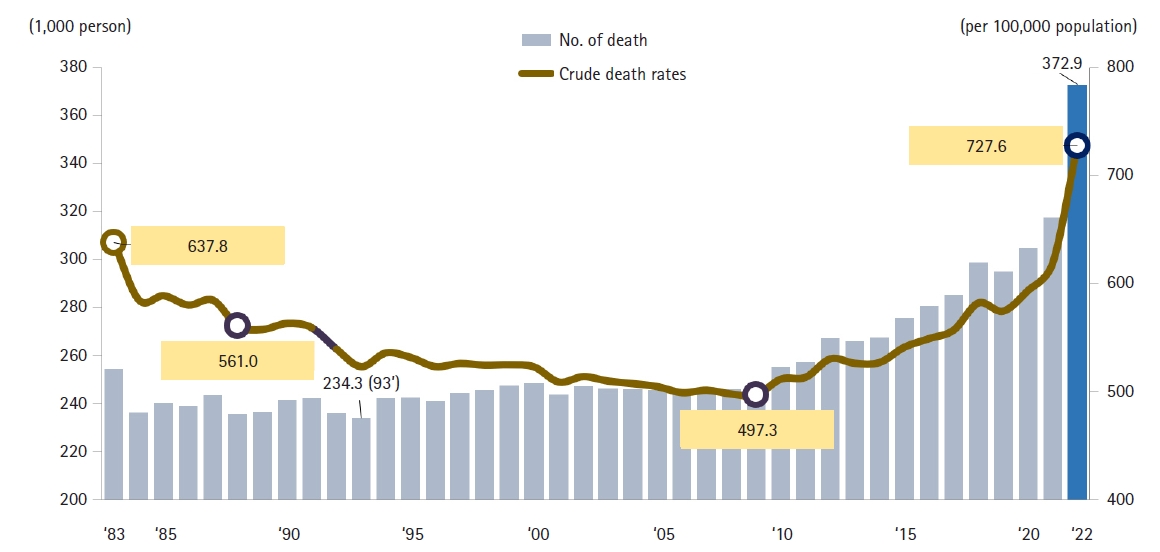
This review examines the challenges associated with occupational disease surveillance in Korea, particularly emphasizing the limitations of current data sources such as the Industrial Accident Compensation Insurance (IACI) statistics and special health examinations. The IACI system undercounts cases due to its emphasis on severe diseases and restrictions on approvals. Special health examinations, although they cover a broad workforce, are constrained by their annual scheduling, which leads to missed acute illnesses and subclinical conditions. The paper also explores the history of occupational disease surveillance in Korea, highlighting the fragmented and disease-specific approach of earlier systems. The authors introduce the newly established Korea Occupational Disease Surveillance Center (KODSC), a comprehensive nationwide system designed to gather, analyze, and interpret data on occupational diseases through a network of regional centers. By incorporating hospital-based surveillance and focusing on acute poisonings and other sentinel events, the KODSC aims to overcome the limitations of previous systems and promote collaboration with various agencies. Although it is still in the early stages of implementation, the KODSC demonstrates potential for improving data accuracy and contributing valuable insights for public health policy.
Citations

Shoulder pain is a common complaint in primary care settings. The prevalence of shoulder pain is on the rise, especially in societies with aging populations. Like other joint-related conditions, shoulder pain is predominantly caused by degenerative diseases. These degenerative changes typically affect bones, tendons, and cartilage, with common conditions including degenerative rotator cuff tears, impingement syndrome, and osteoarthritis. Diagnosing these degenerative diseases in older adults requires a thorough understanding of basic anatomy, general physical examination techniques, and specific diagnostic tests. This review aims to outline the fundamental physical examination methods for diagnosing shoulder pain in older adult patients in primary care. The shoulder's complex anatomy and its broad range of motion underscore the need for a systematic approach to evaluation. Routine inspection and palpation can identify signs such as muscle atrophy, bony protrusions, or indications of degenerative changes. Assessing range of motion, and distinguishing between active and passive deficits, is crucial for differentiating conditions like frozen shoulder from rotator cuff tears. Targeted strength tests, such as the empty can, external rotation lag, liftoff, and belly press tests, are instrumental in isolating specific rotator cuff muscles. Additionally, impingement tests, including Neer’s and Hawkins’ signs, are useful for detecting subacromial impingement. A comprehensive understanding of shoulder anatomy and a systematic physical examination are vital for accurately diagnosing shoulder pain in older adults. When properly executed and interpreted in the clinical context, these maneuvers help differentiate between various conditions, ranging from degenerative changes to rotator cuff pathology.
Health and safety issues in micro and small enterprises (MSEs) are recognized as a global challenge. This study aimed to examine Workers' Health Centers (WHCs) as a representative public organization providing occupational health services to MSEs in Korea. WHCs were established in 2011 after a trial period aimed at addressing occupational diseases in MSEs with limited resources. As of 2024, there are 24 WHCs, 22 branch offices, and 23 trauma counseling centers for workers. These health centers are managed by the Korea Occupational Safety and Health Agency, with their actual operation delegated to private organizations. Each WHC employs an average of 13 staff members and is organized into four specialized teams: cardiovascular disease prevention, workplace environment improvement, musculoskeletal disease prevention, and occupational stress management. These centers also offer common basic programs along with region-specific specialized initiatives. In 2023, the total cumulative number of users reached 203,877, with employees from MSEs comprising approximately 88.5% of the total. WHCs can thus be seen as playing a pivotal role as case managers of health requirements in the workplace by fostering strong relationships with MSEs and linking them to other relevant programs through a problem-solving-oriented approach. Given the limited resources of these enterprises, proactive policies and the equitable application of safety and health regulations are essential. A balanced strategy that combines regulatory enforcement with practical assistance is critical to ensure the success of WHCs in improving health and safety conditions in MSEs.
Shoulder diseases pose a significant health challenge for older adults, often causing pain, functional decline, and decreased independence. This narrative review explores how deep learning (DL) can address diagnostic challenges by automating tasks such as image segmentation, disease detection, and motion analysis. Recent research highlights the effectiveness of DL-based convolutional neural networks and machine learning frameworks in diagnosing various shoulder pathologies. Automated image analysis facilitates the accurate assessment of rotator cuff tear size, muscle degeneration, and fatty infiltration in MRI or CT scans, frequently matching or surpassing the accuracy of human experts. Convolutional neural network-based systems are also adept at classifying fractures and joint conditions, enabling the rapid identification of common causes of shoulder pain from plain radiographs. Furthermore, advanced techniques like pose estimation provide precise measurements of the shoulder joint's range of motion and support personalized rehabilitation plans. These automated approaches have also been successful in quantifying local osteoporosis, utilizing machine learning-derived indices to classify bone density status. DL has demonstrated significant potential to improve diagnostic accuracy, efficiency, and consistency in the management of shoulder diseases in older patients. Machine learning-based assessments of imaging data and motion parameters can help clinicians optimize treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. However, to ensure their generalizability, reproducibility, and effective integration into routine clinical workflows, large-scale, prospective validation studies are necessary. As data availability and computational resources increase, the ongoing development of DL-driven applications is expected to further advance and personalize musculoskeletal care, benefiting both healthcare providers and the aging population.
This review classifies and summarizes the major shoulder diseases affecting older adults, focusing on rotator cuff disease, frozen shoulder, osteoarthritis, and shoulder instability. It explores each condition's pathophysiology, risk factors, clinical presentation, diagnostic approaches, and treatment strategies to guide clinicians in optimizing patient outcomes and enhancing quality of life. Age-related degenerative changes, comorbidities, and distinct etiological factors contribute to the presentation of shoulder disorders in older adults. Rotator cuff disease ranges from tendinopathy to full-thickness tears and is influenced by genetic predispositions, inflammatory cytokines, and muscle quality. Frozen shoulder results from fibroproliferative changes in the capsule, leading to significant pain and restricted motion. Osteoarthritis involves cartilage degeneration and bony remodeling, often necessitating surgical interventions such as arthroplasty. Shoulder instability, though less frequent, is complicated by associated injuries like rotator cuff tears and fractures, requiring tailored management strategies. Advances in imaging techniques, biologic treatments, and surgical procedures, particularly arthroscopic and arthroplasty options, have improved diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic outcomes. A thorough classification of shoulder diseases in older adult patients highlights the complexity of managing these conditions. Effective treatment requires individualized approaches that integrate conservative measures with emerging biologic or surgical therapies. Future research should focus on targeted interventions, standardized diagnostic criteria, and multidisciplinary collaboration to minimize disability, optimize function, and improve overall quality of life in this growing patient population. Multimodal strategies, including patient education, structured rehabilitation, and psychosocial support, further enhance long-term adherence and outcomes. Ongoing vigilance for comorbidities, such as osteoporosis or metabolic disorders, is necessary for comprehensive care.
This study explores the development, roles, and key initiatives of the Regional Environmental Health Centers in Korea, detailing their evolution through four distinct phases and their impact on environmental health policy and local governance. It chronicles the establishment and transformation of these centers from their inception in May 2007, through four developmental stages. Originally named Environmental Disease Research Centers, they were subsequently renamed Environmental Health Centers following legislative changes. The analysis includes the expansion in the number of centers, the transfer of responsibilities to local governments, and the launch of significant projects such as the Korean Children’s Environmental Health Study (Ko-CHENS ). During the initial phase (May 2007–February 2009), the 10 centers concentrated on research-driven activities, shifting from a media-centered to a receptor-centered approach. In the second phase, prompted by the enactment of the Environmental Health Act, six additional centers were established, broadening their scope to address national environmental health issues. The third phase introduced Ko-CHENS, a 20-year national cohort project designed to influence environmental health policy by integrating research findings into policy frameworks. The fourth phase marked a decentralization of authority, empowering local governments and redefining the centers' roles to focus on regional environmental health challenges. The Regional Environmental Health Centers have significantly evolved and now play a crucial role in addressing local environmental health issues and supporting local government policies. Their capacity to adapt and respond to region-specific challenges is essential for the effective implementation of environmental health policies, reflecting geographical, socioeconomic, and demographic differences.
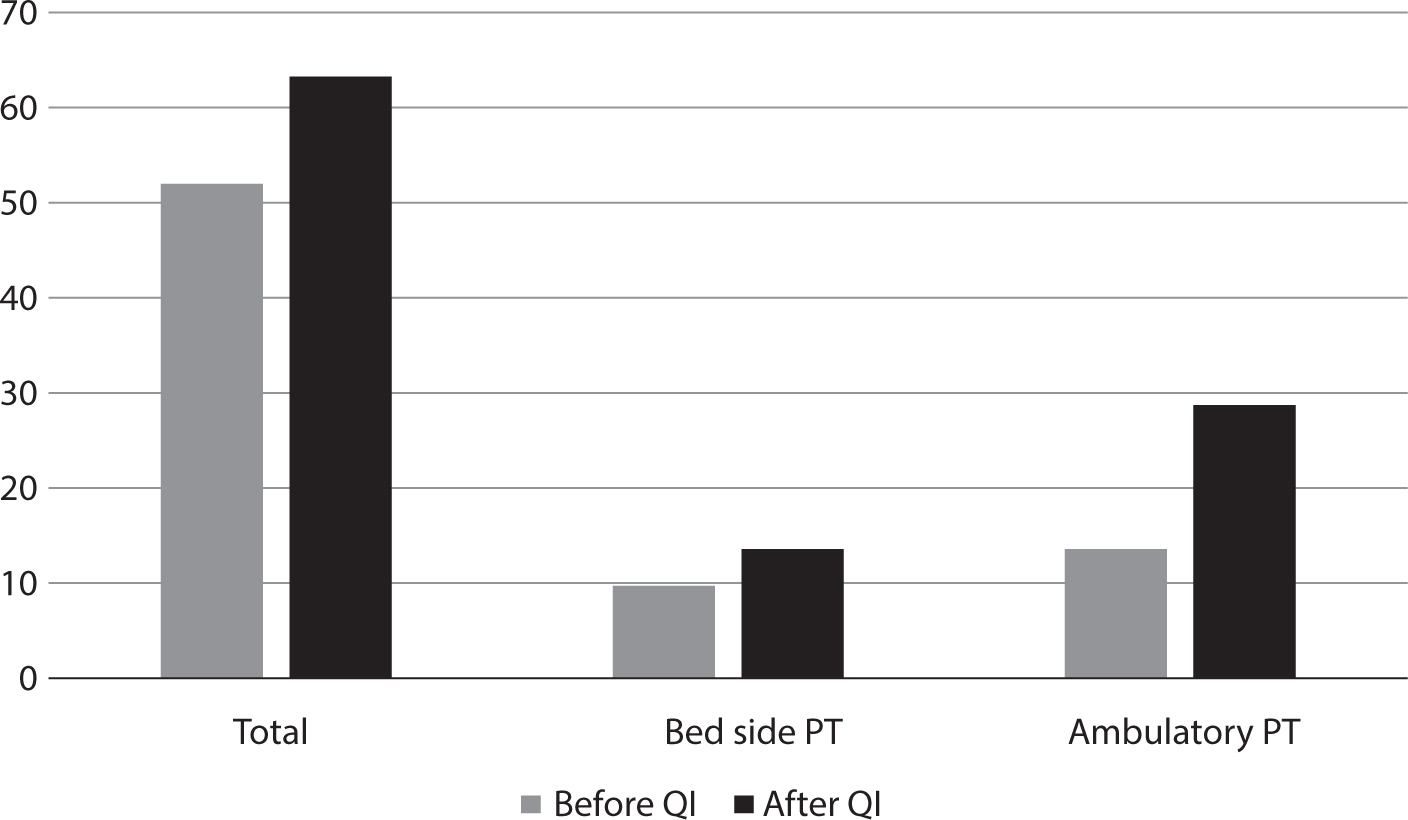
This review describes a psychological support service designed to address post-traumatic stress disorder in workers impacted by workplace injuries, assisting in their recovery and facilitating their return to work. It explores the rationale and context behind establishing trauma counseling centers for these individuals, along with the status, roles, future directions, and recommendations for these centers. The review details the operational framework and functions of the workplace injury trauma management program, the scope of the impacts of such injury, the groups targeted for crisis intervention, and the psychological interventions tailored to each stage of recovery. Initiated as a pilot project in 2018, trauma counseling centers for workers have gradually become more common, with 23 centers in operation across Korea as of 2024.
Citations

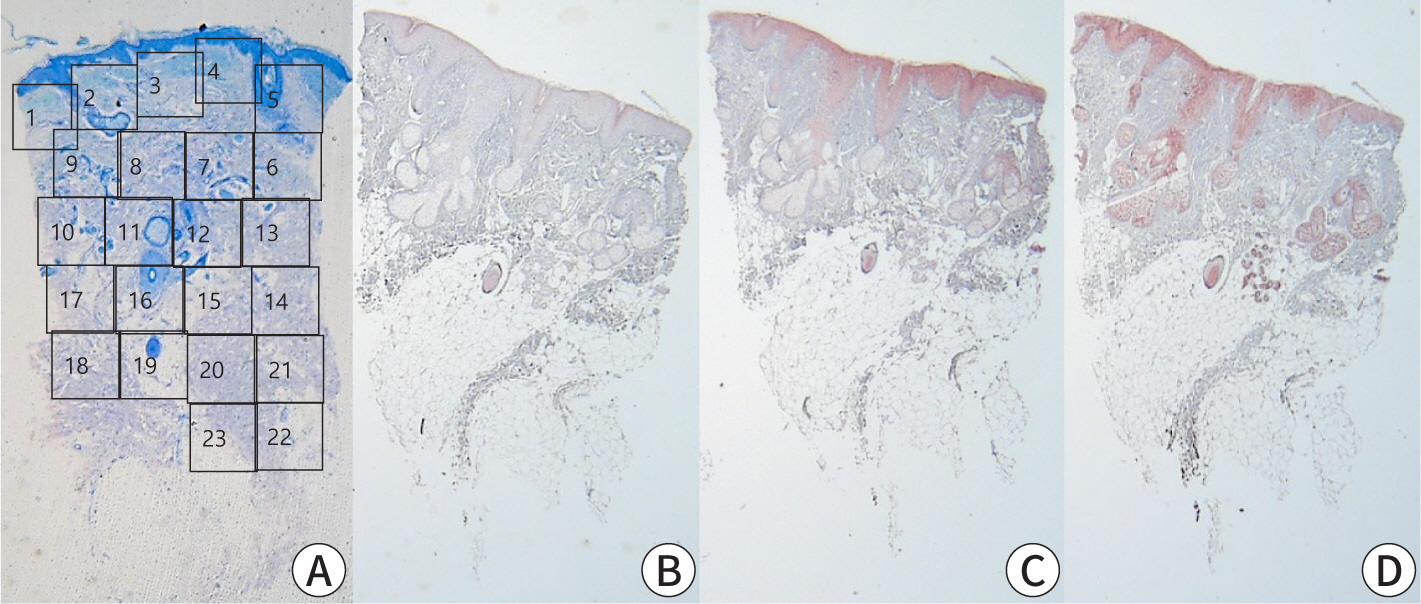
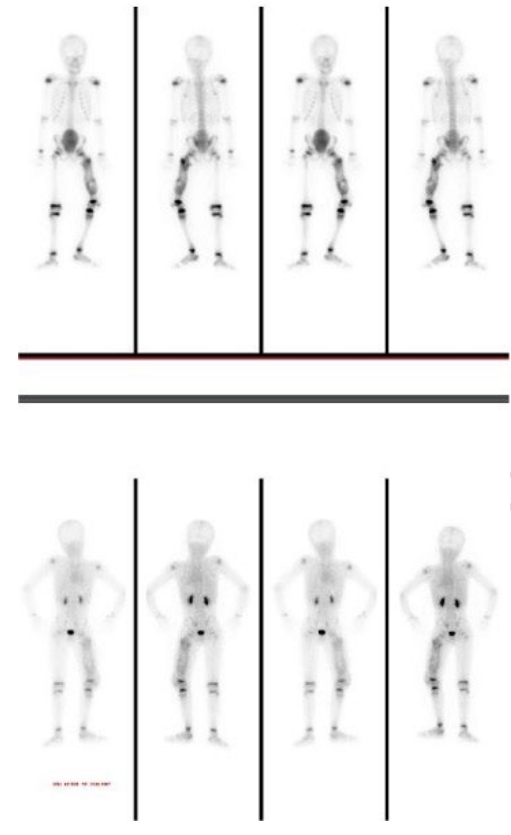
Shoulder diseases, including adhesive capsulitis, rotator cuff tear, and osteoarthritis of the glenohumeral joint, can significantly impair daily activities in older adult patients. This review aims to examine the radiologic findings associated with these shoulder conditions in older patients, providing insights for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Adhesive capsulitis, commonly known as frozen shoulder, leads to pain and restricted movement, thereby causing shoulder dysfunction. Recent advances in diagnostic technology have greatly enhanced the sensitivity and accuracy of diagnosing this condition through radiologic evaluations, including MRI, magnetic resonance arthrography (MRA), and high-resolution ultrasound. Rotator cuff disease is another frequent issue in older adults, with full-thickness tears occurring in 50%–80% of cases. Both MRI and MRA are highly sensitive and specific in identifying rotator cuff tears. Additionally, ultrasonography is recognized for its high sensitivity and specificity in detecting tears of the supraspinatus tendon. Although osteoarthritis of the glenohumeral joint is less commonly prevalent, its advanced stages can severely affect the function of the upper extremity. Plain radiography is typically the first imaging technique used to assess this type of osteoarthritis. As the condition worsens, CT is utilized to measure glenoid bone loss, glenoid version, and inclination, which are crucial for accurate surgical planning. Each imaging modality provides distinct benefits: plain radiographs for initial structural assessment, ultrasonography for real-time evaluation of soft tissues, MRI/MRA for detailed visualization of capsular and tendinous lesions, and CT for precise bony analysis.
Citations

The purpose of this review is to provide a comprehensive guide for managing older adult patients with shoulder diseases, specifically rotator cuff tears and osteoarthritis, and to explore effective nonsurgical treatment options. Chronic rotator cuff tears are typically degenerative, whereas acute tears result from trauma. A key feature of these tears is tendon degeneration accompanied by type III collagen predominance, predisposing tears to progression. Osteoarthritis in the glenohumeral joint arises from wear-and-tear changes that compromise cartilage integrity, leading to pain and restricted motion. Accurate clinical assessment and imaging, including plain radiographs, ultrasonography, and MRI, facilitate diagnosis and guide treatment. The physic-al examination emphasizes range of motion, rotator cuff strength, and scapular stability. Management strategies prioritize pain relief, function preservation, and improving mobility. Nonsurgical modalities, including exercise, manual therapy, and activity modification, constitute first-line treatments, especially for older adults. Pharmacological approaches involve NSAIDs, corticosteroid injections, and neuropathic pain medications. Steroid injections have short-term benefits, but repeated treatments may compromise tissue integrity. Platelet-rich plasma is a regenerative option that may improve tendon healing, but mixed findings highlight the need for further investigation. A structured physical therapy program focusing on range of motion and strengthening is essential, with alternative interventions used judiciously. Patients should be counseled regarding the potential progression of tears and the possible need for future surgical intervention if nonsurgical methods are unsuccessful. Multimodal approaches, including joint mobilization and personalized exercise regimens, hold potential for optimizing functional outcomes and supporting independence in older adults.
Citations

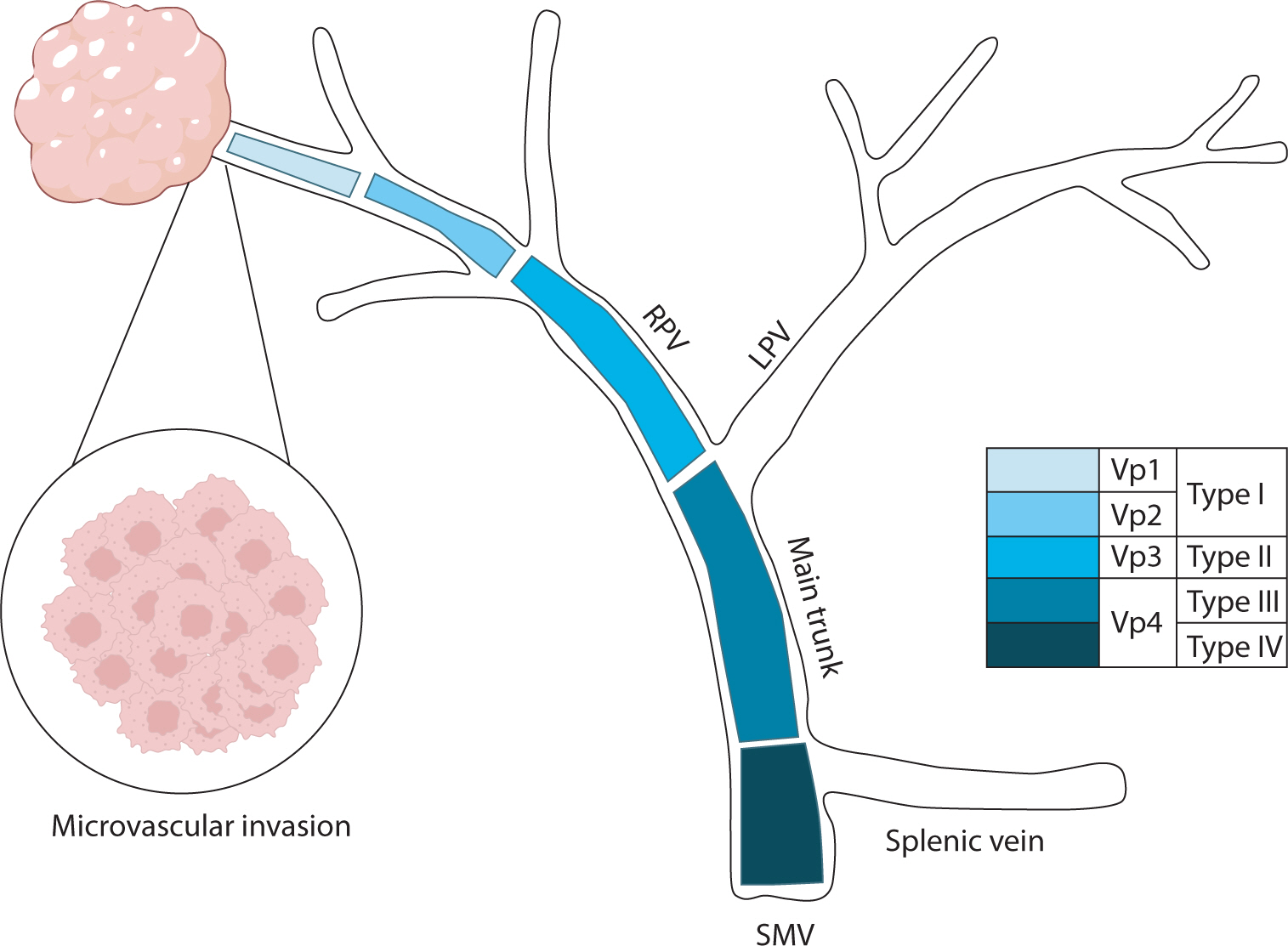
Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis presents a significant therapeutic challenge due to its poor prognosis and limited treatment options. This review thoroughly examines diagnostic methods, including imaging techniques and classification systems such as the Japanese Vp and Cheng’s classifications, to aid in clinical decision-making. Treatment strategies encompass liver resection and liver transplantation, particularly living donor liver transplantation after successful downstaging, which have shown potential benefits in selected cases. Locoregional therapies, including hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy, transarterial chemoembolization, transarterial radioembolization, and external beam radiation therapy, remain vital components of treatment. Recent advancements in systemic therapies, such as sorafenib, lenvatinib, and immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., atezolizumab plus bevacizumab) have demonstrated improvements in overall survival and progression-free survival. These developments underscore the importance of a multidisciplinary and personalized approach to improve outcomes for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombosis.
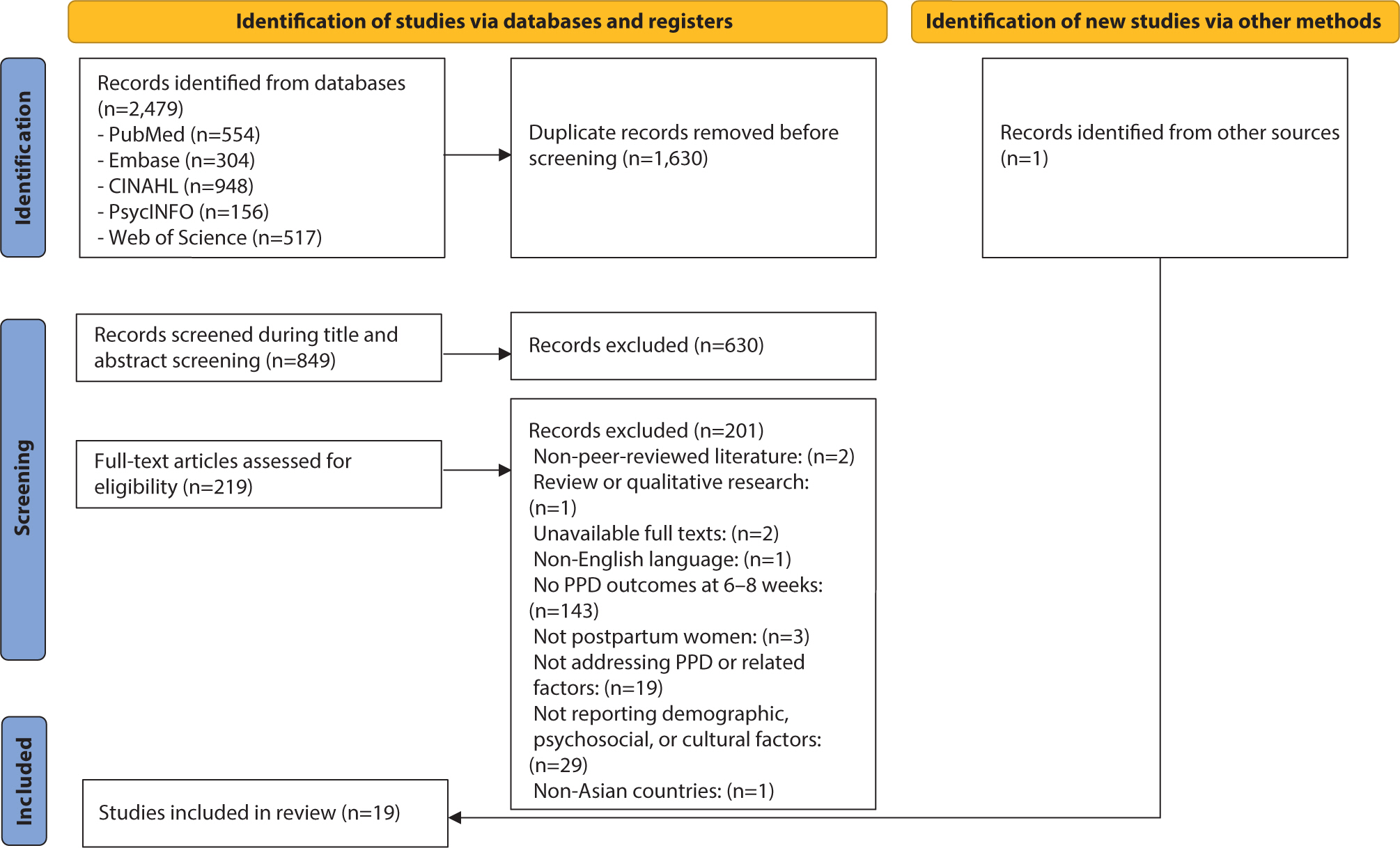
The prevalence of postpartum depression (PPD) in Asia is reported to range from 13.53% to 22.31%. However, there remains a gap in the identification of PPD, particularly regarding cultural cutoff points. Therefore, the purpose of this scoping review was to determine the prevalence and associated factors of PPD in Eastern, South-eastern, Western, and Southern Asian countries and analyze the cutoff points of the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) used across these countries. Following Arksey and O'Malley’s five-step scoping review framework, the population was defined as mothers, the concept as the EPDS, and the context as the Asian region. A literature search was conducted using PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Web of Science. The data analysis focused on demographic characteristics, EPDS cutoffs and features, PPD prevalence, and its associated factors. Nineteen studies were selected. Most countries used translated versions of the EPDS with demonstrated reliability and validity. The cutoff scores varied, with most using scores of 10 or higher. The prevalence of PPD ranged from 5.1% to 78.7%. Key associated factors for PPD included cultural factors such as relationships with in-laws and preferences for the newborn’s sex. To improve the accuracy of PPD screening in Asia, the EPDS should be used consistently, and appropriate cutoff criteria must be established. In addition, prevention strategies and programs that reflect the cultural characteristics and social context of Asia need to be developed for the early detection and prevention of PPD.
Breast cancer is a complex disease influenced by environmental, genetic, dietary, and hormonal factors. This underscores the importance of postoperative nutritional management in supporting recovery, minimizing complications, and enhancing long-term outcomes. This review synthesizes clinical guidelines, expert recommendations, and observational studies to provide a comprehensive overview of dietary interventions for breast cancer patients following surgery. Post-surgical nutritional care is centered around three primary objectives: supporting wound healing through high-quality protein intake, maintaining optimal nutritional status to prevent malnutrition, and promoting healthy lifestyle habits to reduce the risk of recurrence. To achieve these objectives, postoperative dietary strategies focus on several key components: ensuring adequate hydration for metabolic processes and tissue repair, consuming a balanced diet rich in fresh vegetables and fruits to mitigate oxidative stress, incorporating whole grains to support overall healing, and maintaining sufficient intake of high-quality protein from sources such as fish, meat, and dairy products to aid tissue repair and immune system recovery. Patients are also advised to avoid alcohol, limit saturated fats, and reduce intake of salty, sugary, and smoked foods to minimize inflammation. As research progresses, the implementation of personalized dietary plans remains essential for optimizing recovery outcomes in breast cancer patients.
Autism spectrum disorder involves challenges in social communication and restricted, repetitive behaviors. Historically, males have received autism diagnoses at comparatively high rates, prompting an underrepresentation of females in research and an incomplete understanding of sex-specific symptom presentations and comorbidities. This review examines sex differences in the prevalence of common comorbidities of autism to inform tailored clinical practices. These conditions include attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, anxiety disorders, conduct disorder, depression, epilepsy, intellectual disability, and tic disorders. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is prevalent in both sexes; however, females may more frequently exhibit the inattentive subtype. Anxiety disorders display inconsistent sex differences, while conduct disorder more frequently impacts males. Depression becomes more common with age; some studies indicate more pronounced symptoms in adolescent girls, while others suggest greater severity in males. Epilepsy is more prevalent in females, especially those with intellectual disabilities. Despite displaying a male predominance, intellectual disability may exacerbate the severity of autism to a greater degree in females. No clear sex differences have been found regarding tic disorders. Overall, contributors to sex-based differences include biases stemming from male-centric diagnostic tools, compensatory behaviors like camouflaging in females, genetic and neurobiological differences, and the developmental trajectories of comorbidities. Recognizing these factors is crucial for developing sensitive diagnostics and sex-specific interventions. Inconsistencies in the literature highlight the need for longitudinal studies with large, diverse samples to investigate autism comorbidities across the lifespan. Understanding sex differences could facilitate earlier identification, improved care, and personalized interventions, thus enhancing quality of life for individuals with autism.
Citations